![Conformations of [beta]-amino acid residues in peptides: X](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003974629_1-521aa7943d558a5d58755964c90b9e45-300x300.png)
Conformations of [beta]-amino acid residues in peptides: X
... dues. An understanding of the conformational biases imposed by backbone substitution patterns is essential for using b-residues, in a rational manner, in the design of specifically folded peptides. The conformational analysis of a-amino acid containing peptides has benefited enormously by the use of t ...
... dues. An understanding of the conformational biases imposed by backbone substitution patterns is essential for using b-residues, in a rational manner, in the design of specifically folded peptides. The conformational analysis of a-amino acid containing peptides has benefited enormously by the use of t ...
ppt
... May have several Deformational Phases May have an accompanying Metamorphic Cycles with one or more Reaction Events ...
... May have several Deformational Phases May have an accompanying Metamorphic Cycles with one or more Reaction Events ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 23, Metamorpic Textures
... May have several Deformational Phases May have an accompanying Metamorphic Cycles with one or more Reaction Events ...
... May have several Deformational Phases May have an accompanying Metamorphic Cycles with one or more Reaction Events ...
Chapter 1 Magnetic properties of heavy lanthanide metals
... ferrimagnetic cone phase appears, consisting of a commensurate helical structure with an out-of-plane component leading to a net magnetic moment along the c axis [5]. The basic arrangements of the moments in these systems were determined from neutron diffraction experiments by Koehler et. al and are ...
... ferrimagnetic cone phase appears, consisting of a commensurate helical structure with an out-of-plane component leading to a net magnetic moment along the c axis [5]. The basic arrangements of the moments in these systems were determined from neutron diffraction experiments by Koehler et. al and are ...
First-principles study of electronic, optical and thermoelectric
... phase with cubic symmetry for temperatures above 758 K and 903 K, respectively. A series of structural phase transitions are observed in AgNbO3 with the decrease in temperature that shows its suitability for piezoelectric material.11 – 15 Instead of previously studied perovskite with large bandgap, ...
... phase with cubic symmetry for temperatures above 758 K and 903 K, respectively. A series of structural phase transitions are observed in AgNbO3 with the decrease in temperature that shows its suitability for piezoelectric material.11 – 15 Instead of previously studied perovskite with large bandgap, ...
Recrystallization of Drugs: Significance on Pharmaceutical Processing
... and modify physical properties of bulk solids of drugs (Liebenberg et al., 1999; Maghsoodi et al., 2007). Seton et al. evaluated the particle morphology of ibuprofen, an anti-inflammatory drug, by recrystallization from a range of solvents and investigated the following influence on compaction prope ...
... and modify physical properties of bulk solids of drugs (Liebenberg et al., 1999; Maghsoodi et al., 2007). Seton et al. evaluated the particle morphology of ibuprofen, an anti-inflammatory drug, by recrystallization from a range of solvents and investigated the following influence on compaction prope ...
Unusually Dense Crystal Packings of Ellipsoids
... and oblate ellipsoids (we consider the prolate case in the equations in this section). Two sharp maxima with density of about 0.770732 are observed when the ellipsoids in the face-centered layers touch six rather than four inplane neighbors, as √ shown in Fig. 4, i.e., when L√= 2α, which gives α = 3 ...
... and oblate ellipsoids (we consider the prolate case in the equations in this section). Two sharp maxima with density of about 0.770732 are observed when the ellipsoids in the face-centered layers touch six rather than four inplane neighbors, as √ shown in Fig. 4, i.e., when L√= 2α, which gives α = 3 ...
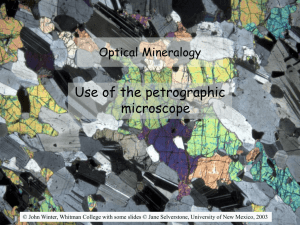
PowerPoint lectures on Optical Mineralogy, by J. Winter
... In this case both rays really do vibrate ^ propagation & follow same path (as we have simplified the random case) We shall consider random and principal as alike, only the value of e ...
... In this case both rays really do vibrate ^ propagation & follow same path (as we have simplified the random case) We shall consider random and principal as alike, only the value of e ...
a biological system producing a self-assembling
... after fixation show parabolic patterns of an electron-light component, set in a continuous matrix of protein. Such patterns arise in helicoidal systems (e.g. arthropod cuticle) and microdensitometric scans of the matrix show a rhythmical electron-density variation consistent with helicoidal structur ...
... after fixation show parabolic patterns of an electron-light component, set in a continuous matrix of protein. Such patterns arise in helicoidal systems (e.g. arthropod cuticle) and microdensitometric scans of the matrix show a rhythmical electron-density variation consistent with helicoidal structur ...
Direct methods and protein crystallography at low
... invariants. To assign initial phases, an extension of the random-phase procedure into reciprocal space is made; trial structures are generated by placing random atoms in the unit cell with distance constraints, i.e. atoms may not be closer than Ê . No angle constraints are applied. A Fourier transfo ...
... invariants. To assign initial phases, an extension of the random-phase procedure into reciprocal space is made; trial structures are generated by placing random atoms in the unit cell with distance constraints, i.e. atoms may not be closer than Ê . No angle constraints are applied. A Fourier transfo ...
document
... crystallization – process by which atoms are arranged to form a material with a crystal structure Minerals can form two ways: 1. Crystallization of magma and lava – minerals form as hot magma cools inside the crust, or as lava hardens on the surface. When these liquids cool to a solid state, they fo ...
... crystallization – process by which atoms are arranged to form a material with a crystal structure Minerals can form two ways: 1. Crystallization of magma and lava – minerals form as hot magma cools inside the crust, or as lava hardens on the surface. When these liquids cool to a solid state, they fo ...
Structure and magnetic behaviour of mononuclear and dinuclear Cu(II)/Zn(II) monocarboxylate-pyridine
... paramagnetic properties of the mononuclear copper(II) monocarboxylate-pyridine derivatives by magnetic measurements. The complexes a and b exhibit small antiferromagnetic interactions (θ = − 0.74 K for a and θ = − 0.44 K for b), albeit much weaker. The temperature dependence of the magnetic suscepti ...
... paramagnetic properties of the mononuclear copper(II) monocarboxylate-pyridine derivatives by magnetic measurements. The complexes a and b exhibit small antiferromagnetic interactions (θ = − 0.74 K for a and θ = − 0.44 K for b), albeit much weaker. The temperature dependence of the magnetic suscepti ...
luminescence studies of rare earth (europium) doped nano
... particles be synthesized and integrated with functional substrates, such as single crystals, ceramic microspheres, and nanofibers. It was demonstrated that such materials, especially the ceramics built from nano-crystals, are characterized by pronounced optical properties. [4] Among the materials in ...
... particles be synthesized and integrated with functional substrates, such as single crystals, ceramic microspheres, and nanofibers. It was demonstrated that such materials, especially the ceramics built from nano-crystals, are characterized by pronounced optical properties. [4] Among the materials in ...
Module 10 Crystal Defects in Metals I Lecture 10 Crystal
... Metals we are familiar with are mostly crystalline. They are made of several crystals having different orientations. Their properties would depend on the properties of the individual crystals (also commonly known as grains) and the way they are arranged. In the previous ...
... Metals we are familiar with are mostly crystalline. They are made of several crystals having different orientations. Their properties would depend on the properties of the individual crystals (also commonly known as grains) and the way they are arranged. In the previous ...
5. GÖCH Symposium 2016 “Physikalische Chemie in Österreich”
... with the STM tip, we measured not only the current flowing through the wire [2,3] but also the forces that are active during the conformational changes in the single oligomer when using an atomic force microscope [4]. An important issue for any functional molecule is the role of the direct environme ...
... with the STM tip, we measured not only the current flowing through the wire [2,3] but also the forces that are active during the conformational changes in the single oligomer when using an atomic force microscope [4]. An important issue for any functional molecule is the role of the direct environme ...
