Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... The density of liquid ethanol (C2H5OH) is 0.790 g/mL. Calculate the number of molecules in a 35.0 mL sample of liquid ethanol. (NOTE: You CAN’T use 22.4 L/mol since this is NOT a ...
... The density of liquid ethanol (C2H5OH) is 0.790 g/mL. Calculate the number of molecules in a 35.0 mL sample of liquid ethanol. (NOTE: You CAN’T use 22.4 L/mol since this is NOT a ...
Slope
... There are 3 methods we can use to find slope! Each one works best for certain situations. Remember this guy? ...
... There are 3 methods we can use to find slope! Each one works best for certain situations. Remember this guy? ...
mole concept type 1 - teko classes bhopal
... Q.13 A sample of calcium carbonate contains impurities which do not react with a mineral acid. When 2 grams of the sample were reacted with the mineral acid, 375 ml of carbon dioxide were obtained at 27°C and 760 mm pressure. Calculate the % purity of the sample of CaCO3? Q.14 One gram of an alloy o ...
... Q.13 A sample of calcium carbonate contains impurities which do not react with a mineral acid. When 2 grams of the sample were reacted with the mineral acid, 375 ml of carbon dioxide were obtained at 27°C and 760 mm pressure. Calculate the % purity of the sample of CaCO3? Q.14 One gram of an alloy o ...
College Chemistry 1 Note Guide(free download)
... College Chemistry I is a course that covers the topics addressed in most first semester college chemistry courses. Many programs of study, particularly certain engineering degrees, require one semester of college chemistry as opposed to a two semester course, hence the year long course has been spli ...
... College Chemistry I is a course that covers the topics addressed in most first semester college chemistry courses. Many programs of study, particularly certain engineering degrees, require one semester of college chemistry as opposed to a two semester course, hence the year long course has been spli ...
The mathematics of PDEs and the wave equation
... moving along to the right at velocity c. Choosing which solution is a question of initial conditions and boundary values. In fact, if we are given the initial values for u = u(x, 0) then this determines f , since u(x, 0) = f (x − c0) = f (x). That is, the initial values for u determine the function ...
... moving along to the right at velocity c. Choosing which solution is a question of initial conditions and boundary values. In fact, if we are given the initial values for u = u(x, 0) then this determines f , since u(x, 0) = f (x − c0) = f (x). That is, the initial values for u determine the function ...
Unit 4 - Calculations and Chemical Reactions
... 1. Write the names, then and formulas of reactants (unit 3 naming). 2. Exchange cations and write the names, then formulas of products (unit 3 naming). 3. Write a chemical equation to showing the formulas of reactants and products. 4. From the solubility rules include the (aq) for soluble and (s) fo ...
... 1. Write the names, then and formulas of reactants (unit 3 naming). 2. Exchange cations and write the names, then formulas of products (unit 3 naming). 3. Write a chemical equation to showing the formulas of reactants and products. 4. From the solubility rules include the (aq) for soluble and (s) fo ...
Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry
... the molecular formula is known, the molecular formula can be obtained. Example: Calculate the molecular formula of a compound with a molecular mass of 84g and an empirical formula of CH2. ...
... the molecular formula is known, the molecular formula can be obtained. Example: Calculate the molecular formula of a compound with a molecular mass of 84g and an empirical formula of CH2. ...
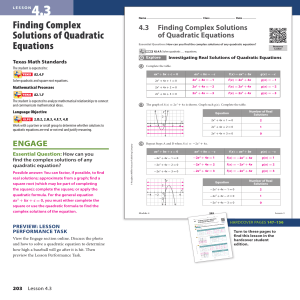
4.3 Notes - Denton ISD
... Some students have trouble completing the square because there are so many steps. Show them how to break the process into three parts: (1) Get the equation into the form needed for completing the square. (2) Complete the square. (3) Finish the solution by taking square roots of both sides and simpli ...
