MATERIALS AND METHODS Materials All chemicals used in the
... CGH buffer at 25 ºC at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min, with detection at 280 nm. The column was calibrated with standard molecular weight markers. Circular Dichroism (CD) measurements- CD measurements were made on JASCO J810 spectropolarimeter calibrated with ammonium (+)-10-camphorsulfonate with 6 µM p ...
... CGH buffer at 25 ºC at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min, with detection at 280 nm. The column was calibrated with standard molecular weight markers. Circular Dichroism (CD) measurements- CD measurements were made on JASCO J810 spectropolarimeter calibrated with ammonium (+)-10-camphorsulfonate with 6 µM p ...
standard sample test
... (a) The solution was found to be acidic. (b) The solution was found to be basic. (c) The solution was found to be neither acidic nor basic, it was neutral. (d) The problem does not have enough information to determine if the solution was found to be acidic, basic or neutral. ...
... (a) The solution was found to be acidic. (b) The solution was found to be basic. (c) The solution was found to be neither acidic nor basic, it was neutral. (d) The problem does not have enough information to determine if the solution was found to be acidic, basic or neutral. ...
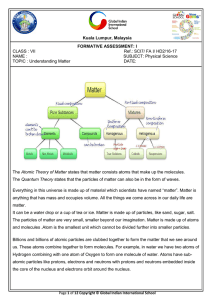
The Atomic Theory
... The chemical action of an electric current is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity which passes through a solution. The weights of the substances deposited by the same quantity of electricity are proportional to their chemical equivalents. Stoney (1874) made the hypothesis that there ...
... The chemical action of an electric current is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity which passes through a solution. The weights of the substances deposited by the same quantity of electricity are proportional to their chemical equivalents. Stoney (1874) made the hypothesis that there ...
2 Carboxyl Groups
... random-coil segments, together with the number and position of disulfide linkages and hydrogen bonds, folds each protein into its tertiary structure. This is its overall threedimensional shape. ...
... random-coil segments, together with the number and position of disulfide linkages and hydrogen bonds, folds each protein into its tertiary structure. This is its overall threedimensional shape. ...
Parallel Computing in Chemistry
... – Compute the derivative of the wavefunction with respect to the nuclear coordinates – Adjust the nuclear coordinates – Repeat until the derivative is within tolerance of zero in every dimension Note that this is a nested iteration: we’re iterating to build a wavefunction, ...
... – Compute the derivative of the wavefunction with respect to the nuclear coordinates – Adjust the nuclear coordinates – Repeat until the derivative is within tolerance of zero in every dimension Note that this is a nested iteration: we’re iterating to build a wavefunction, ...
Chemistry_in_Parallel_Computing_old
... – Compute the derivative of the wavefunction with respect to the nuclear coordinates – Adjust the nuclear coordinates – Repeat until the derivative is within tolerance of zero in every dimension Note that this is a nested iteration: we’re iterating to build a wavefunction, ...
... – Compute the derivative of the wavefunction with respect to the nuclear coordinates – Adjust the nuclear coordinates – Repeat until the derivative is within tolerance of zero in every dimension Note that this is a nested iteration: we’re iterating to build a wavefunction, ...
worksheer format 11-12
... Plasma is a state of matter in which all matter is ionized and it occurs in the form of ions and electrons. Since, we know that for the ionization of the element or matter to occur energy is required to pull the electron from the attraction of the nuclear charge, high energy is required. So for the ...
... Plasma is a state of matter in which all matter is ionized and it occurs in the form of ions and electrons. Since, we know that for the ionization of the element or matter to occur energy is required to pull the electron from the attraction of the nuclear charge, high energy is required. So for the ...
integrated-principles-of-zoology-16th-edition-hickman
... Draw, use transparencies, slides or video to illustrate the different isomeric forms of the hexose sugars glucose, fructose, and galactose, and reasons for their different characteristics. Show how the structures fit into enzymes and why different enzymes would be needed to interact with different i ...
... Draw, use transparencies, slides or video to illustrate the different isomeric forms of the hexose sugars glucose, fructose, and galactose, and reasons for their different characteristics. Show how the structures fit into enzymes and why different enzymes would be needed to interact with different i ...
chapter 2 the origin and chemistry of life
... Draw, use transparencies, slides or video to illustrate the different isomeric forms of the hexose sugars glucose, fructose, and galactose, and reasons for their different characteristics. Show how the structures fit into enzymes and why different enzymes would be needed to interact with different i ...
... Draw, use transparencies, slides or video to illustrate the different isomeric forms of the hexose sugars glucose, fructose, and galactose, and reasons for their different characteristics. Show how the structures fit into enzymes and why different enzymes would be needed to interact with different i ...
L1 – CHEMISTRY FINAL REVIEW
... 32. Describe the Van Der Waals forces between water molecules called dipole interactions or Hydrogen bonds. H-bond is a strong intermolecular bond between the slightly positive Hydrogen end of one water molecule and the slightly neg. oxygen end of an adjacent water molecule. 33. Name 4 unique proper ...
... 32. Describe the Van Der Waals forces between water molecules called dipole interactions or Hydrogen bonds. H-bond is a strong intermolecular bond between the slightly positive Hydrogen end of one water molecule and the slightly neg. oxygen end of an adjacent water molecule. 33. Name 4 unique proper ...
The mole
... 6. Determine the molecular formula of a compound from its empirical formula and its molar mass. 7. Carry out mole-to-mole, mass-to-mole, and mass-to-particles, mass-to-volume calculations for any two species. Composition Stoichiometry is the quantitative analysis of substances. It deals with the mas ...
... 6. Determine the molecular formula of a compound from its empirical formula and its molar mass. 7. Carry out mole-to-mole, mass-to-mole, and mass-to-particles, mass-to-volume calculations for any two species. Composition Stoichiometry is the quantitative analysis of substances. It deals with the mas ...
Sec. 10.3 - Midland Park School District
... volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of particles. Further, one mole (or 6.02 x 1023 particles) of a gas (no matter what it is) will always have the same volume. ...
... volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of particles. Further, one mole (or 6.02 x 1023 particles) of a gas (no matter what it is) will always have the same volume. ...
03_Physical-chemical properties of proteins
... charges, size and solubility of molecules Electrophoresis – effects separation in an electric field on the basis of differences in charges carried by amino acids and proteins under specific condition Ultracentrifugation – effects separation on the basis of molecular weight when large gravitational f ...
... charges, size and solubility of molecules Electrophoresis – effects separation in an electric field on the basis of differences in charges carried by amino acids and proteins under specific condition Ultracentrifugation – effects separation on the basis of molecular weight when large gravitational f ...
File
... 55. Which pair of solutions forms a buffer when equal volumes of each are mixed? A) 0.20 M HCl and 0.20 M NaCl C) 0.20 M HCl and 0.20 M NH3 B) 0.40 M HC2H3O2 and 0.20 M NaOH D) 0.40 M HCl and 0.20 M NH3 56. A student is attempting to standardize a NaOH solution with a 0.500 molar solution of oxalic ...
... 55. Which pair of solutions forms a buffer when equal volumes of each are mixed? A) 0.20 M HCl and 0.20 M NaCl C) 0.20 M HCl and 0.20 M NH3 B) 0.40 M HC2H3O2 and 0.20 M NaOH D) 0.40 M HCl and 0.20 M NH3 56. A student is attempting to standardize a NaOH solution with a 0.500 molar solution of oxalic ...
Bio 263/F94/T2 - millersville.edu
... dotted line indicates labeling of inside-out vesicles. What kind of membrane proteins are A, B, C and D? (i. e., On which surface are they exposed? Do they have polysaccharides and on which side of the membrane are the polysaccharides exposed, if present?) Ignore any preconceived notions about membr ...
