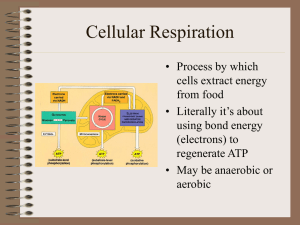
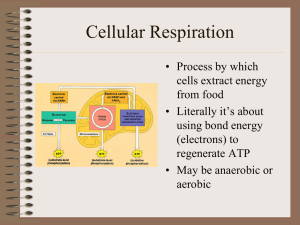
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... 1. How many net ATP are produced by Glycolysis alone per glucose? a) 2 b) 4 c) 12 d) 8 2. Which one of the following is the 2nd molecule in the Glycolysis pathway? a) Glucose – 6 – phosphate b) Fructose – 6 phosphate c) Fructose - 1 ,6 biphosphate d) Glucose 3. Which one of the following is a reduce ...
... 1. How many net ATP are produced by Glycolysis alone per glucose? a) 2 b) 4 c) 12 d) 8 2. Which one of the following is the 2nd molecule in the Glycolysis pathway? a) Glucose – 6 – phosphate b) Fructose – 6 phosphate c) Fructose - 1 ,6 biphosphate d) Glucose 3. Which one of the following is a reduce ...
ATP
... The student will learn how both carbohydrates and fats are utilized to form ATP. The students will learn why and how lactic acid is formed during strenuous activity. ...
... The student will learn how both carbohydrates and fats are utilized to form ATP. The students will learn why and how lactic acid is formed during strenuous activity. ...
RESPIRATION: SYNTHESIS OF ATP
... Synthesis of ATP Anaerobic conditions (fermentation) ! Glycolysis depends on a supply of substrates: glucose, ATP, ADP, Pi, NAD+ ! NAD+, FAD present in only small amounts in cell, and NAD+ and FAD are used up in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. ! Therefore, NAD+ must be regenerated from NADH t ...
... Synthesis of ATP Anaerobic conditions (fermentation) ! Glycolysis depends on a supply of substrates: glucose, ATP, ADP, Pi, NAD+ ! NAD+, FAD present in only small amounts in cell, and NAD+ and FAD are used up in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. ! Therefore, NAD+ must be regenerated from NADH t ...
Guided Practice
... reaction is to form two energy storing compounds to power the next step. In the next part of photosynthesis, the ___________________________ reaction uses carbon atoms from _________________ ___________________ in the air, to produce ________________________. The two main products of photosynthesis ...
... reaction is to form two energy storing compounds to power the next step. In the next part of photosynthesis, the ___________________________ reaction uses carbon atoms from _________________ ___________________ in the air, to produce ________________________. The two main products of photosynthesis ...
AP Biology - gwbiology
... 1. Define the two catabolic pathways: a. Fermentation is a metabolic pathway that uses glucose to form ATP without oxygen, the Kreb’s cycle, or the electron transport chain. It also forms another end product besides ATP, either alcohol or lactic acid. b. Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway u ...
... 1. Define the two catabolic pathways: a. Fermentation is a metabolic pathway that uses glucose to form ATP without oxygen, the Kreb’s cycle, or the electron transport chain. It also forms another end product besides ATP, either alcohol or lactic acid. b. Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway u ...
File
... & the citric acid cycle transfer their electrons to protein complexes in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion as the electrons are passed down the chain, energy is released that drives the transport of H+ ions into the intermembrane space the final electron acceptor in the ETC is O2, which is ...
... & the citric acid cycle transfer their electrons to protein complexes in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion as the electrons are passed down the chain, energy is released that drives the transport of H+ ions into the intermembrane space the final electron acceptor in the ETC is O2, which is ...
Cellular Respiration www.AssignmentPoint.com Cellular respiration
... ΔG = −2880 kJ per mol of C6H12O6 The negative ΔG indicates that the reaction can occur spontaneously. ...
