A crack method, on the BB84 protocol
... the angle between the two linear polarization directions is 45 degrees. For each of the four optical paths described above, a "45 degree linearly polarized beam splitter" is further connected (as shown in the figure below) ...
... the angle between the two linear polarization directions is 45 degrees. For each of the four optical paths described above, a "45 degree linearly polarized beam splitter" is further connected (as shown in the figure below) ...
BACH, the Beamline for Advanced diCHroic and scattering
... UV and X-ray sources able to provide polarization tunability. The efficient use of such sources has required a significant evolution of beam transport, focusing optics and monochromator behavior. Hereafter we present the characteristics of a Beamline for Advanced diCHroism (BACH) under construction ...
... UV and X-ray sources able to provide polarization tunability. The efficient use of such sources has required a significant evolution of beam transport, focusing optics and monochromator behavior. Hereafter we present the characteristics of a Beamline for Advanced diCHroism (BACH) under construction ...
Chiroptical Spectroscopy - Ruhr
... Some materials absorp more light of one particular polarization state than of the other. This anisotropy in absorption is called dichroism. ...
... Some materials absorp more light of one particular polarization state than of the other. This anisotropy in absorption is called dichroism. ...
Optical techniques for molecular manipulation
... Polarizers • many optical elements restrict or modify the polarization state of light • polarization-dependent transmission/reflection • sheet polarizers (Polaroid) • Nicol, Wollaston prisms etc • polarizers, polarizing filters, analyzers • polarization-dependent refractive index • four categories ...
... Polarizers • many optical elements restrict or modify the polarization state of light • polarization-dependent transmission/reflection • sheet polarizers (Polaroid) • Nicol, Wollaston prisms etc • polarizers, polarizing filters, analyzers • polarization-dependent refractive index • four categories ...
Wave Optics
... the surface of the Earth. Determine the approximate size of the smallest feature the camera can resolve when taking a picture of something on the Earth's surface (assume blue light with a λ = 400nm, and ignore the effect of the Earth's atmosphere) ...
... the surface of the Earth. Determine the approximate size of the smallest feature the camera can resolve when taking a picture of something on the Earth's surface (assume blue light with a λ = 400nm, and ignore the effect of the Earth's atmosphere) ...
Lecture 24
... An EM wave that is off the optic axis of a calcite crystal splits into two waves called ordinary and extraordinary waves. These waves have orthogonal polarizations and travel with different velocities. The o-wave has a polarization that is always perpendicular to the optical axis. ...
... An EM wave that is off the optic axis of a calcite crystal splits into two waves called ordinary and extraordinary waves. These waves have orthogonal polarizations and travel with different velocities. The o-wave has a polarization that is always perpendicular to the optical axis. ...
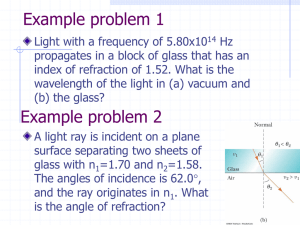
PHYS 242 BLOCK 11 NOTES Sections 33.1 to 33.7 Geometrical
... = 90˚. Therefore, Snell’s law gives na sin θcrit = nb sin 90˚ = nb (1). Solving, sin θcrit = na . Because the sine of an angle cannot be greater than one, nb must be less than na. That is, total internal reflection occurs only for reflection off a material of lower index of refraction. ...
... = 90˚. Therefore, Snell’s law gives na sin θcrit = nb sin 90˚ = nb (1). Solving, sin θcrit = na . Because the sine of an angle cannot be greater than one, nb must be less than na. That is, total internal reflection occurs only for reflection off a material of lower index of refraction. ...
Optical Activity
... which the direction of E is random in the x-y plane (see Fig. 2a) is called unpolarized. However, if the electric vectors are pointing in only one direction, e.g. parallel to the x-axis (see Fig. 2b) then the beam is said to be plane-polarized. With E parallel to the x-axis as shown in Figure 1, the ...
