Document
... Water is a __________. 93. The coefficients are missing from the skeleton equation below. Cr (s) + Fe(NO3)2 (aq) Fe(s) + Cr(NO3)3 (aq) The correct order for the missing coefficients is_________. 94. The equation 2 C3H7OH + 9 O2 6 CO2 + 8 H2O is an example of which type of ...
... Water is a __________. 93. The coefficients are missing from the skeleton equation below. Cr (s) + Fe(NO3)2 (aq) Fe(s) + Cr(NO3)3 (aq) The correct order for the missing coefficients is_________. 94. The equation 2 C3H7OH + 9 O2 6 CO2 + 8 H2O is an example of which type of ...
Ionic Bonding www.AssignmentPoint.com Ionic bonding is a type of
... because the cohesive forces that keep the lattice together are of a more collective nature. This is quite different in the case of covalent bonding, where we can often speak of a distinct bond localized between two particular atoms. However, even if ionic bonding is combined with some covalency, the ...
... because the cohesive forces that keep the lattice together are of a more collective nature. This is quite different in the case of covalent bonding, where we can often speak of a distinct bond localized between two particular atoms. However, even if ionic bonding is combined with some covalency, the ...
Document
... with band gaps in the range of 2-3 eV. Methods for controlled doping of these materials are not well established, mainly because doping often requires the mixing of a redox active small molecular dopant into the organic semiconductor host, which can be mobile under applied electrical fields during d ...
... with band gaps in the range of 2-3 eV. Methods for controlled doping of these materials are not well established, mainly because doping often requires the mixing of a redox active small molecular dopant into the organic semiconductor host, which can be mobile under applied electrical fields during d ...
[A], [B], [C], [D] - Wits Structural Chemistry
... Effect of Ionic Strength, Ion charge and Ion Size on the Activity Coefficient (Over the range of ionic strength from 0 to 0.1M) 1. As ionic strength increases, the activity coefficient decreases. 1 as 0 2. As the charge of the ion increases, the departure of its activity coefficient from un ...
... Effect of Ionic Strength, Ion charge and Ion Size on the Activity Coefficient (Over the range of ionic strength from 0 to 0.1M) 1. As ionic strength increases, the activity coefficient decreases. 1 as 0 2. As the charge of the ion increases, the departure of its activity coefficient from un ...
I. Electric Charge - Otterville R
... • “bigger” light would be dimmer each device receives the total voltage • no change when lights are added ...
... • “bigger” light would be dimmer each device receives the total voltage • no change when lights are added ...
ASSIGNMENT ON PHYSICS CLASS:12 DATE:18-O4
... 2. A charge of 10 μc is brought from point A (0,4 cm,0) to C (3 cm,0,0) via point B (0,0,6 cm) in vacuum. Calculate the work done if the charge at origin is 20 μc. niformly char. Where the energy of capacitor does resides? ...
... 2. A charge of 10 μc is brought from point A (0,4 cm,0) to C (3 cm,0,0) via point B (0,0,6 cm) in vacuum. Calculate the work done if the charge at origin is 20 μc. niformly char. Where the energy of capacitor does resides? ...
3. Short Channel Effects on MOS Transistors.
... • For large values of L or small values of VDS, κ approaches 1 and (7) reduces to (5). • For short channel devices κ<1 and the current is smaller than ...
... • For large values of L or small values of VDS, κ approaches 1 and (7) reduces to (5). • For short channel devices κ<1 and the current is smaller than ...
Date: 13/11/2005
... (8) The electric flux density on a spherical surface r = b is the same for point charge Q located at the origin and for charge Q uniformly distributed on surface r = a (a < b) ( ...
... (8) The electric flux density on a spherical surface r = b is the same for point charge Q located at the origin and for charge Q uniformly distributed on surface r = a (a < b) ( ...
Chap. 4 AQUEOUS RXNS O
... 6. The sum of all O.N. in a neutral compound is 0, otherwise ΣO.N. = ion charge ...
... 6. The sum of all O.N. in a neutral compound is 0, otherwise ΣO.N. = ion charge ...
13 Electric Circuits
... electrons from one terminal (leaving it positively charged) to another terminal (leaving it negatively charged). ...
... electrons from one terminal (leaving it positively charged) to another terminal (leaving it negatively charged). ...
Junior Honours
... dipole of moment p at the origin. Hence, or otherwise, calculate the potential at a point P with spherical polar co-ordinates (r, θ, φ) due to charges −q, 2q and −q at points z = −a, z = 0 and z = +a respectively, where a r. Determine the radial and transverse components Er and Eθ of the electric ...
... dipole of moment p at the origin. Hence, or otherwise, calculate the potential at a point P with spherical polar co-ordinates (r, θ, φ) due to charges −q, 2q and −q at points z = −a, z = 0 and z = +a respectively, where a r. Determine the radial and transverse components Er and Eθ of the electric ...
Electric Currents
... Conceptual Example: How to Connect a Battery. What’s wrong with each of circuits shown below? ...
... Conceptual Example: How to Connect a Battery. What’s wrong with each of circuits shown below? ...
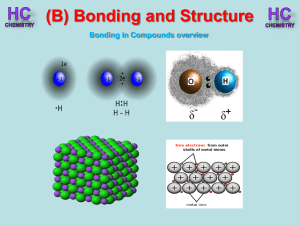
Lesson 1 - Bonding in compounds overview
... Silicon and oxygen make up nearly 75% of the Earth’s crust. They are therefore the most common elements in the Earth’s crust. They combine together to make a covalent network compound called silicon dioxide. This is usually found in the form of sand or quartz. Each Si atom is bonded to 4 O atoms, an ...
... Silicon and oxygen make up nearly 75% of the Earth’s crust. They are therefore the most common elements in the Earth’s crust. They combine together to make a covalent network compound called silicon dioxide. This is usually found in the form of sand or quartz. Each Si atom is bonded to 4 O atoms, an ...
Electricity and Magnetism Test Review
... What is an electrical insulator? What does it have? If like repel, what do opposites do? What does the strength of an electrical field depend on? What happens to magnetic force if the distance between magnets increases? Describe the behavior of magnetic poles. Like poles / Opposite poles. What do el ...
... What is an electrical insulator? What does it have? If like repel, what do opposites do? What does the strength of an electrical field depend on? What happens to magnetic force if the distance between magnets increases? Describe the behavior of magnetic poles. Like poles / Opposite poles. What do el ...
21.1 Magnets & Magnetic Fields
... conductor? Conductors are materials through which charge can flow easily (metal wires) Voltage is induced in a conductor by a changing ...
... conductor? Conductors are materials through which charge can flow easily (metal wires) Voltage is induced in a conductor by a changing ...
Slide 1
... Conventional current- from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. Drift velocity- the speed in which individual electrons move within the conductor, opposite the electric field. The drift velocity is relatively small. ...
... Conventional current- from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. Drift velocity- the speed in which individual electrons move within the conductor, opposite the electric field. The drift velocity is relatively small. ...
Nanofluidic circuitry
Nanofluidic circuitry is a nanotechnology aiming for control of fluids in nanometer scale. Due to the effect of an electrical double layer within the fluid channel, the behavior of nanofluid is observed to be significantly different compared with its microfluidic counterparts. Its typical characteristic dimensions fall within the range of 1–100 nm. At least one dimension of the structure is in nanoscopic scale. Phenomena of fluids in nano-scale structure are discovered to be of different properties in electrochemistry and fluid dynamics.


![[A], [B], [C], [D] - Wits Structural Chemistry](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000095863_1-918f0427052f54159a7c908528a2e159-300x300.png)