Student Health Information Infectious Mononucleosis
... in severity from a mild illness with barely noticeable symptoms to a more serious one, which rarely requires hospital admission. It spreads mainly through intimate contact and exchange of saliva (kissing, sharing a glass, bottle, or eating utensils). It is not highly contagious so it is rare to infe ...
... in severity from a mild illness with barely noticeable symptoms to a more serious one, which rarely requires hospital admission. It spreads mainly through intimate contact and exchange of saliva (kissing, sharing a glass, bottle, or eating utensils). It is not highly contagious so it is rare to infe ...
The Heart
... The Fibrous Skeleton Is an internal connective tissue of the heart 1. Provides attachment for heart’s valves ...
... The Fibrous Skeleton Is an internal connective tissue of the heart 1. Provides attachment for heart’s valves ...
INFORMATION SHEET Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
... Right bundle branch block (RBBB) is an abnormality of the electrical conduction of the heart. There are two main conducting pathways in the heart, the left and the right bundle. In RBBB the right conducting pathway no longer functions so electrical conduction is maintained through the left bundle. R ...
... Right bundle branch block (RBBB) is an abnormality of the electrical conduction of the heart. There are two main conducting pathways in the heart, the left and the right bundle. In RBBB the right conducting pathway no longer functions so electrical conduction is maintained through the left bundle. R ...
Haron Kirikiru Wk 4 discussion Atrial fibrillation They are
... Blood tends to stagnate in the incompletely emptied atria and is therefore more likely to clot. When clot moves to the left ventricle, they may be embolized to the brain causing stroke. Symptoms Common symptoms includes palpitations, which are sensations of a racing, uncomfortable, irregular heart b ...
... Blood tends to stagnate in the incompletely emptied atria and is therefore more likely to clot. When clot moves to the left ventricle, they may be embolized to the brain causing stroke. Symptoms Common symptoms includes palpitations, which are sensations of a racing, uncomfortable, irregular heart b ...
Inflammatory Heart Disease
... All inflammatory heart disorders have the propensity to lead to heart failure, so this is a very serious condition! Definition: ...
... All inflammatory heart disorders have the propensity to lead to heart failure, so this is a very serious condition! Definition: ...
Cardiovascular System 1 - University of Manitoba
... Heart valve with 3 cusps Narrowed blood vessel Lower heart chamber Heart chamber with thicker wall Provides information about electrical activity of heart (abbr) Nervous system controller of heart rate (abbr) Too rapid ventricular contraction Heart sound marking closure of aortic and pulmonary valve ...
... Heart valve with 3 cusps Narrowed blood vessel Lower heart chamber Heart chamber with thicker wall Provides information about electrical activity of heart (abbr) Nervous system controller of heart rate (abbr) Too rapid ventricular contraction Heart sound marking closure of aortic and pulmonary valve ...
Pediatric-Cardiology-Elective
... b. Explain the age-related changes in heart rate and blood pressure and identify normal ranges from birth through adolescence. c. Differentiate between physiologic and pathologic variations in cardiac rhythm. d. Describe the normal fetal circulation, the changes that occur at birth (transitional cir ...
... b. Explain the age-related changes in heart rate and blood pressure and identify normal ranges from birth through adolescence. c. Differentiate between physiologic and pathologic variations in cardiac rhythm. d. Describe the normal fetal circulation, the changes that occur at birth (transitional cir ...
Pediatric Cardiology
... b. Explain the age-related changes in heart rate and blood pressure and identify normal ranges from birth through adolescence. c. Differentiate between physiologic and pathologic variations in cardiac rhythm. d. Describe the normal fetal circulation, the changes that occur at birth (transitional cir ...
... b. Explain the age-related changes in heart rate and blood pressure and identify normal ranges from birth through adolescence. c. Differentiate between physiologic and pathologic variations in cardiac rhythm. d. Describe the normal fetal circulation, the changes that occur at birth (transitional cir ...