... which the direction of E is random in the x-y plane (see Fig. 2a) is called unpolarized. However, if the electric vectors are pointing in only one direction, e.g. parallel to the x-axis (see Fig. 2b) then the beam is said to be plane-polarized. With E parallel to the x-axis as shown in Figure 1, the ...
PHYS 1111 Mechanics, Waves, & Thermodynamics
... For a given material (and nearly all materials), the index of fraction is a function of the wavelength of the incident light, n=n() This implies that the speed of light inside the medium depends on The dependence of wave speed v and n on is called dispersion Since n=n(), Snell’s law of refract ...
... For a given material (and nearly all materials), the index of fraction is a function of the wavelength of the incident light, n=n() This implies that the speed of light inside the medium depends on The dependence of wave speed v and n on is called dispersion Since n=n(), Snell’s law of refract ...
polarization 3
... vibration has been rotated w.r.t that of incident light through a certain angle depends on the phase diff between the two vibrations. ...
... vibration has been rotated w.r.t that of incident light through a certain angle depends on the phase diff between the two vibrations. ...
Suman-AE-AOTFIntro-2..
... Where ∆n is the birefringence of the the TeO2 crystal, Vα and fα are the velocity and frequency of the acoustic wave, and α is a complex parameter depending on the design of the AOTF. The wavelength of the light that is selected by this diffraction can therefore be varied simply by changing the freq ...
... Where ∆n is the birefringence of the the TeO2 crystal, Vα and fα are the velocity and frequency of the acoustic wave, and α is a complex parameter depending on the design of the AOTF. The wavelength of the light that is selected by this diffraction can therefore be varied simply by changing the freq ...
... which the direction of E is random in the x-y plane (see Fig. 2a) is called unpolarized. However, if the electric vectors are pointing in only one direction, e.g. parallel to the x-axis (see Fig. 2b) then the beam is said to be plane-polarized. With E parallel to the x-axis as shown in Figure 1, the ...
Optical Polarimetry
... In a typical polarimetry experiment, monochromatic light is passed through the sample. A sodium lamp is usually used as the light source and the wavelength of its D line is 589.3 nm. The light provided by the source is not polarized so its electromagnetic waves oscillate in all planes perpendicular ...
... In a typical polarimetry experiment, monochromatic light is passed through the sample. A sodium lamp is usually used as the light source and the wavelength of its D line is 589.3 nm. The light provided by the source is not polarized so its electromagnetic waves oscillate in all planes perpendicular ...
Lab 8: Polarization of Light
... retarder; linear polarization is thus converted to elliptical polarization due to the arbitrary phase shift. The phase difference depends on the incident wavelength, the refractive indices (along the two different directhey don’t reduce the intensity of the incident light tions) and the thickness of ...
... retarder; linear polarization is thus converted to elliptical polarization due to the arbitrary phase shift. The phase difference depends on the incident wavelength, the refractive indices (along the two different directhey don’t reduce the intensity of the incident light tions) and the thickness of ...
Lecture 16 - Purdue Physics
... The changing magnetic field creates an electric field (which produces the EMF) It turns out that likewise, a changing electric field produces a magnetic field. This process can continue indefinitely… Light is an oscillating electric-magnetic field propagating through free space. ...
... The changing magnetic field creates an electric field (which produces the EMF) It turns out that likewise, a changing electric field produces a magnetic field. This process can continue indefinitely… Light is an oscillating electric-magnetic field propagating through free space. ...
Chapter 33. Electromagnetic Waves
... on a glass surface. The electric field vectors of the light has two components. The perpendicular components are perpendicular to the plane of incidence The parallel components are parallel to the plane of incidence. Because the light is unpolarized, these two components are of equal magnitude. • Th ...
... on a glass surface. The electric field vectors of the light has two components. The perpendicular components are perpendicular to the plane of incidence The parallel components are parallel to the plane of incidence. Because the light is unpolarized, these two components are of equal magnitude. • Th ...
Optically polarized atoms_ch_4
... • With some trigonometry, one can see that a state of arbitrary polarization is represented by a point on the Poincaré Sphere of unit radius: • Partially polarized light R<1 • R ≡ degree of polarization ...
