Distances in space are so large that it does not make sense to use a
... Name: Date: Light Years Distances in space are so large that it does not make sense to use a typical unit such as kilometers or miles. Instead, astronomers use a special unit called a light year to measure the distances between stars and galaxies. A light year is the distance that light travels in o ...
... Name: Date: Light Years Distances in space are so large that it does not make sense to use a typical unit such as kilometers or miles. Instead, astronomers use a special unit called a light year to measure the distances between stars and galaxies. A light year is the distance that light travels in o ...
Common Lighting Terminology Ambient Light The light already
... Type of lamp in which a tungsten filament is sealed in a clear capsule filled with a halogen gas. ...
... Type of lamp in which a tungsten filament is sealed in a clear capsule filled with a halogen gas. ...
THE FARADAY EFFECT AND DISPERSION IN LIQUIDS
... of the transmitted light. You are to measure Faraday rotation in cinnamic acid at two different wavelengths, the cadmium blue line at λ = 480 nm and the mercury green line at λ = 546 nm. Separate filters at each of these wavelengths can be moved in and out of the beam path. For the green line, the p ...
... of the transmitted light. You are to measure Faraday rotation in cinnamic acid at two different wavelengths, the cadmium blue line at λ = 480 nm and the mercury green line at λ = 546 nm. Separate filters at each of these wavelengths can be moved in and out of the beam path. For the green line, the p ...
Spectral Brightness of Synchrotron Radiation
... Kim’s definition for spectral brightness treats the electric field as a scalar but in reality it is a vector Polarization describes the way in which the direction of this vector changes Types: Linear (horizontal, vertical, ±45º), right and left circular, elliptical ...
... Kim’s definition for spectral brightness treats the electric field as a scalar but in reality it is a vector Polarization describes the way in which the direction of this vector changes Types: Linear (horizontal, vertical, ±45º), right and left circular, elliptical ...
Unit Study Guide - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... iris - a ring of muscles that contracts and relaxes automatically to regulate the amount of light entering the eye; controls the size of the pupil lens – a curved, transparent device that causes light to refract as it passes through; gathers light from an object and produces an image of the object n ...
... iris - a ring of muscles that contracts and relaxes automatically to regulate the amount of light entering the eye; controls the size of the pupil lens – a curved, transparent device that causes light to refract as it passes through; gathers light from an object and produces an image of the object n ...
Solution Derivations for Capa #12
... After the light passes through the second filter, its intensity drops again. However, its initial intensity is that of the light after it passes through filter A. Also, the angle between that which the light is traveling and that which it must pass through is θ2 − θ1 . This is because the first pol ...
... After the light passes through the second filter, its intensity drops again. However, its initial intensity is that of the light after it passes through filter A. Also, the angle between that which the light is traveling and that which it must pass through is θ2 − θ1 . This is because the first pol ...
Walk of Discovery: Light
... second. That’s equivalent to 32.4 million million phone calls per second! ...
... second. That’s equivalent to 32.4 million million phone calls per second! ...
lab sheet - Faculty of Engineering
... 2A.1 Theory The electric field of a propagating transverse electromagnetic wave lies in a plane normal to the direction of propagation. If assumptions are made that the wave propagate out of the page and normal to it, the electric field of the wave can be represented by two orthogonal components in ...
... 2A.1 Theory The electric field of a propagating transverse electromagnetic wave lies in a plane normal to the direction of propagation. If assumptions are made that the wave propagate out of the page and normal to it, the electric field of the wave can be represented by two orthogonal components in ...
Announcements
... • All electromagnetic waves travel through vacuum with a speed c (3 X 108 m/s) • The visible portion of the spectrum forms a tiny portion of the total EM spectrum • For all EM waves, c=λf (true for any type of wave); λ = c/f ...
... • All electromagnetic waves travel through vacuum with a speed c (3 X 108 m/s) • The visible portion of the spectrum forms a tiny portion of the total EM spectrum • For all EM waves, c=λf (true for any type of wave); λ = c/f ...
Name: Period: ______ Date: ______ Group Activity: Light Years
... what represents the year? __________________________________________ 2. How is a “student minute” similar to a “light year”? ...
... what represents the year? __________________________________________ 2. How is a “student minute” similar to a “light year”? ...
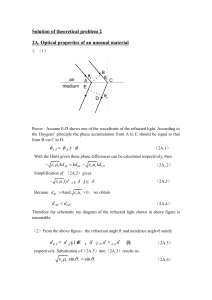
Solution of theoretical problem 2
... The light is negatively refracted at both interfaces, and the refraction angle equals to incidence angle. Meanwhile according to the Hints provided there is no reflected light from each interface. Therefore within the medium light rays converge strictly at a point symmetric to the source about the l ...
... The light is negatively refracted at both interfaces, and the refraction angle equals to incidence angle. Meanwhile according to the Hints provided there is no reflected light from each interface. Therefore within the medium light rays converge strictly at a point symmetric to the source about the l ...
Light 1 Mathematical representation of light (EM waves)
... 3. Elliptical polarization: the electric field again rotates about the direction of propagation nut its magnitude varies with position. The various polarization types may be visualized in Fig. 2. To visualize the different polarizations one may make use of an oscilloscope and combine two sinusoidal ...
... 3. Elliptical polarization: the electric field again rotates about the direction of propagation nut its magnitude varies with position. The various polarization types may be visualized in Fig. 2. To visualize the different polarizations one may make use of an oscilloscope and combine two sinusoidal ...
