Holt Modern Chemistry Workbook
... living things are molecules. A molecule is a neutral group of atoms that are held together by covalent bonds. A molecule formed by polar-covalent bonds is still considered neutral because the sum of the partial charges on either end of the bond is zero. A molecular compound is any chemical compound ...
... living things are molecules. A molecule is a neutral group of atoms that are held together by covalent bonds. A molecule formed by polar-covalent bonds is still considered neutral because the sum of the partial charges on either end of the bond is zero. A molecular compound is any chemical compound ...
Ch3temp
... – Mole ratio (divide all moles by the smallest number of moles) – The numbers represent subscripts. • If the numbers are not whole numbers, multiply by some factor to make them whole. ...
... – Mole ratio (divide all moles by the smallest number of moles) – The numbers represent subscripts. • If the numbers are not whole numbers, multiply by some factor to make them whole. ...
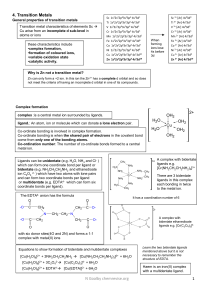
chapter twenty-one transition metals and coordination chemistry
... The crystal field diagrams are different because the geometries of where the ligands point is different. The tetrahedrally oriented ligands point differently in relationship to the d-orbitals than do the octahedrally oriented ligands. Plus, we have more ligands in an octahedral complex. See Figure 2 ...
... The crystal field diagrams are different because the geometries of where the ligands point is different. The tetrahedrally oriented ligands point differently in relationship to the d-orbitals than do the octahedrally oriented ligands. Plus, we have more ligands in an octahedral complex. See Figure 2 ...
Homework Solution 5 (p. 331, 2, 4, 6, 7,10,13,17,19, 21, 23) 2. (a
... (mod 15), 10x + 9y ≡ 8 (mod 15), the idea is (similar to the linear algebra in solving linear equations) to eliminate one variable, say y. To do so, one naturally wants to multiply 9 on the both sides of the first equation and to multiply 2 on the second equation. Let’s see what happened after we mu ...
... (mod 15), 10x + 9y ≡ 8 (mod 15), the idea is (similar to the linear algebra in solving linear equations) to eliminate one variable, say y. To do so, one naturally wants to multiply 9 on the both sides of the first equation and to multiply 2 on the second equation. Let’s see what happened after we mu ...
Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Many ionic compounds are soluble in water; that is, they dissolve in water to form solutions containing hydrated ions. Ionic compounds that do not dissolve to an appreciable extent are insoluble in water. Recall that ionic compounds consist of individual cations and anions held together by ionic for ...
... Many ionic compounds are soluble in water; that is, they dissolve in water to form solutions containing hydrated ions. Ionic compounds that do not dissolve to an appreciable extent are insoluble in water. Recall that ionic compounds consist of individual cations and anions held together by ionic for ...
analytical chemistry - Львівський національний медичний
... The equilibrium-constant expression is defined in terms of the balanced chemical equation. All analytical reactions, as a rule, run in solutions. For solutions we can not change the pressure. Sometimes we might heat or freeze the reaction vessel. But, in general, all reactions (processes) occur at i ...
... The equilibrium-constant expression is defined in terms of the balanced chemical equation. All analytical reactions, as a rule, run in solutions. For solutions we can not change the pressure. Sometimes we might heat or freeze the reaction vessel. But, in general, all reactions (processes) occur at i ...
Chemistry 11 - Correspondence Studies
... formula units. The symbol for the mole unit is mol. The mole is one of the seven base units of the standard SI system of measurement. German chemist, Wilhelm Ostwald, introduced the mole unit around 1900. The mole is used by chemists to communicate the amount of matter they are using. The number 6.0 ...
... formula units. The symbol for the mole unit is mol. The mole is one of the seven base units of the standard SI system of measurement. German chemist, Wilhelm Ostwald, introduced the mole unit around 1900. The mole is used by chemists to communicate the amount of matter they are using. The number 6.0 ...
Tro Ch 3 Lecture PP - Highline Community College
... Naming Binary Ionic Compounds for Metals with Invariant Charge • Contain metal cation + nonmetal anion • Metal listed first in formula and name 1. name metal cation first, name nonmetal anion ...
... Naming Binary Ionic Compounds for Metals with Invariant Charge • Contain metal cation + nonmetal anion • Metal listed first in formula and name 1. name metal cation first, name nonmetal anion ...
23. Oxidation and Reduction
... 1. The oxidation number of an atom of a free element is zero. Elements are free if they are not combined with other elements. If atoms of an element are combined with themselves, they are still considered to be free. For example, a free atom of Ag has an oxidation number of zero. In addition, atoms ...
... 1. The oxidation number of an atom of a free element is zero. Elements are free if they are not combined with other elements. If atoms of an element are combined with themselves, they are still considered to be free. For example, a free atom of Ag has an oxidation number of zero. In addition, atoms ...
Solubility and Reactions
... This activity illustrates the various effects of temperature (and even some effects of pressure) on solubility. It also highlights an interesting point: air dissolves in water, and water dissolves in air! Materials: clear, colourless container (e.g., beaker or drinking glass), a long match, any clea ...
... This activity illustrates the various effects of temperature (and even some effects of pressure) on solubility. It also highlights an interesting point: air dissolves in water, and water dissolves in air! Materials: clear, colourless container (e.g., beaker or drinking glass), a long match, any clea ...