[edit]Occurrence in solution
... metal, in the Earth's crust. It makes up about 8% by weight of the Earth's solid surface. Aluminium metal is too reactive chemically to occur natively. Instead, it is found combined in over 270 differentminerals.[4] The chief ore of aluminium is bauxite. Aluminium is remarkable for the metal's low d ...
... metal, in the Earth's crust. It makes up about 8% by weight of the Earth's solid surface. Aluminium metal is too reactive chemically to occur natively. Instead, it is found combined in over 270 differentminerals.[4] The chief ore of aluminium is bauxite. Aluminium is remarkable for the metal's low d ...
RTF
... changes indicated. Tell how the concentrations of the following substances will change as a result of the stress – will their concentrations increase, decrease, or undergo no change when the indicated change is made: a. Cu2+(aq) + 4 NH3(g) ...
... changes indicated. Tell how the concentrations of the following substances will change as a result of the stress – will their concentrations increase, decrease, or undergo no change when the indicated change is made: a. Cu2+(aq) + 4 NH3(g) ...
POLYMERS
... Polymer Biomaterials There are a large number of uses for polymers in the biomaterials field. These arise due to the wide variety of properties possible. OBJECTIVES to introduce some fundamental polymer properties and the factors that influence them to provide an overview of the uses of polymers ...
... Polymer Biomaterials There are a large number of uses for polymers in the biomaterials field. These arise due to the wide variety of properties possible. OBJECTIVES to introduce some fundamental polymer properties and the factors that influence them to provide an overview of the uses of polymers ...
Intrinsic Transparent Conductors without Doping
... below EF. The carrier (electron) concentration (ne ) and plasma ...
... below EF. The carrier (electron) concentration (ne ) and plasma ...
Microwave Synthesis of Noncentrosymmetric BaTiO3 Truncated
... such as dynamic random access memory (DRAM) that requires polarizability, piezoelectricity, pyroelectricity, and electro-optic activity (3, 6-8). However, the grain size control largely hinders the production of high capacitance devices, which is of great interest in dielectric oxide devices. In MCC ...
... such as dynamic random access memory (DRAM) that requires polarizability, piezoelectricity, pyroelectricity, and electro-optic activity (3, 6-8). However, the grain size control largely hinders the production of high capacitance devices, which is of great interest in dielectric oxide devices. In MCC ...
Graduate Category: Engineering and Technology Degree Level: PhD in Chemical Engineering Abstract ID# 1106
... tunable channel for guest molecule loading. Several studies have established their biocompatibility and applications in nanomedicine such as in coatings for medical devices, materials for tissue engineering and for drug display and delivery. With novel applications in mind, particularly, drug de ...
... tunable channel for guest molecule loading. Several studies have established their biocompatibility and applications in nanomedicine such as in coatings for medical devices, materials for tissue engineering and for drug display and delivery. With novel applications in mind, particularly, drug de ...
The Role of Tetrahedral Building Blocks in Low-Dimensional Oxohalide Materials Iwan Zimmermann
... can be introduced into the crystal structure. Due to their non-bonding electron pair, such elements adopt a one-sided, asymmetric coordination caused by a second order Jahn Teller (SOJT) distortion.[3-4] Lone-pairs do not participate in bonding, and therefore their terminating properties help to ope ...
... can be introduced into the crystal structure. Due to their non-bonding electron pair, such elements adopt a one-sided, asymmetric coordination caused by a second order Jahn Teller (SOJT) distortion.[3-4] Lone-pairs do not participate in bonding, and therefore their terminating properties help to ope ...
Colloidal crystal

A colloidal crystal is an ordered array of colloid particles, analogous to a standard crystal whose repeating subunits are atoms or molecules. A natural example of this phenomenon can be found in the gem opal, where spheres of silica assume a close-packed locally periodic structure under moderate compression. Bulk properties of a colloidal crystal depend on composition, particle size, packing arrangement, and degree of regularity. Applications include photonics, materials processing, and the study of self-assembly and phase transitions.















![[edit]Occurrence in solution](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009755146_1-58e56f0cc08d3d020872dbc6c3acbb66-300x300.png)