6_Autoimmune_2013
... and mucous membranes. The most common type is pemphigus vulgaris, which involves painful sores and blisters on the skin and in mouth. Autoantibodies attack desmosomes. Antigen: Desmoglein 3 ...
... and mucous membranes. The most common type is pemphigus vulgaris, which involves painful sores and blisters on the skin and in mouth. Autoantibodies attack desmosomes. Antigen: Desmoglein 3 ...
NURSING CARE OF THE CHILD WITH A
... • Macular rash on the trunk • Swollen and tender joints, SQ nodules on tendon sheaths • Positive ASO titer and increased ESR and C-reactive protein ...
... • Macular rash on the trunk • Swollen and tender joints, SQ nodules on tendon sheaths • Positive ASO titer and increased ESR and C-reactive protein ...
Autoimmunity 3rd yr
... These are not seen by the developing immune system – will not induce selftolerance. Exposure of T cells to these normally sequestered/tissue-specific self-antigens in the periphery results in their activation ...
... These are not seen by the developing immune system – will not induce selftolerance. Exposure of T cells to these normally sequestered/tissue-specific self-antigens in the periphery results in their activation ...
What`s Going Around - November 2013 Influenza – high fever, chills
... Influenza – high fever, chills, headache, body aches, sore throat, cough, congestion, and extreme tiredness. Medication may help if started in the first 24-48 hours. Even better, get a flu vaccine now, before you get sick. Strep Throat – sore throat, fever, headache, stomach ache. Usually without na ...
... Influenza – high fever, chills, headache, body aches, sore throat, cough, congestion, and extreme tiredness. Medication may help if started in the first 24-48 hours. Even better, get a flu vaccine now, before you get sick. Strep Throat – sore throat, fever, headache, stomach ache. Usually without na ...
How to deal with heart attacks
... Heart attacks are caused by a sudden obstruction of the blood supply to part of the heart muscle. The main risk is that the heart will stop beating. If part of the muscle is starved of blood it can cause the muscle to ‘die’ this interrupts the electrical signal that travels across the heart causing ...
... Heart attacks are caused by a sudden obstruction of the blood supply to part of the heart muscle. The main risk is that the heart will stop beating. If part of the muscle is starved of blood it can cause the muscle to ‘die’ this interrupts the electrical signal that travels across the heart causing ...
Infective endocarditis
... Added “rejected” as a category Added more clinical criteria Improved specificity and clinical utility ...
... Added “rejected” as a category Added more clinical criteria Improved specificity and clinical utility ...
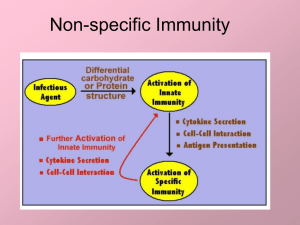
Non-specific Immunity
... • Cellular barrier—cells tightly packed and sloughed off (10B skin cells/day=250 g./year) • Physical barrier—thick, mucousy and sticky secretions trap bacteria ...
... • Cellular barrier—cells tightly packed and sloughed off (10B skin cells/day=250 g./year) • Physical barrier—thick, mucousy and sticky secretions trap bacteria ...
Reportable Diseases List
... Respiratory infection, institutional outbreaks Rubella Rubella, congenital syndrome Salmonellosis Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Shigellosis Smallpox Streptococcal infections, Group A invasive Streptococcal infections, Group B neonatal Streptococcus pneumoniae, invasive Syphilis T ...
... Respiratory infection, institutional outbreaks Rubella Rubella, congenital syndrome Salmonellosis Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Shigellosis Smallpox Streptococcal infections, Group A invasive Streptococcal infections, Group B neonatal Streptococcus pneumoniae, invasive Syphilis T ...
T Healthy Smiles, Healthy Hearts
... Studies have shown that both periodontal (gum) disease and heart disease have similar underlying causes including age, tobacco use, genetics, stress, medications, poor nutrition, and obesity.1 However, another causal factor is the buildup of dental plaque over time. Gingivitis, an early stage of gum ...
