College Grossmont 115
... It is understood that the last digit in any measurement is the estimated digit. Sometimes the last digit is called the “doubtful digit” or “unreliable digit”. Scientists communicate the level of uncertainty by the use of significant figures. A mass of 2.9 g contains two significant figures; a mass o ...
... It is understood that the last digit in any measurement is the estimated digit. Sometimes the last digit is called the “doubtful digit” or “unreliable digit”. Scientists communicate the level of uncertainty by the use of significant figures. A mass of 2.9 g contains two significant figures; a mass o ...
A New Type of a Multifunctional ß-Oxidation
... Enzyme in Euglena Uwe Winkler*, Werner Säftel, and Helmut Stabenau Department of Biology, University of Oldenburg, P.O. Box 2503, D–26111 Oldenburg, Germany The biochemical and molecular properties of the -oxidation enzymes from algae have not been investigated yet. The present study provides such ...
... Enzyme in Euglena Uwe Winkler*, Werner Säftel, and Helmut Stabenau Department of Biology, University of Oldenburg, P.O. Box 2503, D–26111 Oldenburg, Germany The biochemical and molecular properties of the -oxidation enzymes from algae have not been investigated yet. The present study provides such ...
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Chemical Reactions
... individual atomic weights of all atoms or ions present in one particle of the substance. The average atomic weight of an element is generally found at the bottom of the element block (Figure 7.1) ...
... individual atomic weights of all atoms or ions present in one particle of the substance. The average atomic weight of an element is generally found at the bottom of the element block (Figure 7.1) ...
Mass and Moles of a Substance
... The limiting reactant (or limiting reagent) is the reactant that is entirely consumed when the reaction goes to completion. The limiting reactant ultimately determines how much product can be obtained. For example, bicycles require one frame and two wheels. If you have 20 wheels but only 5 frames, i ...
... The limiting reactant (or limiting reagent) is the reactant that is entirely consumed when the reaction goes to completion. The limiting reactant ultimately determines how much product can be obtained. For example, bicycles require one frame and two wheels. If you have 20 wheels but only 5 frames, i ...
Degradable heterobifunctional poly (ethylene glycol) acrylates and
... tion of pairs of reactive moieties, for example, alcohol and carboxylic acid reacting to form carboxylate esters, amine and aldehyde reacting to form imines, hydraZide and alde hyde reacting to form hydraZones, alcohol and phosphate reacting to form phosphate ester, aldehyde and alcohol reacting to ...
... tion of pairs of reactive moieties, for example, alcohol and carboxylic acid reacting to form carboxylate esters, amine and aldehyde reacting to form imines, hydraZide and alde hyde reacting to form hydraZones, alcohol and phosphate reacting to form phosphate ester, aldehyde and alcohol reacting to ...
Общи анестетици - Pharmacy
... Solution (a). Dissolve 0.25 g of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 10 ml with the same solvent. This solution is used to prepare the test solution. Solution (b). Dissolve 50 mg of 2,6-dimethylaniline R in methanol R and dilute to 100 ml with the same solvent. Dilute 1 ml of th ...
... Solution (a). Dissolve 0.25 g of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 10 ml with the same solvent. This solution is used to prepare the test solution. Solution (b). Dissolve 50 mg of 2,6-dimethylaniline R in methanol R and dilute to 100 ml with the same solvent. Dilute 1 ml of th ...
Thin-Layer Chromatography: Applying TLC as a
... However, salicylic acid and acetylsalicylic acid were only separated slightly from one another, having an Rf difference of 0.096, much lower than the theoretical separation of the standards (Rf: 0.654) (Table 2). One possible explanation for this occurrence may be due to internal physical interacti ...
... However, salicylic acid and acetylsalicylic acid were only separated slightly from one another, having an Rf difference of 0.096, much lower than the theoretical separation of the standards (Rf: 0.654) (Table 2). One possible explanation for this occurrence may be due to internal physical interacti ...
Ch 4 Student
... • Limiting Reactant – reactant that is completely consumed and limits amount of product • Reactant in excess – reactant present in greater quantity than limiting reactant • Theoretical Yield – amount of product made based on consumption of all the limiting reactant • Actual Yield – amount of product ...
... • Limiting Reactant – reactant that is completely consumed and limits amount of product • Reactant in excess – reactant present in greater quantity than limiting reactant • Theoretical Yield – amount of product made based on consumption of all the limiting reactant • Actual Yield – amount of product ...
CHAPTER 4: CHEMICAL QUANTITIES and AQUEOUS REACTIONS
... Exercise 2: On the basis of solubility rules, predict whether aluminum nitrate and iron (III) phosphate are soluble in water or not. Aluminum nitrate – Soluble (rule 1) Iron (III) phosphate – Not soluble (rule 6) ...
... Exercise 2: On the basis of solubility rules, predict whether aluminum nitrate and iron (III) phosphate are soluble in water or not. Aluminum nitrate – Soluble (rule 1) Iron (III) phosphate – Not soluble (rule 6) ...
SELECTED ANSWERS
... Chapter 2 Key Ideas 3. simplified but useful 5. motion 7. attract 9. empty space, expands 11. escape 13. straight-line path 15. simpler 17. vertical column 19. solid, liquid, gas 21. sun 23. 10-15 25. cloud 27. gains 29. chemical 31. single atom Chapter 2 Problems 33(a) Strong attractions between th ...
... Chapter 2 Key Ideas 3. simplified but useful 5. motion 7. attract 9. empty space, expands 11. escape 13. straight-line path 15. simpler 17. vertical column 19. solid, liquid, gas 21. sun 23. 10-15 25. cloud 27. gains 29. chemical 31. single atom Chapter 2 Problems 33(a) Strong attractions between th ...
Chem 32 Solutions to Section 15.4 – 15.6 Homework Problems
... 15.78 Only pathway “c” produces energy that can be harnessed to make ATP. Pathway “a” does not produce or consume a significant amount of energy. Pathway “b” is an activation step, and consumes energy (the body breaks down ATP in this step). 15.86 The starting materials of the citric acid cycle are ...
... 15.78 Only pathway “c” produces energy that can be harnessed to make ATP. Pathway “a” does not produce or consume a significant amount of energy. Pathway “b” is an activation step, and consumes energy (the body breaks down ATP in this step). 15.86 The starting materials of the citric acid cycle are ...
Purification and Some: Characteristics of a Monomeric Racemase
... NaCl connected to a fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC) system. El&on was carried out with the standard buffer containing 0.2 M NaCl at a flow rate of 0.5 ml/min. After the active fractions were pooled, concentrated and dialyzed against the standard buffer, the solution was frozen and stored a ...
... NaCl connected to a fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC) system. El&on was carried out with the standard buffer containing 0.2 M NaCl at a flow rate of 0.5 ml/min. After the active fractions were pooled, concentrated and dialyzed against the standard buffer, the solution was frozen and stored a ...
HEAd START TO A LEVEL CHEMISTRY WORKbOOK
... and also on page 92 of this book. You can see there are only about 100 of them. The middle part of the atom, the nucleus, contains one or more protons. It is the number of protons that make the atom what it is. An atom with one proton is always a hydrogen atom; one with two protons is a helium atom ...
... and also on page 92 of this book. You can see there are only about 100 of them. The middle part of the atom, the nucleus, contains one or more protons. It is the number of protons that make the atom what it is. An atom with one proton is always a hydrogen atom; one with two protons is a helium atom ...
6 theoretical problems 2 practical problems
... 3.1 Draw the structures of cis- and trans-diammine dichloroplatinum(II) and label each structure as cis or trans. ...
... 3.1 Draw the structures of cis- and trans-diammine dichloroplatinum(II) and label each structure as cis or trans. ...
The Mole
... The familiar blue crystals of ‘copper sulfate’ owe their colour to the presence of water of crystallisation. When copper sulfate crystals are heated they turn a paler blue until all the water is removed. You are left with just a white powder. Hydrated describes the crystalline compound which contain ...
... The familiar blue crystals of ‘copper sulfate’ owe their colour to the presence of water of crystallisation. When copper sulfate crystals are heated they turn a paler blue until all the water is removed. You are left with just a white powder. Hydrated describes the crystalline compound which contain ...
Mole Concept
... cC + dD, we know that a moles of A will react with b moles Give a reaction aA +bB of B to give c moles of C and d moles of D. This means, for instance, that Y moles of A will require Y mol A x (b mol B / a mol A) = Yb/a mol B, since the stoichiometric coefficients are conversion factors between diff ...
... cC + dD, we know that a moles of A will react with b moles Give a reaction aA +bB of B to give c moles of C and d moles of D. This means, for instance, that Y moles of A will require Y mol A x (b mol B / a mol A) = Yb/a mol B, since the stoichiometric coefficients are conversion factors between diff ...
