Rheumatic Fever & Rheumatic Heart Disease
... •Rheumatic fever (RF) is an acute, immunologically mediated, multisystem inflammatory disease that occurs a few weeks following an episode of group A streptococcal pharyngitis. •Major involvement of systemic connective tissue, it often violate connective tissue of heart, joint, skin, and subcutaneou ...
... •Rheumatic fever (RF) is an acute, immunologically mediated, multisystem inflammatory disease that occurs a few weeks following an episode of group A streptococcal pharyngitis. •Major involvement of systemic connective tissue, it often violate connective tissue of heart, joint, skin, and subcutaneou ...
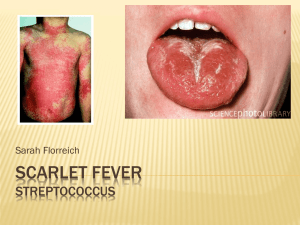
Scarlet Fever Streptococcus
... Begin a ten day treatment with antibiotics to treat scarlet fever. Ensure the patient gets plenty of fluid and bed rest. Aspirin should not be given to anyone with an infection under the age of 20 years since it can damage the liver. ...
... Begin a ten day treatment with antibiotics to treat scarlet fever. Ensure the patient gets plenty of fluid and bed rest. Aspirin should not be given to anyone with an infection under the age of 20 years since it can damage the liver. ...
Steps of rheumatic fever
... (caused by bacterial infection or bug called Group A Streptococcus). ...
... (caused by bacterial infection or bug called Group A Streptococcus). ...
Rheumatic heart disease
... process, leading to thrombotic manifestations on valves because of hypercoagulability. Natural history is characterized by worsening of HVD over time with an increased risk for stroke. APS patients undergoing valve-replacement surgery are at high risk of thrombotic and bleeding complications. Thus a ...
... process, leading to thrombotic manifestations on valves because of hypercoagulability. Natural history is characterized by worsening of HVD over time with an increased risk for stroke. APS patients undergoing valve-replacement surgery are at high risk of thrombotic and bleeding complications. Thus a ...
Presentazione standard di PowerPoint
... Carditis occurs in at least 60% of ARF patients and although any heart valve can be involved, the mitral and aortic valves are most frequently affected . RHD has a variable clinical course, ranging from asymptomatic valvular dysfunction to cardiac failure. Later complications include infective endo ...
... Carditis occurs in at least 60% of ARF patients and although any heart valve can be involved, the mitral and aortic valves are most frequently affected . RHD has a variable clinical course, ranging from asymptomatic valvular dysfunction to cardiac failure. Later complications include infective endo ...
Strep
... Streptococcal disease has been reported in your child’s classroom. Identification: Streptococcal disease (group A-Beta Hemolytic) often called "strep" cause a wide variety of infections. The most common is sore throat or skin infections (impetigo). Other diseases such as scarlet fever, middle ear in ...
... Streptococcal disease has been reported in your child’s classroom. Identification: Streptococcal disease (group A-Beta Hemolytic) often called "strep" cause a wide variety of infections. The most common is sore throat or skin infections (impetigo). Other diseases such as scarlet fever, middle ear in ...
6._Rheumatic_Heart_Disease
... In 0.3-3% of cases, infection leads to rheumatic fever several weeks after the sore throat has resolved. The organism spreads by direct contact with oral or respiratory secretions, and spread is ...
... In 0.3-3% of cases, infection leads to rheumatic fever several weeks after the sore throat has resolved. The organism spreads by direct contact with oral or respiratory secretions, and spread is ...
Cardiovascular disease What is a cardiovascular disease?
... blood clots in the leg veins, which can annually dislodge and move to the heart and lungs ...
... blood clots in the leg veins, which can annually dislodge and move to the heart and lungs ...
Rheumatic Fever 2010 1st yr2010-10-03 11:1464 KB
... the front of the knees. Erythema marginatum: a long lasting rash that begins on the trunk or arms. This rash never starts on the face and it is made worse with heat. Sydenham's chorea (St. Vitus' dance): a characteristic series of rapid movements without purpose of the face and arms. This can occur ...
... the front of the knees. Erythema marginatum: a long lasting rash that begins on the trunk or arms. This rash never starts on the face and it is made worse with heat. Sydenham's chorea (St. Vitus' dance): a characteristic series of rapid movements without purpose of the face and arms. This can occur ...
Acute rheumatic fever
... Acute rheumatic fever is diagnosed using the revised Jones criteria, which consist of clinical and laboratory findings . • The presence of either two major criteria or one major and two minor criteria, along with evidence of an antecedent streptococcal infection, confirm a diagnosis of acute rheumat ...
... Acute rheumatic fever is diagnosed using the revised Jones criteria, which consist of clinical and laboratory findings . • The presence of either two major criteria or one major and two minor criteria, along with evidence of an antecedent streptococcal infection, confirm a diagnosis of acute rheumat ...
Rheumatic Heart Disease
... atrial arrhythmias are the most common cardiac manifestations of chronic rheumatic heart disease (CRHD). Mitral stenosis occurs in 25% of patients with CRHD and is associated with mitral valve insufficiency in another 40%. Aortic stenosis from CRHD is associated with aortic insufficiency. The valve ...
... atrial arrhythmias are the most common cardiac manifestations of chronic rheumatic heart disease (CRHD). Mitral stenosis occurs in 25% of patients with CRHD and is associated with mitral valve insufficiency in another 40%. Aortic stenosis from CRHD is associated with aortic insufficiency. The valve ...
Recommended Duration of Prophylaxis for Rheumatic Fever
... 1. Benzathine penicillin G, 0.6 to 1.2 million units intramuscularly, is given to eradicate streptococci. This serves as the first dose of penicillin prophylaxis as well . In patients allergic to penicillin, erythromycin, 40 mg/kg per day in two to four doses for 10 days, may be substituted for peni ...
... 1. Benzathine penicillin G, 0.6 to 1.2 million units intramuscularly, is given to eradicate streptococci. This serves as the first dose of penicillin prophylaxis as well . In patients allergic to penicillin, erythromycin, 40 mg/kg per day in two to four doses for 10 days, may be substituted for peni ...
lecture 1 - Rheumatic Fever and Heart Disease (2013).
... • Rheumatic fever affect the peri-arteriolar connective tissue • It is believed to be caused by antibody crossreactivity • This cross-reactivity is a Type II hypersensitivity reaction and is termed molecular mimicry ...
... • Rheumatic fever affect the peri-arteriolar connective tissue • It is believed to be caused by antibody crossreactivity • This cross-reactivity is a Type II hypersensitivity reaction and is termed molecular mimicry ...
Lecture 1- Rheumatic Fever and Heart Disease
... • Rheumatic fever affect the peri-arteriolar connective tissue • It is believed to be caused by antibody crossreactivity • This cross-reactivity is a Type II hypersensitivity reaction and is termed molecular mimicry ...
... • Rheumatic fever affect the peri-arteriolar connective tissue • It is believed to be caused by antibody crossreactivity • This cross-reactivity is a Type II hypersensitivity reaction and is termed molecular mimicry ...
SDL 9- Rheumatic Heart Disease and Rheumatic Fever Acute
... Latent period: 3 weeks (1-5 weeks) between precipitating group A infection (onset of pharyngitis) and the appearance of the clinical features of ARF Exception is chorea lasting up to 6 months Infection is commonly subclinical—only confirmed using streptococcal Ab testing such as anti-streptolysin O, ...
... Latent period: 3 weeks (1-5 weeks) between precipitating group A infection (onset of pharyngitis) and the appearance of the clinical features of ARF Exception is chorea lasting up to 6 months Infection is commonly subclinical—only confirmed using streptococcal Ab testing such as anti-streptolysin O, ...
Rheumatic Fever and Heart Disease
... Leaflets are thickened, fibrotic, shrunken with fusion. Dilatation and hypertrophy of left atrium. Secondary deposition of Ca++ ...
... Leaflets are thickened, fibrotic, shrunken with fusion. Dilatation and hypertrophy of left atrium. Secondary deposition of Ca++ ...
Rheumatic Fever
... • Anti-inflammatory medications such as aspirin or corticosteroids reduce inflammation to help manage acute rheumatic fever. • You may have to take low doses of antibiotics (such as penicillin, sulfadiazine, or erythromycin) over the long term to prevent strep throat from returning. ...
