Electromagnetic Waves - University of Toronto Physics
... respective views onto the screen, each with a different polarization. • The glasses allow only one of the images into each eye. ...
... respective views onto the screen, each with a different polarization. • The glasses allow only one of the images into each eye. ...
Basic Polarization Techniques and Devices
... If the orthogonal electric field components are equivalent, a phase shift in one component will result in circularly polarized light, as shown in part C of Figure 1. Retarders that cause this shift are known as quarter wave retarders. They have the unique property of turning elliptically polarized l ...
... If the orthogonal electric field components are equivalent, a phase shift in one component will result in circularly polarized light, as shown in part C of Figure 1. Retarders that cause this shift are known as quarter wave retarders. They have the unique property of turning elliptically polarized l ...
A transparent material like glass allows light to pass
... direction both rays of light travels with different velocities, even though they are traveling in the same direction. They are plane polarized in mutually perpendicular planes as usual. It is easy to produce linearly (or plane polarized) polarized light from a birefringent material. By some techniqu ...
... direction both rays of light travels with different velocities, even though they are traveling in the same direction. They are plane polarized in mutually perpendicular planes as usual. It is easy to produce linearly (or plane polarized) polarized light from a birefringent material. By some techniqu ...
Slides for circular dichroism
... difference in refractive index results in color refractive index is an intrinsic property of material and is related to composition ...
... difference in refractive index results in color refractive index is an intrinsic property of material and is related to composition ...
Demonstration: quarter-wave plate and half-wave plate
... shape of a plate with properly chosen optical axis orientation and thickness. The optical axis of the crystal should be parallel to the plate surface, as in Fig. 1 we set the x-axis parallel to the optical axis. In such a way, two polarization directions can be defined for a normal incident plane wa ...
... shape of a plate with properly chosen optical axis orientation and thickness. The optical axis of the crystal should be parallel to the plate surface, as in Fig. 1 we set the x-axis parallel to the optical axis. In such a way, two polarization directions can be defined for a normal incident plane wa ...
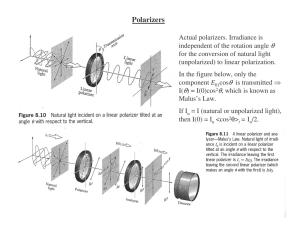
Polarizers θ
... Retarders: Methods for changing the polarization state of a beam Cut and polish a calcite crystal so that its optic axis will be ⊥ to both the front and back surfaces, as shown below. o- and e-waves propagate without any relative changes in phases, i.e., the components with all polarization orienta ...
... Retarders: Methods for changing the polarization state of a beam Cut and polish a calcite crystal so that its optic axis will be ⊥ to both the front and back surfaces, as shown below. o- and e-waves propagate without any relative changes in phases, i.e., the components with all polarization orienta ...
5. Reflection, refraction and polarization
... incident on birefringent crystal birefringent crystal, the two polarization components of the incident beam will experience different refractive indices (provided that the beam is not propagating along the crystal’s optic axis) and different phase changes as they go through the crystal. Third, the c ...
... incident on birefringent crystal birefringent crystal, the two polarization components of the incident beam will experience different refractive indices (provided that the beam is not propagating along the crystal’s optic axis) and different phase changes as they go through the crystal. Third, the c ...
PPT
... Initially unpolarized light of intensity I0 is sent into a system of three polarizers as shown. Wghat fraction of the initial intensity emerges from the system? What is the polarization of the exiting light? • Through the first polarizer: unpolarized to polarized, so I1=½I0. • Into the second polari ...
... Initially unpolarized light of intensity I0 is sent into a system of three polarizers as shown. Wghat fraction of the initial intensity emerges from the system? What is the polarization of the exiting light? • Through the first polarizer: unpolarized to polarized, so I1=½I0. • Into the second polari ...
Physics Tute Sheet-6 - College of Engineering Roorkee
... reflected beam is found to be plane polarized. Calculate the refractive index of the glass with respect to air if the refractive index of water with respect to air is 1.33. Ans. 1.585 3. The critical angle of light in certain substance is 50o. Calculate the polarizing angle for it. ...
... reflected beam is found to be plane polarized. Calculate the refractive index of the glass with respect to air if the refractive index of water with respect to air is 1.33. Ans. 1.585 3. The critical angle of light in certain substance is 50o. Calculate the polarizing angle for it. ...
