Bacteriology Practice Questions
... A. Streptococcus pyogenes - XLD agar B. Neisseria gonorrhoeae – Thayer-Martin agar C. Legionella pneumophilia – Buffered charcoal yeast extract D. Mycobacterium tuberculosis - Lowenstein-Jensen agar E. Mycoplasma pneumoniae SP4 agar ...
... A. Streptococcus pyogenes - XLD agar B. Neisseria gonorrhoeae – Thayer-Martin agar C. Legionella pneumophilia – Buffered charcoal yeast extract D. Mycobacterium tuberculosis - Lowenstein-Jensen agar E. Mycoplasma pneumoniae SP4 agar ...
-453.3- Rule (2) GUIDELINES FOR THE HANDLING OF BODY
... lesions, feces, urine, vomitus, respiratory secretions (for example, nasal discharge), and, saliva. Contact with body fluids presents a risk of infection with a variety of infectious agents. In general, however, the risk is very low and dependent on a variety of factors including the type of fluid w ...
... lesions, feces, urine, vomitus, respiratory secretions (for example, nasal discharge), and, saliva. Contact with body fluids presents a risk of infection with a variety of infectious agents. In general, however, the risk is very low and dependent on a variety of factors including the type of fluid w ...
Document
... Free living in soil, water or debris (generally rare) Crown gall pathogen and bacterial scab pathogens of root & tuber crops (soil), soft rotters (ponds, oceans) ...
... Free living in soil, water or debris (generally rare) Crown gall pathogen and bacterial scab pathogens of root & tuber crops (soil), soft rotters (ponds, oceans) ...
BOSY_DEFENCE__ARISTO_
... – skin arterioles in the infected area dilates so that more blood flows to the area – the permeability of skin capillaries increases so that more phagocytes & fluid come into the ...
... – skin arterioles in the infected area dilates so that more blood flows to the area – the permeability of skin capillaries increases so that more phagocytes & fluid come into the ...
AIDS/HIV Fact Sheet - Cornerstone Foundation Belize
... Within 2-4 weeks after exposure to HIV, many, but not all people who are infected experience flu-like symptoms, often described as the “worst flu ever.” Many HIV+ people do not have symptoms, they don’t look or feel sick, often people only begin to feel sick when they progress towards AIDS If you th ...
... Within 2-4 weeks after exposure to HIV, many, but not all people who are infected experience flu-like symptoms, often described as the “worst flu ever.” Many HIV+ people do not have symptoms, they don’t look or feel sick, often people only begin to feel sick when they progress towards AIDS If you th ...
Coevolution: a pattern of reciprocal adaptation, caused by two
... For a parasite to evolve to become gentle and prudent in its treatment of its host requires some form of group selection since natural selection operating at the level of the individual parasite often favors virulence ...
... For a parasite to evolve to become gentle and prudent in its treatment of its host requires some form of group selection since natural selection operating at the level of the individual parasite often favors virulence ...
Module 1
... The disease is highly contagious! It is transmitted by infected blood or body fluids through direct or indirect contact: • direct contact with sick or deceased persons • during care at home or in hospital • certain burial practices • contact with clothing, bed sheets, or other objects contaminated w ...
... The disease is highly contagious! It is transmitted by infected blood or body fluids through direct or indirect contact: • direct contact with sick or deceased persons • during care at home or in hospital • certain burial practices • contact with clothing, bed sheets, or other objects contaminated w ...
What infections do returned travellers bring back to Australia?
... HIV, hepatitis B and C, STIs ...
... HIV, hepatitis B and C, STIs ...
Chapter 1
... 1. Infecting organisms, such as bacteria and viruses, must survive outside their host—an infected person, an animal, or an insect. 2. The infecting organism must then move from one place to another. 3. The infecting organism must then invade a new person’s body and begin to multiply there. ...
... 1. Infecting organisms, such as bacteria and viruses, must survive outside their host—an infected person, an animal, or an insect. 2. The infecting organism must then move from one place to another. 3. The infecting organism must then invade a new person’s body and begin to multiply there. ...
The lessons which rare maladies can teach
... Sir Archibald Garrod was a pioneer in the field of metabolic diseases and discovered the rare genetic disorder alkaptonuria, which causes bones to turn black and brittle, leading to early joint degeneration. Whereas alkaptonuria affects around 80 people in the UK, it is actually a severe form of ost ...
... Sir Archibald Garrod was a pioneer in the field of metabolic diseases and discovered the rare genetic disorder alkaptonuria, which causes bones to turn black and brittle, leading to early joint degeneration. Whereas alkaptonuria affects around 80 people in the UK, it is actually a severe form of ost ...
Chapter 25 - Illini West High School
... Therefore making the immune system more susceptible to disease • ________________ Infections are infections that occur in individuals who do not have healthy immune systems ...
... Therefore making the immune system more susceptible to disease • ________________ Infections are infections that occur in individuals who do not have healthy immune systems ...
lecture_29_Mar 24_Co-evolution of parasites and hosts
... For a parasite to evolve to become gentle and prudent in its treatment of its host requires some form of group selection since natural selection operating at the level of the individual parasite often favors virulence ...
... For a parasite to evolve to become gentle and prudent in its treatment of its host requires some form of group selection since natural selection operating at the level of the individual parasite often favors virulence ...
GIS in context of bioterroryzm
... intentional or the alleged use of infectious biological agents as: viruses, bacteria, fungi, toxins or germs to cause illness and produce death or disease in humans, animals or ...