Chapter 4 – Part 1
... Know that Antoine Lavoisier introduced the law of conservation of matter. Define combustion Know what products and reactants are Be able to write combustion equations Know when to label the substances solid (s) , gas (g), liquid (l), or aqueous (aq) Know how to balance equations Be abl ...
... Know that Antoine Lavoisier introduced the law of conservation of matter. Define combustion Know what products and reactants are Be able to write combustion equations Know when to label the substances solid (s) , gas (g), liquid (l), or aqueous (aq) Know how to balance equations Be abl ...
Web Appendix 6
... can never be computed without reference to a chemical reaction in which that compound is, directly or indirectly, a participant. Similarly, the normality of a solution can never be specified without knowledge about how the solution will be used. Equivalent Weights in Neutralization Reactions One equ ...
... can never be computed without reference to a chemical reaction in which that compound is, directly or indirectly, a participant. Similarly, the normality of a solution can never be specified without knowledge about how the solution will be used. Equivalent Weights in Neutralization Reactions One equ ...
Solution - HCC Learning Web
... Solutions • Solutions are defined as homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances. • The solvent is present in greatest abundance. • All other substances are solutes. • When water is the solvent, the solution is called an aqueous solution. Aqueous Reactions © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Solutions • Solutions are defined as homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances. • The solvent is present in greatest abundance. • All other substances are solutes. • When water is the solvent, the solution is called an aqueous solution. Aqueous Reactions © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Purification and Characterization of a Novel Pumpkin Short
... hydrophobic-interaction, hydroxyapatite, affinity, and anion-exchange chromatography. The purified enzyme is a tetrameric protein, consisting of apparently identical 47-kD subunits. The protein structure of this oxidase differs from other plant and mammalian ACOXs, but is similar to the protein stru ...
... hydrophobic-interaction, hydroxyapatite, affinity, and anion-exchange chromatography. The purified enzyme is a tetrameric protein, consisting of apparently identical 47-kD subunits. The protein structure of this oxidase differs from other plant and mammalian ACOXs, but is similar to the protein stru ...
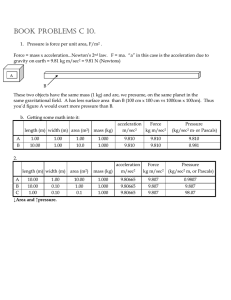
book problems c 10.
... in 1010. The relative atomic mass of silicon is particularly important, since silicon crystals are used in the x-ray methods mentioned above. As a continuation of this approach, one of the 1999 NIST Precision Measurement Grants has been awarded to David Pritchard, physics professor at the Massachuse ...
... in 1010. The relative atomic mass of silicon is particularly important, since silicon crystals are used in the x-ray methods mentioned above. As a continuation of this approach, one of the 1999 NIST Precision Measurement Grants has been awarded to David Pritchard, physics professor at the Massachuse ...
Electrophoresis Basi..
... An important purpose of a gel matrix is to introduce a sieving action which allows separations of molecules based on molecular size. Gel matrix viscosity, density, and pore size are all factors in determining the ‘speed’ of ...
... An important purpose of a gel matrix is to introduce a sieving action which allows separations of molecules based on molecular size. Gel matrix viscosity, density, and pore size are all factors in determining the ‘speed’ of ...
Module 2
... 9. gels and the influence of different factors on it. The determination of isoelectric point of proteins ● The final control of the acquirement the Module 2 Totally: ...
... 9. gels and the influence of different factors on it. The determination of isoelectric point of proteins ● The final control of the acquirement the Module 2 Totally: ...
Chemistry Bridging Work
... The aims are for you to understand if you like the course and for you to be ready to start learning at post 16 level. Chemistry is fun but extremely hard work. Please use resources such as the internet, library and your chemistry GCSE notes to help you complete this work. The AS Course comprises of ...
... The aims are for you to understand if you like the course and for you to be ready to start learning at post 16 level. Chemistry is fun but extremely hard work. Please use resources such as the internet, library and your chemistry GCSE notes to help you complete this work. The AS Course comprises of ...
Size-exclusion chromatography

Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size, and in some cases molecular weight. It is usually applied to large molecules or macromolecular complexes such as proteins and industrial polymers. Typically, when an aqueous solution is used to transport the sample through the column, the technique is known as gel-filtration chromatography, versus the name gel permeation chromatography, which is used when an organic solvent is used as a mobile phase. SEC is a widely used polymer characterization method because of its ability to provide good molar mass distribution (Mw) results for polymers.