Physics 228 Today: Polarization, Scattering
... Polarizing Visible Light Although the wavelength of visible light is < 1 μm, we can linearly polarize it using arrays of molecules, as in a polaroid filter. We can think of this similarly to microwaves and the metal plate: if the electric field orientation can accelerate electrons in the material - ...
... Polarizing Visible Light Although the wavelength of visible light is < 1 μm, we can linearly polarize it using arrays of molecules, as in a polaroid filter. We can think of this similarly to microwaves and the metal plate: if the electric field orientation can accelerate electrons in the material - ...
Light -1 - Physics
... The fundamental sources of all electromagnetic radiation are electric charges in accelerated motion. All objects emit electromagnetic radiation as a result of thermal motion of their molecules; this radiation, called thermal radiation, is a mixture of different wavelengths. Unlike mechanical waves, ...
... The fundamental sources of all electromagnetic radiation are electric charges in accelerated motion. All objects emit electromagnetic radiation as a result of thermal motion of their molecules; this radiation, called thermal radiation, is a mixture of different wavelengths. Unlike mechanical waves, ...
Revised Experiment 4
... Diffraction and interference experiments provide evidence that light may behave as a wave in some cases. They do not, however, indicate whether the waves are longitudinal or transverse. Polarization experiments demonstrate that light waves are transverse waves. In this experiment, you will produce a ...
... Diffraction and interference experiments provide evidence that light may behave as a wave in some cases. They do not, however, indicate whether the waves are longitudinal or transverse. Polarization experiments demonstrate that light waves are transverse waves. In this experiment, you will produce a ...
Lab
... goes to zero at some angle between 0° and 90°, the reflected light at that angle is linearly polarized with its electric field vectors perpendicular to the plane of incidence. The angle at which this occurs is called the polarizing angle or the Brewster angle. At other angles the reflected light is ...
... goes to zero at some angle between 0° and 90°, the reflected light at that angle is linearly polarized with its electric field vectors perpendicular to the plane of incidence. The angle at which this occurs is called the polarizing angle or the Brewster angle. At other angles the reflected light is ...
Types of polarization
... If we plot components Ex and Ey (Fig 2) using Eq.2 and Eq.3 for various times starting at t =0, we see that E = E0 starts off oriented along OY and rotates in a clockwise direction with increasing t, pointing along OX after a quarter period ( ωt = ...
... If we plot components Ex and Ey (Fig 2) using Eq.2 and Eq.3 for various times starting at t =0, we see that E = E0 starts off oriented along OY and rotates in a clockwise direction with increasing t, pointing along OX after a quarter period ( ωt = ...
lecture_five_2016
... sheet. The sheet is stretched aligning molecules and causing them to be birefringent. The molecules selectively attach themselves to aligned polymer molecules, so that absorption is high in one plane and weak in the other. The transmitted beam is linearly polarized. 5.2.4 Polarization of scattered l ...
... sheet. The sheet is stretched aligning molecules and causing them to be birefringent. The molecules selectively attach themselves to aligned polymer molecules, so that absorption is high in one plane and weak in the other. The transmitted beam is linearly polarized. 5.2.4 Polarization of scattered l ...
Physics 422 - Spring 2016 - Assignment #8, Due April... 1. Total internal reflection occurs when the angle of incidence, θ
... (a) Describe in detail the polarization states of each of these. (b) Determine the resulting Stokes parameters of the combined beam and describe its polarization state. (c) What is its degree of polarization? (d) What is the resulting light produced by overlapping the incoherent beams (1, 1, 0, 0) a ...
... (a) Describe in detail the polarization states of each of these. (b) Determine the resulting Stokes parameters of the combined beam and describe its polarization state. (c) What is its degree of polarization? (d) What is the resulting light produced by overlapping the incoherent beams (1, 1, 0, 0) a ...
Module 27: Polarization-II Lecture 27: Polarization-II
... Nicol prism is a smart device often used in the laboratories to produce linearly polarized beam. Here two calcite pieces cut in a special way (SQP and PQR) are cemented in a manner shown in the left of Figure 27.2. The two prisms are glued with a material called Canada balsam, a transparent material ...
... Nicol prism is a smart device often used in the laboratories to produce linearly polarized beam. Here two calcite pieces cut in a special way (SQP and PQR) are cemented in a manner shown in the left of Figure 27.2. The two prisms are glued with a material called Canada balsam, a transparent material ...
Polarization Practice
... 4. Light is reflected from a glass coffee table. When the angle of incidence is 56.70, the reflected light is completely polarized parallel to the surface of the glass. What is the index of refraction of the glass? ...
... 4. Light is reflected from a glass coffee table. When the angle of incidence is 56.70, the reflected light is completely polarized parallel to the surface of the glass. What is the index of refraction of the glass? ...
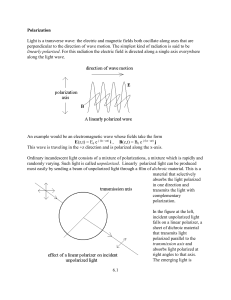
6.1 Polarization Light is a transverse wave: the electric and magnetic
... so that travel through the material leads to a phase difference between the components polarized along the x and y axes of = 2 - 1 = 2 (n2 - n1) t / . When = /2, the light polarized along one axis will have traveled through an optical path length one quarter of a wavelength longer than light polariz ...
... so that travel through the material leads to a phase difference between the components polarized along the x and y axes of = 2 - 1 = 2 (n2 - n1) t / . When = /2, the light polarized along one axis will have traveled through an optical path length one quarter of a wavelength longer than light polariz ...
pptx
... the electric fields. The magnetic field will be horizontal. The radio wave generated is said to be “polarized”. In general light sources produce “unpolarized waves”emitted by atomic motions in random directions. Completely unpolarized light will have equal components in horizontal and vertical direc ...
... the electric fields. The magnetic field will be horizontal. The radio wave generated is said to be “polarized”. In general light sources produce “unpolarized waves”emitted by atomic motions in random directions. Completely unpolarized light will have equal components in horizontal and vertical direc ...
IO.5 Elliptically Polarized Light - FSU
... to give plane polarized light. Let’s say they are in phase and the light is polarized along OD. Then if the plane of extinction of the analyzer is rotated through an angle β, the light will again be extinguished. Now it is clear from the figure that the orientation of one of the axes of the ellipse ...
... to give plane polarized light. Let’s say they are in phase and the light is polarized along OD. Then if the plane of extinction of the analyzer is rotated through an angle β, the light will again be extinguished. Now it is clear from the figure that the orientation of one of the axes of the ellipse ...
Polarization of Light Mica Sheet
... next to a puddle, and could see that the glare caused by reflected sunlight off of the water was also polarized. This is why you would want polarized sunglasses – they reduced glare! (but they don’t work if you tilt your head sideways!). Finally, was also talked about 3D vision as our last example o ...
... next to a puddle, and could see that the glare caused by reflected sunlight off of the water was also polarized. This is why you would want polarized sunglasses – they reduced glare! (but they don’t work if you tilt your head sideways!). Finally, was also talked about 3D vision as our last example o ...
Lecture 33 : Chiral molecules and Optical Activity
... consider a case where the refractive index in x direction is larger than the y direction. The wavelengths and speeds of light in the two directions are different. Therefore, a plane polarized light will emerge from the sample, however it’s plane of polarization will be rotated by an angle . ...
... consider a case where the refractive index in x direction is larger than the y direction. The wavelengths and speeds of light in the two directions are different. Therefore, a plane polarized light will emerge from the sample, however it’s plane of polarization will be rotated by an angle . ...
The Polarization of Light
... elliptically polarized. There is a class of materials, crystals, that are birefringent; as the name implies there two indices of refraction, depending on direction of propagation and the direction the electric field points. The two indices are call the ordinary index (no ) and the extraordinary inde ...
... elliptically polarized. There is a class of materials, crystals, that are birefringent; as the name implies there two indices of refraction, depending on direction of propagation and the direction the electric field points. The two indices are call the ordinary index (no ) and the extraordinary inde ...
Polarizer

A polarizer or polariser is an optical filter that passes light of a specific polarization and blocks waves of other polarizations. It can convert a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam with well-defined polarization, polarized light. The common types of polarizers are linear polarizers and circular polarizers. Polarizers are used in many optical techniques and instruments, and polarizing filters find applications in photography and liquid crystal display technology. Polarizers can also be made for other types of electromagnetic waves besides light, such as radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays.