Chapter 40-2
... that breaks down the cell walls of bacteria Oil & sweat glands produce an acidic environment on the skin that kills many bacteria Mucus in mouth & nose help trap pathogens Stomach acids & digestive enzymes destroy many pathogens that get in your stomach ...
... that breaks down the cell walls of bacteria Oil & sweat glands produce an acidic environment on the skin that kills many bacteria Mucus in mouth & nose help trap pathogens Stomach acids & digestive enzymes destroy many pathogens that get in your stomach ...
Introduction and Innate Immunity
... NK cells do not require prior immunization or activation They attach to ‘target’ cells (ADCC) Cytotoxic granules are released onto surface of cell Effector proteins penetrate cell membrane and induce programmed cell death ...
... NK cells do not require prior immunization or activation They attach to ‘target’ cells (ADCC) Cytotoxic granules are released onto surface of cell Effector proteins penetrate cell membrane and induce programmed cell death ...
The Immune System
... body can no longer activate B cells or killer T cells – The immune system has no way to fight the pathogen – In other words, the immune system shuts down – Other antigens or pathogens can enter and your body has no way to fight against them ...
... body can no longer activate B cells or killer T cells – The immune system has no way to fight the pathogen – In other words, the immune system shuts down – Other antigens or pathogens can enter and your body has no way to fight against them ...
THE IMMUNE RESPONSE AGAINST INTRACELLULAR BACTERIA
... Evasion of immune mechanisms by intracellular bacteria Inhibition of phagolysosome formation Mycobacterium tuberculosis ...
... Evasion of immune mechanisms by intracellular bacteria Inhibition of phagolysosome formation Mycobacterium tuberculosis ...
Intro to the Immune System
... 2) diversity – the immune system can produce a hugely diverse set of recognition molecules which allows us to recognize literally billions of molecular shapes 3) memory – once it has responded to an antigen, the system maintains a memory of that Ag 4) self-nonself recognition –the system typically r ...
... 2) diversity – the immune system can produce a hugely diverse set of recognition molecules which allows us to recognize literally billions of molecular shapes 3) memory – once it has responded to an antigen, the system maintains a memory of that Ag 4) self-nonself recognition –the system typically r ...
Innate immune responses to cationic antimicrobial peptides in the lung
... Effector cells of the innate immune response include neutrophils, monocytes and immature dendritic cells. LL-37 has been demonstrated to have a variety of effects on all these cell types; however, the mechanisms by which it exerts these effects have not yet been determined. The objective of this res ...
... Effector cells of the innate immune response include neutrophils, monocytes and immature dendritic cells. LL-37 has been demonstrated to have a variety of effects on all these cell types; however, the mechanisms by which it exerts these effects have not yet been determined. The objective of this res ...
Aseptic Technique: Media and Equipment
... – 2. IgG – monomer, the major AB in the blood that appears 24-48 hrs after antigen appears, provides long-term resistance, crosses placenta to give immunity to fetus ...
... – 2. IgG – monomer, the major AB in the blood that appears 24-48 hrs after antigen appears, provides long-term resistance, crosses placenta to give immunity to fetus ...
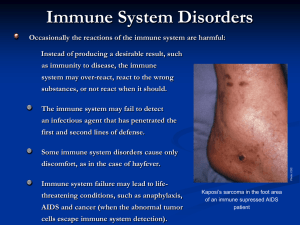
Immune System Disorders
... vigorous overreaction of the immune system to a previously encountered antigen. Mast cells are immune cells involved in allergic responses, they are non- motile, found around blood vessels, in connective tissue and in the lungs. Mast cells release active agents such as Histamine, which cause contrac ...
... vigorous overreaction of the immune system to a previously encountered antigen. Mast cells are immune cells involved in allergic responses, they are non- motile, found around blood vessels, in connective tissue and in the lungs. Mast cells release active agents such as Histamine, which cause contrac ...
Beat The Flu with These Essential Vitamins
... Beat The Flu Essential Vitamins The immune system can be weakened by all kinds of stressors, including diseases or chronic conditions, invading organisms, poor diet or nutrient absorption issues, side-effects of medications, general organ health, and ageing. It is a proven fact that there is a link ...
... Beat The Flu Essential Vitamins The immune system can be weakened by all kinds of stressors, including diseases or chronic conditions, invading organisms, poor diet or nutrient absorption issues, side-effects of medications, general organ health, and ageing. It is a proven fact that there is a link ...
The One and Only… The Famous… IMMUNE SYSTEM!!!!
... • Kinins – cause vasodilatation, and pain. • Leukotrienes – groups of lipids, derived from mast cells and basophils, cause contraction of bronchiolar and inflammation. • Prostaglandins – group of lipids; varied effects: inflammation, vasodilatation, and pain. • Cytokines (messengers) – stimulate act ...
... • Kinins – cause vasodilatation, and pain. • Leukotrienes – groups of lipids, derived from mast cells and basophils, cause contraction of bronchiolar and inflammation. • Prostaglandins – group of lipids; varied effects: inflammation, vasodilatation, and pain. • Cytokines (messengers) – stimulate act ...
October 9, 2014
... HIV-specific T-cell functionality. Through in vitro and ex vivo cellular assays, the study demonstrated that antibodies used in combination against CD160 and PD-1, significantly increased HIV-specific CD8+ T-cell proliferation. The enhanced immune response observed from this co-targeting strategy r ...