... • With some trigonometry, one can see that a state of arbitrary polarization is represented by a point on the Poincaré Sphere of unit radius: • Partially polarized light R<1 • R ≡ degree of polarization ...
Devil physics The baddest class on campus IB Physics
... unpolarized light passing through a polarizer is equal to ½ no matter what the orientation of the polarizing film ...
... unpolarized light passing through a polarizer is equal to ½ no matter what the orientation of the polarizing film ...
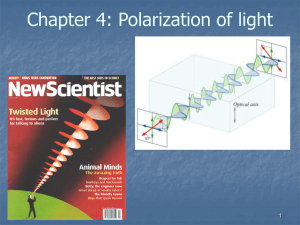
Polarization
... • Some materials are isotropic and leave EM waves unchanged; others do not and are called optically active • A polarizer is a special type of filter that only transmits one polarization ...
... • Some materials are isotropic and leave EM waves unchanged; others do not and are called optically active • A polarizer is a special type of filter that only transmits one polarization ...
EP421 Assignment 4: Polarization II: Applications of Optical
... (d) The air-‐gap polarizing prism you designed above is called a “Glan-‐Foucault” or” Glan-‐Air” polarizing prism (Fig. 1) and is useful for separating polarization components of powerful laser bea ...
... (d) The air-‐gap polarizing prism you designed above is called a “Glan-‐Foucault” or” Glan-‐Air” polarizing prism (Fig. 1) and is useful for separating polarization components of powerful laser bea ...
Photoelectric Effect When light shines on a metal surface, electrons are emitted
... Photoelectric Effect When light shines on a metal surface, electrons are emitted from the surface. ...
... Photoelectric Effect When light shines on a metal surface, electrons are emitted from the surface. ...
Optically polarized atoms_Light_Polarization
... • With some trigonometry, one can see that a state of arbitrary polarization is represented by a point on the Poincaré Sphere of unit radius: • Partially polarized light R<1 • R ≡ degree of polarization ...
... • With some trigonometry, one can see that a state of arbitrary polarization is represented by a point on the Poincaré Sphere of unit radius: • Partially polarized light R<1 • R ≡ degree of polarization ...
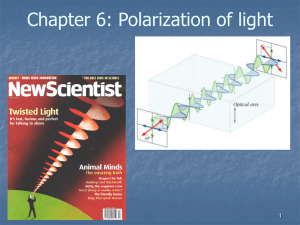
Chapter 8
... November 5 Birefringence 8.2 Polarizers Polarizer: An optical device whose output is a certain form of polarized light. Example: Linear polarizers, circular polarizers. Polarizer and analyzer, transmission axis, extinction axis Physical mechanisms of polarizers: • Dichroism (selective absorption) • ...
... November 5 Birefringence 8.2 Polarizers Polarizer: An optical device whose output is a certain form of polarized light. Example: Linear polarizers, circular polarizers. Polarizer and analyzer, transmission axis, extinction axis Physical mechanisms of polarizers: • Dichroism (selective absorption) • ...
Experiment VI Polarized Light
... 4. For this experiment, you need to make sure that the polarizers are oriented correctly with respect to each other. To do this, first set the analyzing polarizer to zero degrees. Then click “COLLECT” and rotate the “first polarizer” until a maximum is shown on the screen plot. Now the angle θ read ...
... 4. For this experiment, you need to make sure that the polarizers are oriented correctly with respect to each other. To do this, first set the analyzing polarizer to zero degrees. Then click “COLLECT” and rotate the “first polarizer” until a maximum is shown on the screen plot. Now the angle θ read ...
Polarizer

A polarizer or polariser is an optical filter that passes light of a specific polarization and blocks waves of other polarizations. It can convert a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam with well-defined polarization, polarized light. The common types of polarizers are linear polarizers and circular polarizers. Polarizers are used in many optical techniques and instruments, and polarizing filters find applications in photography and liquid crystal display technology. Polarizers can also be made for other types of electromagnetic waves besides light, such as radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays.