Lecture 11
... physical phenomena Molecular example – If the atoms in the molecule do not move too far, the forces between them can be modeled as if there were springs between the atoms – The potential energy acts similar to that of the SHM oscillator ...
... physical phenomena Molecular example – If the atoms in the molecule do not move too far, the forces between them can be modeled as if there were springs between the atoms – The potential energy acts similar to that of the SHM oscillator ...
a notes
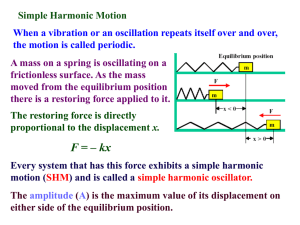
... For a vertical spring and mass system . . . • When the mass is above equilibrium, the restoring force points down. • At equilibrium, the net force is zero. • When the mass is below equilibrium, the restoring force points up. ...
... For a vertical spring and mass system . . . • When the mass is above equilibrium, the restoring force points down. • At equilibrium, the net force is zero. • When the mass is below equilibrium, the restoring force points up. ...
File
... Reflection and Interference of Waves When a wave hits a barrier or an obstacle, it is reflected. Wave in a string is inverted if the end of the string is fixed. If the end is not fixed, it will be reflected right side up. ...
... Reflection and Interference of Waves When a wave hits a barrier or an obstacle, it is reflected. Wave in a string is inverted if the end of the string is fixed. If the end is not fixed, it will be reflected right side up. ...
A x
... Summary Simple harmonic motion (SHM) is that motion in which a body moves back and forth over a fixed path, returning to each position and velocity after a definite interval of time. The frequency (rev/s) is the reciprocal of the period (time for one revolution). ...
... Summary Simple harmonic motion (SHM) is that motion in which a body moves back and forth over a fixed path, returning to each position and velocity after a definite interval of time. The frequency (rev/s) is the reciprocal of the period (time for one revolution). ...
SHM1simpleHarm
... 4N force on the spring will cause a displacement of 0.02 meters. A 2kg block is pulled a distance of 0.04 meters and then released, setting the system in motion. a. Find the spring constant. b. Find the period and frequency of oscillation. c. Calculate the maximum velocity attained. d. Calculate the ...
... 4N force on the spring will cause a displacement of 0.02 meters. A 2kg block is pulled a distance of 0.04 meters and then released, setting the system in motion. a. Find the spring constant. b. Find the period and frequency of oscillation. c. Calculate the maximum velocity attained. d. Calculate the ...
Simple Harmonic Motion: a system that oscillates with a constant
... 2. Watch MythBusters. They did two different episodes with oscillators that tried to shake bridges. One was a suspended bridge with marching feet; the other was a large metal framed bridge like the one in East Troy. This is their test of the actuator on a steel beam. 3. A person periodically pushed ...
... 2. Watch MythBusters. They did two different episodes with oscillators that tried to shake bridges. One was a suspended bridge with marching feet; the other was a large metal framed bridge like the one in East Troy. This is their test of the actuator on a steel beam. 3. A person periodically pushed ...
Unit 13: Periodic Motion
... o Periodic motion is motion that repeats itself in a definite cycle. It occurs whenever a body has a stable equilibrium position and a restoring force that acts when it is displaced from equilibrium. o Period is the time for one cycle. Frequency is the number of cycles per unit time. Angular frequen ...
... o Periodic motion is motion that repeats itself in a definite cycle. It occurs whenever a body has a stable equilibrium position and a restoring force that acts when it is displaced from equilibrium. o Period is the time for one cycle. Frequency is the number of cycles per unit time. Angular frequen ...
Kollmorgen 4Ch-Digital-Input Datasheet en
... 4-Channel Digital Inputs, 24 V DC The 4 channel digital input terminals acquire the binary 24 V control signals and transmit them, in an electrically isolated form, to the higher-level automation unit. These terminals contain four channels that indicate their signal state by means of LEDs and have d ...
... 4-Channel Digital Inputs, 24 V DC The 4 channel digital input terminals acquire the binary 24 V control signals and transmit them, in an electrically isolated form, to the higher-level automation unit. These terminals contain four channels that indicate their signal state by means of LEDs and have d ...