... intentional or the alleged use of infectious biological agents as: viruses, bacteria, fungi, toxins or germs to cause illness and produce death or disease in humans, animals or ...
Who created the process known as pasteurization?
... Although an average student in his early years, he earned several college degrees including both a BA and BS degree. He later studied at the Ecole Normale Superieure in Paris. He married and had five children. The death of one of his children from typhoid fever drove Pasteur to find cures for diseas ...
... Although an average student in his early years, he earned several college degrees including both a BA and BS degree. He later studied at the Ecole Normale Superieure in Paris. He married and had five children. The death of one of his children from typhoid fever drove Pasteur to find cures for diseas ...
Topic 19: Virulence and disease
... avian flu elements. Two hypotheses could be formulated: the 1918 flu involved recombination between human and avian flu strains, or the 1918 flu involved an avian strain shifting to humans. Imagine that you had access to flu sequences from 1900, 1905, 1910, and 1918 for ducks and humans and that you ...
... avian flu elements. Two hypotheses could be formulated: the 1918 flu involved recombination between human and avian flu strains, or the 1918 flu involved an avian strain shifting to humans. Imagine that you had access to flu sequences from 1900, 1905, 1910, and 1918 for ducks and humans and that you ...
Autoimmune dz`s
... – Mumps; WNV, EEE, hantavirus; influenza, common cold, RSV (but CDC won’t collaborate) – Avian influenza (but WHO won’t collaborate) – Viral bioterrorist threats: Ebola, Dengue, etc.—epidemics already exist Next Generation Disease Management™ ...
... – Mumps; WNV, EEE, hantavirus; influenza, common cold, RSV (but CDC won’t collaborate) – Avian influenza (but WHO won’t collaborate) – Viral bioterrorist threats: Ebola, Dengue, etc.—epidemics already exist Next Generation Disease Management™ ...
CHAPTER 42 Pathogenesis of Fungal Infections
... III. IMMUNITY A. Innate Immunity 1. Normal persons have a high level of innate immunity to most fungal infections 2. Important receptors include a lectin-like structure on phagocytes and Toll-like receptors 3. Most fungi are readily killed by phagocytes 4. Tissue phases of dimorphic fungi resist pha ...
... III. IMMUNITY A. Innate Immunity 1. Normal persons have a high level of innate immunity to most fungal infections 2. Important receptors include a lectin-like structure on phagocytes and Toll-like receptors 3. Most fungi are readily killed by phagocytes 4. Tissue phases of dimorphic fungi resist pha ...
No Slide Title
... Pathogenomics Goal: Identify previously unrecognized mechanisms of microbial pathogenicity using a unique combination of informatics, evolutionary biology, microbiology and genetics. ...
... Pathogenomics Goal: Identify previously unrecognized mechanisms of microbial pathogenicity using a unique combination of informatics, evolutionary biology, microbiology and genetics. ...
Crescent Healthcare IVIG
... debilitating chronic complications despite receiving recommended treatment. Now scientists have developed a new method to explore if these arthritic and neurologic symptoms result from the body's immune system turning against itself. Knowing the answer is key to developing better ways to diagnose Ly ...
... debilitating chronic complications despite receiving recommended treatment. Now scientists have developed a new method to explore if these arthritic and neurologic symptoms result from the body's immune system turning against itself. Knowing the answer is key to developing better ways to diagnose Ly ...
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
... Increase risk of upper respiratory infections. Any patient suspected of having a pyogenic complication of CD or any serious infection should undergo adequate drainage and treatment with antibiotics before starting infliximab. Reactivation of tuberculosis has been observed and has resulted in dissemi ...
... Increase risk of upper respiratory infections. Any patient suspected of having a pyogenic complication of CD or any serious infection should undergo adequate drainage and treatment with antibiotics before starting infliximab. Reactivation of tuberculosis has been observed and has resulted in dissemi ...
B.002 Communicable Diseases - Halifax Regional School Board
... Promote with students the importance of regularly washing hands with soap and water as it the most effective way to prevent communicable diseases, illnesses and infections from spreading; ...
... Promote with students the importance of regularly washing hands with soap and water as it the most effective way to prevent communicable diseases, illnesses and infections from spreading; ...
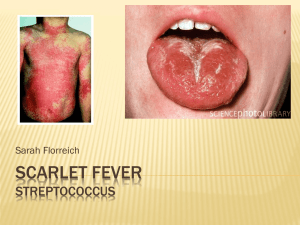
Scarlet Fever Streptococcus
... Streptococcus is a group of bacteria, familiarly known as strep, that cause a multitude of diseases, such as strep throat, pneumonia, scarlet fever, rheumatic fever and others ...
... Streptococcus is a group of bacteria, familiarly known as strep, that cause a multitude of diseases, such as strep throat, pneumonia, scarlet fever, rheumatic fever and others ...
Health Care Associated Infections: Sources and
... 3.2 The role of airborne transmission Many respiratory pathogens are transmitted from patient to patient by the airborne route. The large majority are carried by large droplets. This applies particularly to RSV, influenza and common cold viruses, and to bacteria like pneumococci, meningococci and ha ...
... 3.2 The role of airborne transmission Many respiratory pathogens are transmitted from patient to patient by the airborne route. The large majority are carried by large droplets. This applies particularly to RSV, influenza and common cold viruses, and to bacteria like pneumococci, meningococci and ha ...