... Studies have shown that both periodontal (gum) disease and heart disease have similar underlying causes including age, tobacco use, genetics, stress, medications, poor nutrition, and obesity.1 However, another causal factor is the buildup of dental plaque over time. Gingivitis, an early stage of gum ...
Glossary - Maggi Grace
... close look at your heart's valves and chambers without interference from the ribs or lungs. TEE is often combined with Doppler ultrasound and color Doppler to evaluate blood flow across the heart’s valves. TEE is often used when the results from standard echo studies were not sufficient or when your ...
... close look at your heart's valves and chambers without interference from the ribs or lungs. TEE is often combined with Doppler ultrasound and color Doppler to evaluate blood flow across the heart’s valves. TEE is often used when the results from standard echo studies were not sufficient or when your ...
Pulmonary valve stenosis
... To start you will see your family doctor then you will be referred to a general practitioner or a child’s physician. Lastly they will send you to a doctor specializing in the heart, usually a child’s ...
... To start you will see your family doctor then you will be referred to a general practitioner or a child’s physician. Lastly they will send you to a doctor specializing in the heart, usually a child’s ...
Snippets From the Past: Imaginative Designs—Separating
... “incident” cases was unusual for that period. The attempt to validate the parents’ reports of rheumatic fever in the uncles, aunts, and grandparents was another strength. Even though not explicitly stated, the choice of control children admitted to a tuberculosis clinic must have enhanced the compar ...
... “incident” cases was unusual for that period. The attempt to validate the parents’ reports of rheumatic fever in the uncles, aunts, and grandparents was another strength. Even though not explicitly stated, the choice of control children admitted to a tuberculosis clinic must have enhanced the compar ...
Cardiac Pathophysiology
... • Cause often unknown, but commonly caused by – infection, – uremia (renal failure), – neoplasm (tumor), – myocardial infarction (heart attack), – surgery or trauma. ...
... • Cause often unknown, but commonly caused by – infection, – uremia (renal failure), – neoplasm (tumor), – myocardial infarction (heart attack), – surgery or trauma. ...
Rheumatic fever

Rheumatic fever, also known as acute rheumatic fever (ARF), is an inflammatory disease that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a throat infection. Signs and symptoms include fever, multiple painful joints, involuntary muscle movements, and a characteristic but uncommon non itchy rash known as erythema marginatum. The heart is involved in about half of cases. Permanent damage to the heart valves, known as rheumatic heart disease (RHD), usually only occurs after multiple attacks but may occasionally occur after a single case of ARF. The damaged valves may result in heart failure. The abnormal valves also increase the risk of the person developing atrial fibrillation and infection of the valves.Acute rheumatic fever may occur following an infection of the throat by the bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes. If it is untreated ARF occurs in up to three percent of people. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve the production of antibodies against a person's own tissues. Some people due to their genetics are more likely to get the disease when exposed to the bacteria than others. Other risk factors include malnutrition and poverty. Diagnosis of ARF is often based on the presence of signs and symptoms in combination with evidence of a recent streptococcal infection.Treating people who have strep throat with antibiotics, such as penicillin, decreases their risk of getting ARF. This often involves testing people with sore throats for the infection, which may not be available in the developing world. Other preventative measures include improved sanitation. In those with ARF and RHD prolonged periods of antibiotics are sometimes recommended. Gradual return to normal activities may occur following an attack. Once RHD develops, treatment is more difficult. Occasionally valve replacement surgery or repair is required. Otherwise complications are treated as per normal.Acute rheumatic fever occurs in about 325,000 children each year and about 18 million people currently have rheumatic heart disease. Those who get ARF are most often between the ages of 5 and 14, with 20% of first-time attacks occurring in adults. The disease is most common in the developing world and among indigenous peoples in the developed world. In 2013 it resulted in 275,000 deaths down from 374,000 deaths in 1990. Most deaths occur in the developing world where as many as 12.5% of people affected may die each year. Descriptions of the condition are believed to date back to at least the 5th century BCE in the writings of Hippocrates. The disease is so named because its symptoms are similar to those of some rheumatic disorders.