ECON 401 November 19, 2012 Fragile Economy in the 1990s
... completed. It grew rapidly, and reached 20% by 1997. In 1993, shortly before the onset of the crisis almost all the central government’ s budgetary expenditures were being allocated to current expenditures (mainly wage and salary payments), interest payments on domestic and external debt and transfe ...
... completed. It grew rapidly, and reached 20% by 1997. In 1993, shortly before the onset of the crisis almost all the central government’ s budgetary expenditures were being allocated to current expenditures (mainly wage and salary payments), interest payments on domestic and external debt and transfe ...
Skidelsky comment - The Wincott Foundation
... The economy never returned to the levels of unemployment it experienced from 1950 to 1970. In the UK average unemployment went up from 1.6% a year between 1950 and 1970 to 7.5% between 1980 and 2008. And even after demand deficiency had been removed, structural unemployment was twice as high as it h ...
... The economy never returned to the levels of unemployment it experienced from 1950 to 1970. In the UK average unemployment went up from 1.6% a year between 1950 and 1970 to 7.5% between 1980 and 2008. And even after demand deficiency had been removed, structural unemployment was twice as high as it h ...
Economic Geography
... Total value of all goods and services by a country over one year. Includes facilities overseas owned by ...
... Total value of all goods and services by a country over one year. Includes facilities overseas owned by ...
Growth - Jubilee Debt Campaign
... afford to go on growing, particularly if we want to give people in poorer countries a chance of being able to at least meet their basic needs…Growth is a side issue. The end goal is about prosperity in terms of greater wellbeing, in terms of greater equality, in terms of having a cleaner environment ...
... afford to go on growing, particularly if we want to give people in poorer countries a chance of being able to at least meet their basic needs…Growth is a side issue. The end goal is about prosperity in terms of greater wellbeing, in terms of greater equality, in terms of having a cleaner environment ...
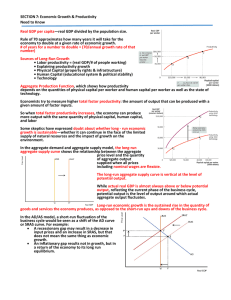
SECTION 7: Economic Growth & Productivity Need to Know —real GDP divided by the population size.
... • Physical Capital (property rights & infrastructure) • Human Capital (educational system & political stability) • Technology ...
... • Physical Capital (property rights & infrastructure) • Human Capital (educational system & political stability) • Technology ...
Presentation to the Tucson Chapter of the Association of Investment... Skyline Country Club, Tucson, AZ
... 1. One is the stimulus in the pipeline both from fiscal policy and from monetary policy. a. On the fiscal side, (1) there’s some extra stimulus from the pickup in defense spending to support the action in Iraq. (2) In addition, Congress passed stimulus packages in 2001 and 2002, (a) and, of course, ...
... 1. One is the stimulus in the pipeline both from fiscal policy and from monetary policy. a. On the fiscal side, (1) there’s some extra stimulus from the pickup in defense spending to support the action in Iraq. (2) In addition, Congress passed stimulus packages in 2001 and 2002, (a) and, of course, ...
JPEPA and Current Economic Situation in the Philippines
... differences, e.g. mobility of factors of production – Challenge to China in wielding/asserting global influence (FDIs, ODAs, Africa engagement, participation in multilateral noneconomic initiatives e.g. security, health, disaster assistance, etc.) as a huge country-market – Efforts by ASEAN and rest ...
... differences, e.g. mobility of factors of production – Challenge to China in wielding/asserting global influence (FDIs, ODAs, Africa engagement, participation in multilateral noneconomic initiatives e.g. security, health, disaster assistance, etc.) as a huge country-market – Efforts by ASEAN and rest ...
Honduras.pdf
... this level for the second half of the year. Up to August, real monetary aggregates posted annual declines of 11% (in the case of M2) and 7% (for M3). The real growth rate of credit to the private sector is predicted to close the year at 5% (compared with growth of 21% in 2007). To tackle the interna ...
... this level for the second half of the year. Up to August, real monetary aggregates posted annual declines of 11% (in the case of M2) and 7% (for M3). The real growth rate of credit to the private sector is predicted to close the year at 5% (compared with growth of 21% in 2007). To tackle the interna ...
Economic Systems - Schoolwires.net
... I. Economic Systems A. Traditional: People produce their __________________ and __________________ for what they need. B. Market: People and businesses _________________________________________. 1. Also known as __________________ and __________________. C. Command: The __________________ makes the ...
... I. Economic Systems A. Traditional: People produce their __________________ and __________________ for what they need. B. Market: People and businesses _________________________________________. 1. Also known as __________________ and __________________. C. Command: The __________________ makes the ...
Developments in the SA economy
... – Growth rate1.9 % in 2013 – NT projected GDP of 2.7 % in 2014 & 3.2 % in 2015; – Drivers of growth: • New power plants & transport infrastructure; • Stronger global recovery expected to support exports; • Growth in sub-Saharan Africa will promote expanded trade & investment. ...