... ΔG = −2880 kJ per mol of C6H12O6 The negative ΔG indicates that the reaction can occur spontaneously. ...
Cellular Respiration PPT 12-13-Cooke
... – NADH and FADH2 drop off electrons that go through the ETC – O2 is the final electron acceptor creating H2O – Hydrogen ions are pumped through the ATP synthase to create ATP ...
... – NADH and FADH2 drop off electrons that go through the ETC – O2 is the final electron acceptor creating H2O – Hydrogen ions are pumped through the ATP synthase to create ATP ...
Camp 1 - Evangel University
... • Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP releases energy • In the coupling of biochemical reactions, the energy released by one reaction, such as ATP hydrolysis, provides energy for another ...
... • Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP releases energy • In the coupling of biochemical reactions, the energy released by one reaction, such as ATP hydrolysis, provides energy for another ...
Cellular Respiration notes HONORS
... form another 4C compound. This time FAD is reduced to form FADH2 5. The 4C from step 4 releases an H atom to regenerate oxaloacetic acid, which keeps the Krebs cycle operating. The H atom reduces NAD+ to NADH ...
... form another 4C compound. This time FAD is reduced to form FADH2 5. The 4C from step 4 releases an H atom to regenerate oxaloacetic acid, which keeps the Krebs cycle operating. The H atom reduces NAD+ to NADH ...
Energy Conversions PowerPoint
... •Why do you think the man set up that experiment? •What is he trying to prove? •Describe the relationship you see between photosynthesis & cellular respiration. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7oOHuEix3oY ...
... •Why do you think the man set up that experiment? •What is he trying to prove? •Describe the relationship you see between photosynthesis & cellular respiration. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7oOHuEix3oY ...
Topics
... electron carriers • NADH generates 3 ATP, FADH2 = 2 ATP • Membrane bound carriers transfer electrons (redox reactions) • The final electron acceptor completes the terminal step (ex. Oxygen) • Chemiosmosis • Proton motive force (PMF) ...
... electron carriers • NADH generates 3 ATP, FADH2 = 2 ATP • Membrane bound carriers transfer electrons (redox reactions) • The final electron acceptor completes the terminal step (ex. Oxygen) • Chemiosmosis • Proton motive force (PMF) ...
Energy Exam Review - Lewiston School District
... A).Light reaction of photosynthesis B).Dark reaction of photosynthesis C).Formation of ATP from ADP D).”Excited” electrons in the chlorophyll ...
... A).Light reaction of photosynthesis B).Dark reaction of photosynthesis C).Formation of ATP from ADP D).”Excited” electrons in the chlorophyll ...
chapter07
... Also known as the Krebs cycle and tricarboxylic acid (TCA). Two acetyl-CoA produced from one glucose molecule enter the citric acid cycle. It takes place in the mitochondrial matrix and a specific enzyme catalyzes each step. The acetate group of acetyl-CoA combines with a 4-C molecule of oxaloacetat ...
... Also known as the Krebs cycle and tricarboxylic acid (TCA). Two acetyl-CoA produced from one glucose molecule enter the citric acid cycle. It takes place in the mitochondrial matrix and a specific enzyme catalyzes each step. The acetate group of acetyl-CoA combines with a 4-C molecule of oxaloacetat ...
Cellular Respiration
... • 6C glucose split • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
... • 6C glucose split • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
SCI_7726_files/Cellular Respiration
... • 6C glucose split • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
... • 6C glucose split • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
HB_Cell_Resp_KEYS_and_Review_Notes_12_BH
... If all the energy in glucose were released at once, it would be wasted. Most of the energy would be lost all at once as heat, burning up the cell. ...
