Circuits_-_Parallel_with_Ohms_Law.doc
... coulomb=6.24151*1018 electrons. Therefore, 1 amp means that 6 followed by 18 zeros, or 6 billion billion electrons are flowing past a point in one second. Since 1 Coulomb=6.24*1018 electrons, each electron has a charge of 1/(6.24*1018) =1.6*10-19C. When measuring current in a circuit, we put an amme ...
... coulomb=6.24151*1018 electrons. Therefore, 1 amp means that 6 followed by 18 zeros, or 6 billion billion electrons are flowing past a point in one second. Since 1 Coulomb=6.24*1018 electrons, each electron has a charge of 1/(6.24*1018) =1.6*10-19C. When measuring current in a circuit, we put an amme ...
Chemistry Post-Enrolment Worksheet C
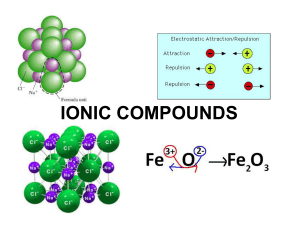
... lithium oxide is made up of Li+ ions and O2- ions. The overall formula is Li2O Polyatomic ions are those that contain more than one atom e.g. the hydroxide ion (OH -), which is made up of an oxygen atom and a hydrogen atom and has an overall 1- charge. Brackets can be used if we need more than one o ...
... lithium oxide is made up of Li+ ions and O2- ions. The overall formula is Li2O Polyatomic ions are those that contain more than one atom e.g. the hydroxide ion (OH -), which is made up of an oxygen atom and a hydrogen atom and has an overall 1- charge. Brackets can be used if we need more than one o ...
current electricity
... A. Charges need energy to ‘flow’ in a circuit B. The force that causes the ‘flow’ is called voltage C. Potential energy – energy an object has as a result of it’s position or height, energy is stored up in the object, remember the roller coaster 1. rollercoaster at top – has high potential energy ...
... A. Charges need energy to ‘flow’ in a circuit B. The force that causes the ‘flow’ is called voltage C. Potential energy – energy an object has as a result of it’s position or height, energy is stored up in the object, remember the roller coaster 1. rollercoaster at top – has high potential energy ...
2.4 Revision 1: There were two atoms. One got hit by an extremely
... c. Conducts electricity when solid and melted? d. Conducts electricity when dissolved or melted but not as a solid? e. Forces that hold non-polar molecular solids together. f. Can conduct heat and electrical charge. g. Which of the following solids have hydrogen bonds between molecules; hydrogen chl ...
... c. Conducts electricity when solid and melted? d. Conducts electricity when dissolved or melted but not as a solid? e. Forces that hold non-polar molecular solids together. f. Can conduct heat and electrical charge. g. Which of the following solids have hydrogen bonds between molecules; hydrogen chl ...
Ohm
... Unit = Ohm (Ω) When electrons flow through a resistor, it causes a loss of electric potential (voltage drop) ...
... Unit = Ohm (Ω) When electrons flow through a resistor, it causes a loss of electric potential (voltage drop) ...
The membrane potential
... We define the transmembrane potential to be v = φi − φe The value of the transmembrane potential at zero flux is then Ve = ...
... We define the transmembrane potential to be v = φi − φe The value of the transmembrane potential at zero flux is then Ve = ...
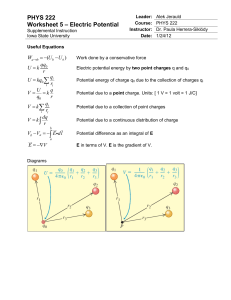
PHYS 222 Worksheet 5 Electric Potential
... 1) A point charge q1 = +2.40 µC is held stationary at the origin. A second point charge q2 = -4.30 µC moves from the point x = 0.150 m, y = 0 to the point x = 0.250 m, y = 0.250 m. How much work is done by the electric force on q2? W (U b U a ) ...
... 1) A point charge q1 = +2.40 µC is held stationary at the origin. A second point charge q2 = -4.30 µC moves from the point x = 0.150 m, y = 0 to the point x = 0.250 m, y = 0.250 m. How much work is done by the electric force on q2? W (U b U a ) ...
2.5 Chemical Bonding - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... • Covalent bonding can explain the existence of diatomic elements (please see Fig.4&5 p.178) ...
... • Covalent bonding can explain the existence of diatomic elements (please see Fig.4&5 p.178) ...
4-Calculate the Equilibrium Potential of Potassium
... The Resting Potential will be equal to -69mV. 8) Define and explain the space constant. What does it depend on? The space constant (λ) is the length in the fiber from the site of current injection to when the voltage has decayed to 37% of its initial value. ...
... The Resting Potential will be equal to -69mV. 8) Define and explain the space constant. What does it depend on? The space constant (λ) is the length in the fiber from the site of current injection to when the voltage has decayed to 37% of its initial value. ...
Conductors and insulators
... Why does a light bulb burn out when you switch the light on and never when you turn it off? ...
... Why does a light bulb burn out when you switch the light on and never when you turn it off? ...
Ionic vs Molecular Compounds Name Period Unit 4 – HW 1
... 16. Chemical formulas can also be written for ionic compounds. In this case, however, the formula does ...
... 16. Chemical formulas can also be written for ionic compounds. In this case, however, the formula does ...
File
... 5.6 Resistance Resistance is how difficult it is for current to flow Resistance is the opposite of conductance! A resistor is used to slow current down and convert electrical energy into heat energy (e.g. light bulb, stove element). ...
... 5.6 Resistance Resistance is how difficult it is for current to flow Resistance is the opposite of conductance! A resistor is used to slow current down and convert electrical energy into heat energy (e.g. light bulb, stove element). ...
Writing Ionic Formulas continued
... 2. Write the ionic formula for the compound lithium chloride. 3. Copper is found in a number of different ores, among them cuprite (copper(I) oxide), nantokite (copper(I) chloride), and chalcocite (copper( I) sulfide). Write the formulas for these three compounds. 4. Titanium is a metal commonly use ...
... 2. Write the ionic formula for the compound lithium chloride. 3. Copper is found in a number of different ores, among them cuprite (copper(I) oxide), nantokite (copper(I) chloride), and chalcocite (copper( I) sulfide). Write the formulas for these three compounds. 4. Titanium is a metal commonly use ...
Electric Current and Ohm`s Law
... lower resistance than dry skin. As the resistance of the skin goes down, the current will increase which is detected by the meter. ...
... lower resistance than dry skin. As the resistance of the skin goes down, the current will increase which is detected by the meter. ...
Chapters 20 and 21: Electricity
... • Static discharge – loss of static electricity as electrons move until both objects have the same charge ...
... • Static discharge – loss of static electricity as electrons move until both objects have the same charge ...
Nanofluidic circuitry
Nanofluidic circuitry is a nanotechnology aiming for control of fluids in nanometer scale. Due to the effect of an electrical double layer within the fluid channel, the behavior of nanofluid is observed to be significantly different compared with its microfluidic counterparts. Its typical characteristic dimensions fall within the range of 1–100 nm. At least one dimension of the structure is in nanoscopic scale. Phenomena of fluids in nano-scale structure are discovered to be of different properties in electrochemistry and fluid dynamics.