... – Growth rate1.9 % in 2013 – NT projected GDP of 2.7 % in 2014 & 3.2 % in 2015; – Drivers of growth: • New power plants & transport infrastructure; • Stronger global recovery expected to support exports; • Growth in sub-Saharan Africa will promote expanded trade & investment. ...
South Africa: Staff Concluding Statement of an IMF Staff Visit
... Since 1994, economic growth and sound policies have been mutually reinforcing, fostering economic transformation and improving living conditions. However, the long-run economic growth rate has gradually slowed over the years. Following the onset of adverse shocks such as the decline in commodity pri ...
... Since 1994, economic growth and sound policies have been mutually reinforcing, fostering economic transformation and improving living conditions. However, the long-run economic growth rate has gradually slowed over the years. Following the onset of adverse shocks such as the decline in commodity pri ...
Asia and Pacific Regional Round Table: “The China and
... their hands’ to help other developing countries, especially the LDCs to ‘play along the value chain’ more expandedly more ‘knowledge and technology touch’ to enhance added value, or even to shift up the chain into a higher position. In this respect, the incoming South-south Cooperation initiative on ...
... their hands’ to help other developing countries, especially the LDCs to ‘play along the value chain’ more expandedly more ‘knowledge and technology touch’ to enhance added value, or even to shift up the chain into a higher position. In this respect, the incoming South-south Cooperation initiative on ...
Overview
... the normalization process in the monetary policy in the US keep the sensitivity of global markets to data flow at high levels. In such a conjuncture, the US dollar has appreciated against other currencies and capital movements in emerging economies have fluctuated. ...
... the normalization process in the monetary policy in the US keep the sensitivity of global markets to data flow at high levels. In such a conjuncture, the US dollar has appreciated against other currencies and capital movements in emerging economies have fluctuated. ...
Panama_en.pdf
... to support the crop-growing sector, including soft loans, purchases of inputs at wholesale prices, subsidized sale prices and tax exemptions for low-income households. The aims of these measures, reflected in an increase in the areas sown and in swelling crop volumes, include an end to rice imports ...
... to support the crop-growing sector, including soft loans, purchases of inputs at wholesale prices, subsidized sale prices and tax exemptions for low-income households. The aims of these measures, reflected in an increase in the areas sown and in swelling crop volumes, include an end to rice imports ...
1-2 ch1
... Poverty Poor environmental accounting Ecological ignorance Economic growth provides people with goods/services. Measured in gross domestic product (GDP) market value of goods/services produced in a country for use within a year. Requires more production/consumption. Economic development: ...
... Poverty Poor environmental accounting Ecological ignorance Economic growth provides people with goods/services. Measured in gross domestic product (GDP) market value of goods/services produced in a country for use within a year. Requires more production/consumption. Economic development: ...
Chinese economic reform

The Chinese economic reform (simplified Chinese: 改革开放; traditional Chinese: 改革開放; pinyin: Gǎigé kāifàng; literally: ""Reform & Opening up"") refers to the program of economic reforms called ""Socialism with Chinese characteristics"" in the People's Republic of China (PRC) that was started in December 1978 by reformists within the Communist Party of China (CPC) led by Deng Xiaoping.China had one of the world's largest and most advanced economies prior to the nineteenth century. In the 18th century, Adam Smith claimed China had long been one of the richest, that is, one of the most fertile, best cultivated, most industrious, most prosperous and most urbanized countries in the world. The economy stagnated since the 16th century and even declined in absolute terms in the nineteenth and much of the twentieth century, with a brief recovery in the 1930s.Economic reforms introducing market principles began in 1978 and were carried out in two stages. The first stage, in the late 1970s and early 1980s, involved the decollectivization of agriculture, the opening up of the country to foreign investment, and permission for entrepreneurs to start businesses. However, most industry remained state-owned. The second stage of reform, in the late 1980s and 1990s, involved the privatization and contracting out of much state-owned industry and the lifting of price controls, protectionist policies, and regulations, although state monopolies in sectors such as banking and petroleum remained. The private sector grew remarkably, accounting for as much as 70 percent of China gross domestic product by 2005. From 1978 until 2013, unprecedented growth occurred, with the economy increasing by 9.5% a year. The conservative Hu-Wen Administration more heavily regulated and controlled the economy after 2005, reversing some reforms.The success of China's economic policies and the manner of their implementation has resulted in immense changes in Chinese society. Large-scale government planning programs alongside market characteristics have minimized poverty, while incomes and income inequality have increased, leading to a backlash led by the New Left. In the academic scene, scholars have debated the reason for the success of the Chinese ""dual-track"" economy, and have compared them to attempts to reform socialism in the East Bloc and the Soviet Union, and the growth of other developing economies.