... If all the energy in glucose were released at once, it would be wasted. Most of the energy would be lost all at once as heat, burning up the cell. ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration
... Concept 9.2: Glycolysis Harvests Chemical Energy By Oxidizing Glucose To Pyruvate Concept 9.3: The Citric Acid Cycle Concept 9.4: During Oxidative Phosphorylation, Chemiososmosis Couples Electron Transport to ATP Synthesis o The Pathway of Electron Transport o Chemiosmosis: The Energy-Coupling Mecha ...
... Concept 9.2: Glycolysis Harvests Chemical Energy By Oxidizing Glucose To Pyruvate Concept 9.3: The Citric Acid Cycle Concept 9.4: During Oxidative Phosphorylation, Chemiososmosis Couples Electron Transport to ATP Synthesis o The Pathway of Electron Transport o Chemiosmosis: The Energy-Coupling Mecha ...
Bio 110 S.I. chapters 6 & 7
... pyruvate reduction citric acid cycle electron transport chain fermentation ...
... pyruvate reduction citric acid cycle electron transport chain fermentation ...
Keigo Tanaka Chapter 9 – Cellular Respiration: Harvesting
... Beta-oxidation: A metabolic sequence of lipid catabolism that breaks down fatty acids into twocarbon fragments that can enter the citric acid cycle as acetyl CoA ...
... Beta-oxidation: A metabolic sequence of lipid catabolism that breaks down fatty acids into twocarbon fragments that can enter the citric acid cycle as acetyl CoA ...
Solutions - MIT OpenCourseWare
... c) In step 7 (see attached diaragm) of glycolysis 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) is converted into 3Phosphoglycerate (3PG). Which of these molecules, BPG or 3PG would you expect is at a higher energy level? Explain your answer. BPG is at a higher energy level than 3PG. You can infer this because BPG ...
... c) In step 7 (see attached diaragm) of glycolysis 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) is converted into 3Phosphoglycerate (3PG). Which of these molecules, BPG or 3PG would you expect is at a higher energy level? Explain your answer. BPG is at a higher energy level than 3PG. You can infer this because BPG ...
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme often called the ""molecular unit of currency"" of intracellular energy transfer.ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism. It is one of the end products of photophosphorylation, cellular respiration, and fermentation and used by enzymes and structural proteins in many cellular processes, including biosynthetic reactions, motility, and cell division. One molecule of ATP contains three phosphate groups, and it is produced by a wide variety of enzymes, including ATP synthase, from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and various phosphate group donors. Substrate-level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration, and photophosphorylation in photosynthesis are three major mechanisms of ATP biosynthesis.Metabolic processes that use ATP as an energy source convert it back into its precursors. ATP is therefore continuously recycled in organisms: the human body, which on average contains only 250 grams (8.8 oz) of ATP, turns over its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day.ATP is used as a substrate in signal transduction pathways by kinases that phosphorylate proteins and lipids. It is also used by adenylate cyclase, which uses ATP to produce the second messenger molecule cyclic AMP. The ratio between ATP and AMP is used as a way for a cell to sense how much energy is available and control the metabolic pathways that produce and consume ATP. Apart from its roles in signaling and energy metabolism, ATP is also incorporated into nucleic acids by polymerases in the process of transcription. ATP is the neurotransmitter believed to signal the sense of taste.The structure of this molecule consists of a purine base (adenine) attached by the 9' nitrogen atom to the 1' carbon atom of a pentose sugar (ribose). Three phosphate groups are attached at the 5' carbon atom of the pentose sugar. It is the addition and removal of these phosphate groups that inter-convert ATP, ADP and AMP. When ATP is used in DNA synthesis, the ribose sugar is first converted to deoxyribose by ribonucleotide reductase.ATP was discovered in 1929 by Karl Lohmann, and independently by Cyrus Fiske and Yellapragada Subbarow of Harvard Medical School, but its correct structure was not determined until some years later. It was proposed to be the intermediary molecule between energy-yielding and energy-requiring reactions in cells by Fritz Albert Lipmann in 1941. It was first artificially synthesized by Alexander Todd in 1948.