Calculations and the Chemical Equation
... Just as a mole of atoms is based on the atomic mass or atomic weight, a mole of a compound is based upon the formula mass or formula weight. To calculate the formula weight, the formula unit must be known. The Chemical Equation and the Information it Conveys In a chemical equation, the identity of r ...
... Just as a mole of atoms is based on the atomic mass or atomic weight, a mole of a compound is based upon the formula mass or formula weight. To calculate the formula weight, the formula unit must be known. The Chemical Equation and the Information it Conveys In a chemical equation, the identity of r ...
ExamView - 1984 AP Chemistry Exam.tst
... When the concentration of substance B in the reaction above is doubled, all other factors being held constant, it is found that the rate of the reaction remains unchanged. The most probable explanation for this observation is that ...
... When the concentration of substance B in the reaction above is doubled, all other factors being held constant, it is found that the rate of the reaction remains unchanged. The most probable explanation for this observation is that ...
Multiple-choice questions : 1. Which of the following solutions
... Each question below consists of two separate statements. Decide whether each of the two statements is true or false; if both are true, then decide whether or not the second statement is a correct explanation of the first statement. Then select one option from A to D according to the following table ...
... Each question below consists of two separate statements. Decide whether each of the two statements is true or false; if both are true, then decide whether or not the second statement is a correct explanation of the first statement. Then select one option from A to D according to the following table ...
F:\Users\Steven\Documents\Chemistry\CHEM120\Problem Set
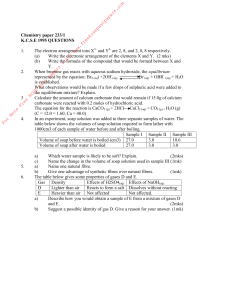
... the following reaction; 2 Ag(NO3) + (NH4)2S ----> Ag2S + 2 NH4NO3 a) If 25.0 mL of 0.10 M Ammonium sulfide is added to 60.0 mL of 0.10 M silver nitrate how much silver sulfide will form? b) Calculate the final concentration of the silver after all the precipitate (solid) has formed. 2) When 75 mL of ...
... the following reaction; 2 Ag(NO3) + (NH4)2S ----> Ag2S + 2 NH4NO3 a) If 25.0 mL of 0.10 M Ammonium sulfide is added to 60.0 mL of 0.10 M silver nitrate how much silver sulfide will form? b) Calculate the final concentration of the silver after all the precipitate (solid) has formed. 2) When 75 mL of ...
MEDICAL CHEMISTRY STUDY GUIDE
... location of fire extinguishers and, if available, safety showers and safety blankets as soon as you enter the laboratory so that you may use them if needed. Never perform an unauthorized experiment in the laboratory. Never assume that it is not necessary to inform your instructor for small accidents ...
... location of fire extinguishers and, if available, safety showers and safety blankets as soon as you enter the laboratory so that you may use them if needed. Never perform an unauthorized experiment in the laboratory. Never assume that it is not necessary to inform your instructor for small accidents ...
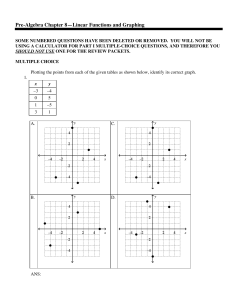
Pre-Algebra Chapter 8—Linear Functions and Graphing
... a. Write the values from the table as a set of ordered pairs (side length, area). b. Graph the relation. Describe the graph and explain whether it is a function. c. Describe the relationship between the side length and the area of the gardens. d. Suppose the area of a garden is 3,600 square feet. De ...
... a. Write the values from the table as a set of ordered pairs (side length, area). b. Graph the relation. Describe the graph and explain whether it is a function. c. Describe the relationship between the side length and the area of the gardens. d. Suppose the area of a garden is 3,600 square feet. De ...
mclintock.ch6 [Compatibility Mode]
... called a salt is also produced. The “salt” produced need not be common table salt. Any ionic compound produced in an acid–base reaction is called a salt. ► Oxidation–reduction reactions, or redox reactions, are processes in which one or more electrons are transferred between reaction partners (atoms ...
... called a salt is also produced. The “salt” produced need not be common table salt. Any ionic compound produced in an acid–base reaction is called a salt. ► Oxidation–reduction reactions, or redox reactions, are processes in which one or more electrons are transferred between reaction partners (atoms ...
Document
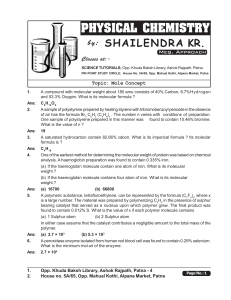
... Example 12: Calculate the # molecules of NH3 formed by the reaction of 150. g H2. 1 mole H2 2 moles NH3 6.022 x 1023 molecules NH3 = 2.23 x 1025 112 g H2 x x x 2.016 g H2 3 moles H2 1 mole NH3 molecules NH3. Starting Step 1 Step 3 result compound Step 2 Limiting Reactant and Yield Calculations The a ...
... Example 12: Calculate the # molecules of NH3 formed by the reaction of 150. g H2. 1 mole H2 2 moles NH3 6.022 x 1023 molecules NH3 = 2.23 x 1025 112 g H2 x x x 2.016 g H2 3 moles H2 1 mole NH3 molecules NH3. Starting Step 1 Step 3 result compound Step 2 Limiting Reactant and Yield Calculations The a ...
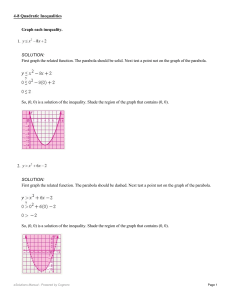
Graph each inequality. 1. SOLUTION: First graph the related function
... First graph the related function. The parabola should be dashed. Next test a point not on the graph of the parabola. ...
... First graph the related function. The parabola should be dashed. Next test a point not on the graph of the parabola. ...
CSEC Chemistry Revision Guide Answers.indd
... 8. a) Cooking oil and water are immiscible and the water has a higher density than the oil. When a mixture containing both is placed into a separating funnel, the oil floats on the water. By opening the tap of the funnel, the water can be run off into a conical flask, leaving the oil in the funnel. ...
... 8. a) Cooking oil and water are immiscible and the water has a higher density than the oil. When a mixture containing both is placed into a separating funnel, the oil floats on the water. By opening the tap of the funnel, the water can be run off into a conical flask, leaving the oil in the funnel. ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Net Ionic Equation • To form the net ionic equation, cross out anything that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. Ag+(aq) + NO3-(aq) + K+(aq) + Cl-(aq) AgCl (s) + K+(aq) + NO3-(aq) • The only things left in the equation are those things that change (i.e., react) durin ...
... Net Ionic Equation • To form the net ionic equation, cross out anything that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. Ag+(aq) + NO3-(aq) + K+(aq) + Cl-(aq) AgCl (s) + K+(aq) + NO3-(aq) • The only things left in the equation are those things that change (i.e., react) durin ...












![mclintock.ch6 [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003971396_1-780a12aa3165c9221aca3ac594a06674-300x300.png)