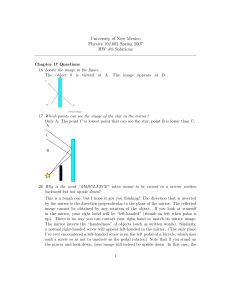
HW #8 Solutions
... Light reflect off of a transparent material (like glass) is decreased in amplitude– some of the light intensity is transmitted through the material. Since intensity is power per unit area, energy conservation requires that the reflected plus transmitted intensity (plus absorbed intensity, if any) is ...
... Light reflect off of a transparent material (like glass) is decreased in amplitude– some of the light intensity is transmitted through the material. Since intensity is power per unit area, energy conservation requires that the reflected plus transmitted intensity (plus absorbed intensity, if any) is ...
Optics I
... A 50 calcite prism is cut with its optic axis as shown in the figure. Sodium light is used in a spectrometer experiment to find no and ne. Two images of the slit are seen and minimum deviation is measured for each. Find no and ne if the angles of minimum deviation are 27.83 and 38.99. Explain how ...
... A 50 calcite prism is cut with its optic axis as shown in the figure. Sodium light is used in a spectrometer experiment to find no and ne. Two images of the slit are seen and minimum deviation is measured for each. Find no and ne if the angles of minimum deviation are 27.83 and 38.99. Explain how ...
Powerpoint Slides
... the difference in path (from the two slits) is equal to an integral number of wavelengths. In other words, when: ...
... the difference in path (from the two slits) is equal to an integral number of wavelengths. In other words, when: ...
Theory of relativistic harmonic generation
... Wlcm’,) that relativistic effects are expected to be important. The harmonic radiation is found to be emitted in a narrow cone (of radius 5.6 degrees) in the near forward direction, with a reasonably large (2 x lo-*) conversion efficiency. Perhaps most surprisingly they found that the intensity of t ...
... Wlcm’,) that relativistic effects are expected to be important. The harmonic radiation is found to be emitted in a narrow cone (of radius 5.6 degrees) in the near forward direction, with a reasonably large (2 x lo-*) conversion efficiency. Perhaps most surprisingly they found that the intensity of t ...
Scientific Notation Introduction Activity
... [note: conversion from m to km is three decimal places to the left 1000m = 1.0 km [standard] so 103m = 100km [exponent] and 1.0 x 103m = 1.0 x 100 km [scientific notation] always remember that 100 is equal to 1] ...
... [note: conversion from m to km is three decimal places to the left 1000m = 1.0 km [standard] so 103m = 100km [exponent] and 1.0 x 103m = 1.0 x 100 km [scientific notation] always remember that 100 is equal to 1] ...
Chem 115 - Waves, Radiation and Spectroscopy (lecture 16) 3/31
... Ultraviolet light is more dangerous because it has higher energy. Infrared is associated with lower energy. Note: energy follows frequency How light waves differ from each other Adjectives used in chemistry to describe wavelength are longer and shorter Adjectives used to refer to frequency are high ...
... Ultraviolet light is more dangerous because it has higher energy. Infrared is associated with lower energy. Note: energy follows frequency How light waves differ from each other Adjectives used in chemistry to describe wavelength are longer and shorter Adjectives used to refer to frequency are high ...
Physical Optics: Diffraction, Interference, and Polarization of Light
... however, the individual light waves coming from a source have randomly oriented electric vectors the light is said to be "randomly polarized" or "unpolarized." Unpolarized light can be conveniently plane-polarized by use of a Polaroid sheet. This is a sheet of transparent plastic in which special n ...
... however, the individual light waves coming from a source have randomly oriented electric vectors the light is said to be "randomly polarized" or "unpolarized." Unpolarized light can be conveniently plane-polarized by use of a Polaroid sheet. This is a sheet of transparent plastic in which special n ...
Anisotropic Minerals
... cancelling each other out, producing the resultant wave (R), which has no amplitude or wavelength. ...
... cancelling each other out, producing the resultant wave (R), which has no amplitude or wavelength. ...
Birefringence for facetors I : what is birefringence? First published in
... (higher) velocity of light in a vacuum. The crystal in Fig 1.2 has two refractive indices: one higher (corresponding to slow propagation) for light polarized in the direction in which charge can move and another , lower, value for light polarized perpendicular to this. These two indices are usually ...
... (higher) velocity of light in a vacuum. The crystal in Fig 1.2 has two refractive indices: one higher (corresponding to slow propagation) for light polarized in the direction in which charge can move and another , lower, value for light polarized perpendicular to this. These two indices are usually ...
Problem 2
... 2A. Optical properties of an unusual material (7 points) The optical properties of a medium are governed by its relative permittivity ( r ) and relative permeability ( r ). For conventional materials like water or glass, which are usually optically transparent, both of their r and r are posi ...
... 2A. Optical properties of an unusual material (7 points) The optical properties of a medium are governed by its relative permittivity ( r ) and relative permeability ( r ). For conventional materials like water or glass, which are usually optically transparent, both of their r and r are posi ...
Stokes Polarimetry - Hinds Instruments
... The setup above is not sufficient for determining the complete polarization state in situations where the linear polarization direction is not initially defined. Thus, two measurements at 45 degrees with respect to each other must be made. This is a requirement of all general purpose polarimeters. W ...
... The setup above is not sufficient for determining the complete polarization state in situations where the linear polarization direction is not initially defined. Thus, two measurements at 45 degrees with respect to each other must be made. This is a requirement of all general purpose polarimeters. W ...
Polarizer

A polarizer or polariser is an optical filter that passes light of a specific polarization and blocks waves of other polarizations. It can convert a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam with well-defined polarization, polarized light. The common types of polarizers are linear polarizers and circular polarizers. Polarizers are used in many optical techniques and instruments, and polarizing filters find applications in photography and liquid crystal display technology. Polarizers can also be made for other types of electromagnetic waves besides light, such as radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays.