DC500VBC625A DC500V
... under conditions specified by SOC. These data are for reference only and are not intended to infer any guaranteed values. ...
... under conditions specified by SOC. These data are for reference only and are not intended to infer any guaranteed values. ...
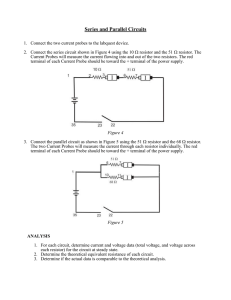
Series and Parallel Circuits
... 1. Connect the two current probes to the labquest device. 2. Connect the series circuit shown in Figure 4 using the 10 resistor and the 51 resistor. The Current Probes will measure the current flowing into and out of the two resistors. The red terminal of each Current Probe should be toward the ...
... 1. Connect the two current probes to the labquest device. 2. Connect the series circuit shown in Figure 4 using the 10 resistor and the 51 resistor. The Current Probes will measure the current flowing into and out of the two resistors. The red terminal of each Current Probe should be toward the ...
High Voltage CMOS Amplifier Enables High Impedance Sensing
... operational amplifier, so constructing an electrometergrade buffer stage is simply a matter of providing 100% feedback with the classic unity-gain circuit. No discrete FETs or floating biasing supplies are needed. As shown in Figure 2, the LTC6090 can easily be powered with a split supply, such as a ...
... operational amplifier, so constructing an electrometergrade buffer stage is simply a matter of providing 100% feedback with the classic unity-gain circuit. No discrete FETs or floating biasing supplies are needed. As shown in Figure 2, the LTC6090 can easily be powered with a split supply, such as a ...
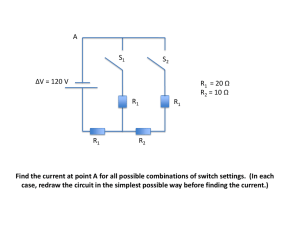
What is the current running through each resistor in the circuit?
... Find the current at point A for all possible combinations of switch settings. (In each case, redraw the circuit in the simplest possible way before finding the current.) ...
... Find the current at point A for all possible combinations of switch settings. (In each case, redraw the circuit in the simplest possible way before finding the current.) ...
Physics 160 Lecture 6
... What are the DC bias currents and voltages in this circuit? Note that 2 supplies are used here, with the input source referenced to ground ground, between the supplies supplies. The input source must supply the bias current to the transistor base. April 15, 2015 ...
... What are the DC bias currents and voltages in this circuit? Note that 2 supplies are used here, with the input source referenced to ground ground, between the supplies supplies. The input source must supply the bias current to the transistor base. April 15, 2015 ...
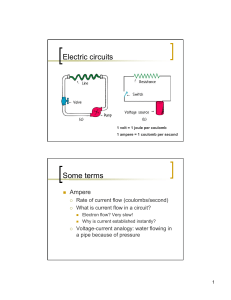
A or amp Q/t I Current C or coulomb Q Charge sec t Time Unit
... Voltage in the Circuit o The algebraic sum of all voltages in a complete circuit is equal to zero o If we consider the source voltage to be positive, there will be a negative “voltage drop” across each resistor o The voltage drop across each resistor can be calculated with Ohms law -4v -8v 4v ...
... Voltage in the Circuit o The algebraic sum of all voltages in a complete circuit is equal to zero o If we consider the source voltage to be positive, there will be a negative “voltage drop” across each resistor o The voltage drop across each resistor can be calculated with Ohms law -4v -8v 4v ...
Written - Rose
... connected to ground through a 400Ω resistor and a feedback resistor is connected between the inverting terminal and the output node. The output voltage of the first op amp becomes one of the input voltages of the second op amp. We want to find the output voltage of the second op amp. Firstly we need ...
... connected to ground through a 400Ω resistor and a feedback resistor is connected between the inverting terminal and the output node. The output voltage of the first op amp becomes one of the input voltages of the second op amp. We want to find the output voltage of the second op amp. Firstly we need ...
Name - Mr. Nickels
... The complex number c di is equal to (2 i) 2 . What is the value of c? ...
... The complex number c di is equal to (2 i) 2 . What is the value of c? ...
Regulated Power Supplies
... If we measured the output of a power supply that just had rectified AC, we would find that how much voltage we measured changed with how much current we drew from the supply. As we draw more current from the transformer, we lose voltage in the windings of the transformer, itself. At no load, we may ...
... If we measured the output of a power supply that just had rectified AC, we would find that how much voltage we measured changed with how much current we drew from the supply. As we draw more current from the transformer, we lose voltage in the windings of the transformer, itself. At no load, we may ...
Signal Resistance of the Current Mirror
... The output voltage of the long-tailed pair circuits above will not be zero when both the inputs are zero. As the circuits stand, the quiescent VO will be 12 - (4.7 2.43/2) = 6.3 V; it would be much better if it were zero! Several methods exist of making the quiescent value zero. 1. Take the output ...
... The output voltage of the long-tailed pair circuits above will not be zero when both the inputs are zero. As the circuits stand, the quiescent VO will be 12 - (4.7 2.43/2) = 6.3 V; it would be much better if it were zero! Several methods exist of making the quiescent value zero. 1. Take the output ...
SHUNT REGULATOR
... If there is no load on the supply, all the current goes through the transistor. If there is a resistive load, some current goes through the load and the rest goes through the transistor. But here's the important part: if something tries to drive current back into the supply, the transistor will shun ...
... If there is no load on the supply, all the current goes through the transistor. If there is a resistive load, some current goes through the load and the rest goes through the transistor. But here's the important part: if something tries to drive current back into the supply, the transistor will shun ...
PHYS1120ExamIIReview.. - University of Colorado Boulder
... elements in parallel always have the same voltage: Ibig V same across both R's ...
... elements in parallel always have the same voltage: Ibig V same across both R's ...
Wilson current mirror

A Wilson current mirror is a three-terminal circuit (Fig. 1) that accepts an input current at the input terminal and provides a ""mirrored"" current source or sink output at the output terminal. The mirrored current is a precise copy of the input current. It may be used as a Wilson current source by applying a constant bias current to the input branch as in Fig. 2. The circuit is named after George R. Wilson, an integrated circuit design engineer who worked for Tektronix. Wilson devised this configuration in 1967 when he and Barrie Gilbert challenged each other to find an improved current mirror overnight that would use only three transistors. Wilson won the challenge.