... dotted line indicates labeling of inside-out vesicles. What kind of membrane proteins are A, B, C and D? (i. e., On which surface are they exposed? Do they have polysaccharides and on which side of the membrane are the polysaccharides exposed, if present?) Ignore any preconceived notions about membr ...
Curriculum for UG
... b.Molecular cell biology- chemical composition, current concepts of the structure of eukaryotic cell membrane, Membrane assembly- features, targeting proteins to their destinations by signal sequences- signal hypothesis, molecular chaperones, specialized functions- transfer of material and informati ...
... b.Molecular cell biology- chemical composition, current concepts of the structure of eukaryotic cell membrane, Membrane assembly- features, targeting proteins to their destinations by signal sequences- signal hypothesis, molecular chaperones, specialized functions- transfer of material and informati ...
Molecules of Life Powerpoint
... The primary structure of any protein is simply its sequence of amino acids. This sequence determines everything else about the protein’s final shape. ...
... The primary structure of any protein is simply its sequence of amino acids. This sequence determines everything else about the protein’s final shape. ...
Anaerobic metabolism is the production of ATP with oxygen
... 2. True or False: An enzyme is not changed by the reaction it causes. 3. True or False: An enzyme does not need to fit precisely with the reactant to catalyze the reaction. 4. True or False: The electron transport system is where most of the ATP is produced during aerobic metabolism. 5. True or Fals ...
... 2. True or False: An enzyme is not changed by the reaction it causes. 3. True or False: An enzyme does not need to fit precisely with the reactant to catalyze the reaction. 4. True or False: The electron transport system is where most of the ATP is produced during aerobic metabolism. 5. True or Fals ...
Metathesis Problems (and Some Solutions) Identified Through
... molecules to pass but large solute molecules cannot • Osmosis: flow of solvent through a semipermeable membrane to equalize solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane • π = MRT (M = molar conc., R = gas constant, T = absolute temperature) • Reverse osmosis: apply greater pressure to more co ...
... molecules to pass but large solute molecules cannot • Osmosis: flow of solvent through a semipermeable membrane to equalize solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane • π = MRT (M = molar conc., R = gas constant, T = absolute temperature) • Reverse osmosis: apply greater pressure to more co ...
Ch.5
... Formula Units - represented by the formula of an IONIC compound (NaCl, AgNO3, Fe2O3, etc.) 1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 particles (a conversion factor) ...
... Formula Units - represented by the formula of an IONIC compound (NaCl, AgNO3, Fe2O3, etc.) 1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 particles (a conversion factor) ...
Organic Molecules Packet
... together to form small molecules which join together, or bond, to form large molecules. Another characteristic of all organic molecules is that each is built from a single type of building block, or monomer. For example, the monomer of carbohydrates are simple sugars called monosaccharides. The mono ...
... together to form small molecules which join together, or bond, to form large molecules. Another characteristic of all organic molecules is that each is built from a single type of building block, or monomer. For example, the monomer of carbohydrates are simple sugars called monosaccharides. The mono ...
Macromolecules Notes
... PS! Things with carbon are organic UNLESS they are exclusively C & H (or CO2)… these are not organic. ie. Hydrogencarbonate : CH4 ...
... PS! Things with carbon are organic UNLESS they are exclusively C & H (or CO2)… these are not organic. ie. Hydrogencarbonate : CH4 ...
Size-exclusion chromatography

Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size, and in some cases molecular weight. It is usually applied to large molecules or macromolecular complexes such as proteins and industrial polymers. Typically, when an aqueous solution is used to transport the sample through the column, the technique is known as gel-filtration chromatography, versus the name gel permeation chromatography, which is used when an organic solvent is used as a mobile phase. SEC is a widely used polymer characterization method because of its ability to provide good molar mass distribution (Mw) results for polymers.