... Some students have trouble completing the square because there are so many steps. Show them how to break the process into three parts: (1) Get the equation into the form needed for completing the square. (2) Complete the square. (3) Finish the solution by taking square roots of both sides and simpli ...
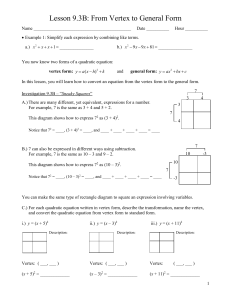
Lesson 9 - TCAPS Moodle
... C.) For each quadratic equation written in vertex form, describe the transformation, name the vertex, and convert the quadratic equation from vertex form to standard form. ii.) y = (x – 3)2 ...
... C.) For each quadratic equation written in vertex form, describe the transformation, name the vertex, and convert the quadratic equation from vertex form to standard form. ii.) y = (x – 3)2 ...
Topic 4
... Different ways to define acids/bases If you learn the acids and bases in water, it will inform you how water reacts in the reaction. We know that nitric acid is an acid in water; therefore, water must be the base and proton acceptor in the reaction. ...
... Different ways to define acids/bases If you learn the acids and bases in water, it will inform you how water reacts in the reaction. We know that nitric acid is an acid in water; therefore, water must be the base and proton acceptor in the reaction. ...
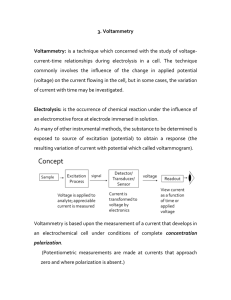
Solutions
... ‣ Electrolytic solutions contain dissociated ions. ‣ Substances that release H+ are acids. ‣ Substances that accept H+ are bases. ‣ Equilibrium is the state of a reversible reaction where the forward and reverse reactions are happening at the same rate. ‣ At equilibrium the ratio of products to reac ...
... ‣ Electrolytic solutions contain dissociated ions. ‣ Substances that release H+ are acids. ‣ Substances that accept H+ are bases. ‣ Equilibrium is the state of a reversible reaction where the forward and reverse reactions are happening at the same rate. ‣ At equilibrium the ratio of products to reac ...
AP Chemistry
... 11. A reaction is spontaneous below 400 K but is not spontaneous above 400 K. If So for the reaction is –50.0 J•mol-1 K-1, then the value of Ho for the reaction is (A) -50.0 kJ mol-1 (B) -20 kJ mol-1 (C) -0.050 kJ mol-1 (D) 2.0 x 104 kJ mol-1 ...
... 11. A reaction is spontaneous below 400 K but is not spontaneous above 400 K. If So for the reaction is –50.0 J•mol-1 K-1, then the value of Ho for the reaction is (A) -50.0 kJ mol-1 (B) -20 kJ mol-1 (C) -0.050 kJ mol-1 (D) 2.0 x 104 kJ mol-1 ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... Law of Conservation of Mass (Antoine Lavoisier, 1789) This law states that matter can neither be created nor destroyed; it can only change from one form to another. - According to this Law: during any chemical reaction, the total mass of the reactants or starting materials must equal the mass of th ...
... Law of Conservation of Mass (Antoine Lavoisier, 1789) This law states that matter can neither be created nor destroyed; it can only change from one form to another. - According to this Law: during any chemical reaction, the total mass of the reactants or starting materials must equal the mass of th ...
IX Chemistry Chapter 02
... A formula is a combination of symbols for atoms or ions, that are held together chemically in a compound. By formula we mean not only the elements present but also ratios in which the atoms are combined. Hence we will discuss two types of formulas i.e. Empirical formula and Molecular formula. 2.2.1 ...
... A formula is a combination of symbols for atoms or ions, that are held together chemically in a compound. By formula we mean not only the elements present but also ratios in which the atoms are combined. Hence we will discuss two types of formulas i.e. Empirical formula and Molecular formula. 2.2.1 ...