... HIV-specific T-cell functionality. Through in vitro and ex vivo cellular assays, the study demonstrated that antibodies used in combination against CD160 and PD-1, significantly increased HIV-specific CD8+ T-cell proliferation. The enhanced immune response observed from this co-targeting strategy r ...
An Agent-Based Model Demonstrates that the
... the simulated immune response to a virus. The agents representing cells were programmed to count their meaningful interactions with other agents, to characterize the connectivity of the immune system network. The connectivity data generated during the simulated immune response demonstrated behavior ...
... the simulated immune response to a virus. The agents representing cells were programmed to count their meaningful interactions with other agents, to characterize the connectivity of the immune system network. The connectivity data generated during the simulated immune response demonstrated behavior ...
Immunity PP - TeacherWeb
... II. Immunity: reaction of the body to foreign agents (microbes, parasites, chemicals, cancer). Takes four forms: A. Natural : immunity that the body makes on its own, innate B. Acquired: immunity after exposure to an antigen, or, vaccine C. Nonspecific: does not target specific organisms D. Specifi ...
... II. Immunity: reaction of the body to foreign agents (microbes, parasites, chemicals, cancer). Takes four forms: A. Natural : immunity that the body makes on its own, innate B. Acquired: immunity after exposure to an antigen, or, vaccine C. Nonspecific: does not target specific organisms D. Specifi ...
Immunology Notes
... plasma cell is essentially a factory for producing antibody. Each of the plasma cells descended from a given B cell (which are all members of the same family, or clone) manufactures millions of identical antibody molecules and pours them into the bloodstream. A given antibody matches an antigen much ...
... plasma cell is essentially a factory for producing antibody. Each of the plasma cells descended from a given B cell (which are all members of the same family, or clone) manufactures millions of identical antibody molecules and pours them into the bloodstream. A given antibody matches an antigen much ...
- SGTB Khalsa College
... Class I MHC Study of structure of Class I MHC Molecule molecules and their interaction with Tc cells and Antigen Study of structure of Class II MHC Class II MHC molecule molecules and their interaction with Th cells and Antigen ...
... Class I MHC Study of structure of Class I MHC Molecule molecules and their interaction with Tc cells and Antigen Study of structure of Class II MHC Class II MHC molecule molecules and their interaction with Th cells and Antigen ...
www.informatics.indiana.edu
... antigens that have been partly degraded inside the antigenpresenting cell. The peptide fragments are then carried to the surface of the presenting cell on special molecules called MHC proteins; The second difference is that, once activated, effector T cells act only at short range, either within a s ...
... antigens that have been partly degraded inside the antigenpresenting cell. The peptide fragments are then carried to the surface of the presenting cell on special molecules called MHC proteins; The second difference is that, once activated, effector T cells act only at short range, either within a s ...
Immune Primer - Life Sciences Outreach Program
... 9. How might a pathogen enter your body without having to pass through your skin? (Hint: Think of organ systems that are most commonly infected.) Skin works with many other substances to block the entry of pathogens. Explain the role of the following substances in preventing infection. 10. Sweat 11. ...
... 9. How might a pathogen enter your body without having to pass through your skin? (Hint: Think of organ systems that are most commonly infected.) Skin works with many other substances to block the entry of pathogens. Explain the role of the following substances in preventing infection. 10. Sweat 11. ...
Human Defence System
... Comment briefly on the difficulty in classifying viruses as living organisms. Name two diseases of humans caused by viruses. Name two types of lymphocyte and state a role of each when viruses or other micro-organisms enter the blood. “Immunity that results from vaccination is effectively the same as ...
... Comment briefly on the difficulty in classifying viruses as living organisms. Name two diseases of humans caused by viruses. Name two types of lymphocyte and state a role of each when viruses or other micro-organisms enter the blood. “Immunity that results from vaccination is effectively the same as ...
Immune system

The immune system is a system of many biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease. To function properly, an immune system must detect a wide variety of agents, known as pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, and distinguish them from the organism's own healthy tissue. In many species, the immune system can be classified into subsystems, such as the innate immune system versus the adaptive immune system, or humoral immunity versus cell-mediated immunity.Pathogens can rapidly evolve and adapt, and thereby avoid detection and neutralization by the immune system; however, multiple defense mechanisms have also evolved to recognize and neutralize pathogens. Even simple unicellular organisms such as bacteria possess a rudimentary immune system, in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryotes and remain in their modern descendants, such as plants and insects. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system. Jawed vertebrates, including humans, have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms, including the ability to adapt over time to recognize specific pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive (or acquired) immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination.Disorders of the immune system can result in autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases and cancer.Immunodeficiency occurs when the immune system is less active than normal, resulting in recurring and life-threatening infections. In humans, immunodeficiency can either be the result of a genetic disease such as severe combined immunodeficiency, acquired conditions such as HIV/AIDS, or the use of immunosuppressive medication. In contrast, autoimmunity results from a hyperactive immune system attacking normal tissues as if they were foreign organisms. Common autoimmune diseases include Hashimoto's thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus type 1, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology covers the study of all aspects of the immune system.