... • Anti-inflammatory medications such as aspirin or corticosteroids reduce inflammation to help manage acute rheumatic fever. • You may have to take low doses of antibiotics (such as penicillin, sulfadiazine, or erythromycin) over the long term to prevent strep throat from returning. ...
prevalence of streptococcus a tonsillitis and rheumatic fever among
... 100,000 urban children aged from 2 to 14 years in the United States.Currently, it is less than 2 per 100,000 with a prevalence of rheumatic heart diseases of less than 1 per 1,000 school-aged children. In the past, the attack rate of rheumatic fever caused by streptococcal infections was about 3% in ...
... 100,000 urban children aged from 2 to 14 years in the United States.Currently, it is less than 2 per 100,000 with a prevalence of rheumatic heart diseases of less than 1 per 1,000 school-aged children. In the past, the attack rate of rheumatic fever caused by streptococcal infections was about 3% in ...
Rheumatic fever
... • The antibodies which the immune system generates against the "M proteins" may cross react with cardiac myofiber protein myosin and smooth muscle cells of arteries, inducing cytokine release and tissue destruction. • This inflammation occurs through direct attachment of complement and Fc receptor-m ...
... • The antibodies which the immune system generates against the "M proteins" may cross react with cardiac myofiber protein myosin and smooth muscle cells of arteries, inducing cytokine release and tissue destruction. • This inflammation occurs through direct attachment of complement and Fc receptor-m ...
Streptococcal Serology powerpoint
... • Delayed consequence of an untreated upper respiratory infection with group A streptococci • Causes serious, debilitating damage to the heart. • Associated with large amount of M protein and a capsule • Due to immune response against Strep antigens similar to heart antigens. ...
... • Delayed consequence of an untreated upper respiratory infection with group A streptococci • Causes serious, debilitating damage to the heart. • Associated with large amount of M protein and a capsule • Due to immune response against Strep antigens similar to heart antigens. ...
Team Case Study 4 Chelsea Doyle Del Marie
... How long has the sore on arm been inflamed If there are sores anywhere else besides arm ...
... How long has the sore on arm been inflamed If there are sores anywhere else besides arm ...
Rheumatic fever

Rheumatic fever, also known as acute rheumatic fever (ARF), is an inflammatory disease that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a throat infection. Signs and symptoms include fever, multiple painful joints, involuntary muscle movements, and a characteristic but uncommon non itchy rash known as erythema marginatum. The heart is involved in about half of cases. Permanent damage to the heart valves, known as rheumatic heart disease (RHD), usually only occurs after multiple attacks but may occasionally occur after a single case of ARF. The damaged valves may result in heart failure. The abnormal valves also increase the risk of the person developing atrial fibrillation and infection of the valves.Acute rheumatic fever may occur following an infection of the throat by the bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes. If it is untreated ARF occurs in up to three percent of people. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve the production of antibodies against a person's own tissues. Some people due to their genetics are more likely to get the disease when exposed to the bacteria than others. Other risk factors include malnutrition and poverty. Diagnosis of ARF is often based on the presence of signs and symptoms in combination with evidence of a recent streptococcal infection.Treating people who have strep throat with antibiotics, such as penicillin, decreases their risk of getting ARF. This often involves testing people with sore throats for the infection, which may not be available in the developing world. Other preventative measures include improved sanitation. In those with ARF and RHD prolonged periods of antibiotics are sometimes recommended. Gradual return to normal activities may occur following an attack. Once RHD develops, treatment is more difficult. Occasionally valve replacement surgery or repair is required. Otherwise complications are treated as per normal.Acute rheumatic fever occurs in about 325,000 children each year and about 18 million people currently have rheumatic heart disease. Those who get ARF are most often between the ages of 5 and 14, with 20% of first-time attacks occurring in adults. The disease is most common in the developing world and among indigenous peoples in the developed world. In 2013 it resulted in 275,000 deaths down from 374,000 deaths in 1990. Most deaths occur in the developing world where as many as 12.5% of people affected may die each year. Descriptions of the condition are believed to date back to at least the 5th century BCE in the writings of Hippocrates. The disease is so named because its symptoms are similar to those of some rheumatic disorders.