MC-vragen: 23 - Di-Et-Tri
... 21. Cellular repair is a relatively uncommon form of repair; [ ] Because damaged cells automatically go into apoptosis; [ ] Because membrane damage always results into autolysis by the released enzymes; [ ] As in most tissue types damaged cells die and are replaced by proliferation of surrounding h ...
... 21. Cellular repair is a relatively uncommon form of repair; [ ] Because damaged cells automatically go into apoptosis; [ ] Because membrane damage always results into autolysis by the released enzymes; [ ] As in most tissue types damaged cells die and are replaced by proliferation of surrounding h ...
MC-vragen: 23 - Di-Et-Tri
... 21. Cellular repair is a relatively uncommon form of repair; [ ] Because damaged cells automatically go into apoptosis; [ ] Because membrane damage always results into autolysis by the released enzymes; [ ] As in most tissue types damaged cells die and are replaced by proliferation of surrounding h ...
... 21. Cellular repair is a relatively uncommon form of repair; [ ] Because damaged cells automatically go into apoptosis; [ ] Because membrane damage always results into autolysis by the released enzymes; [ ] As in most tissue types damaged cells die and are replaced by proliferation of surrounding h ...
Cells - Bonar Law Memorial
... A thick wall found in the plant cell only. Its function is to give shape and additional support to the plant cell. Cytoplasm Gel-like substance that holds the nucleus and other organelles in place. The cytoplasm also allows nutrients to flow within the cell. Nucleus The nucleus encloses the cel ...
... A thick wall found in the plant cell only. Its function is to give shape and additional support to the plant cell. Cytoplasm Gel-like substance that holds the nucleus and other organelles in place. The cytoplasm also allows nutrients to flow within the cell. Nucleus The nucleus encloses the cel ...
Immunology Notes
... one B cell will make an antibody that blocks a virus that causes the common cold, while another produces antibody that zeros in on a bacterium that causes pneumonia. When a B cell encounters its triggering antigen(along with collaborating T cells and accessory cells), it gives rise to many large pla ...
... one B cell will make an antibody that blocks a virus that causes the common cold, while another produces antibody that zeros in on a bacterium that causes pneumonia. When a B cell encounters its triggering antigen(along with collaborating T cells and accessory cells), it gives rise to many large pla ...
Studying cells_online activity
... 1. The activity of the scientific method that sets science apart from many other human endeavors is _________________________________________ . ...
... 1. The activity of the scientific method that sets science apart from many other human endeavors is _________________________________________ . ...
infection and microbial pathogenecity (host microbe
... Two signals are needed for ‘B’ cell activation First signal is the specific binding of the antigenic receptor with the membrane bound form of immunoglobin present in the surface of the ‘B’ cells ...
... Two signals are needed for ‘B’ cell activation First signal is the specific binding of the antigenic receptor with the membrane bound form of immunoglobin present in the surface of the ‘B’ cells ...
投影片 1
... -Suppressor T cells assist in down-regulating the activity of plasma cells and cytotoxic T cells -Memory T cells “remember” the antigen and provide for a rapid production of cytotoxic T cells subsequent encounters with the same antigen ...
... -Suppressor T cells assist in down-regulating the activity of plasma cells and cytotoxic T cells -Memory T cells “remember” the antigen and provide for a rapid production of cytotoxic T cells subsequent encounters with the same antigen ...
Name_________________________________ Thompson 211
... 10. In 2 hours it has infected 5000 cells in the body. 11. If it gets into her lungs she could become critically ill. 12. The body’s front line defense is Natural Killer cells that spray a poison onto the virus which unfortunately destroys throat cells too. 13. Cell debris piles up in her throat. 14 ...
... 10. In 2 hours it has infected 5000 cells in the body. 11. If it gets into her lungs she could become critically ill. 12. The body’s front line defense is Natural Killer cells that spray a poison onto the virus which unfortunately destroys throat cells too. 13. Cell debris piles up in her throat. 14 ...
Overview of the Immune System Zoran Galic Ph.D.
... Can detect subtle changes in proteins, carbohydrates (sugars), and lipids This response is specific It must detect self versus non-self It must differentiate different forms of non-self (flu virus looks different than HIV) Antigen (Ag)- the molecule or structure against which the immune response is ...
... Can detect subtle changes in proteins, carbohydrates (sugars), and lipids This response is specific It must detect self versus non-self It must differentiate different forms of non-self (flu virus looks different than HIV) Antigen (Ag)- the molecule or structure against which the immune response is ...
Lecture 5
... a few cytotoxic T cells that are involved in some allergic reactions (poison ivy) and rejection of transplanted tissue. ...
... a few cytotoxic T cells that are involved in some allergic reactions (poison ivy) and rejection of transplanted tissue. ...
6_Autoimmune_2013
... Normal tissue cells do not express MHC class II NO SIGNAL 1. for CD4+ Th activation Normal tissue cells do not express co-stimulatory molecules and do not produce T cell differentiating cytokines NO SIGNAL 2. for CD4+ Th activation Migration of naive T lymphocytes to normal tissues is limited Antige ...
... Normal tissue cells do not express MHC class II NO SIGNAL 1. for CD4+ Th activation Normal tissue cells do not express co-stimulatory molecules and do not produce T cell differentiating cytokines NO SIGNAL 2. for CD4+ Th activation Migration of naive T lymphocytes to normal tissues is limited Antige ...
Chapter 43 - Immune System
... Class I MHC molecules: found on all nucleated cells Class II MHC molecules: found on macrophages, B cells, and activated T cells Antigen presentation: process by which an MHC molecule “presents’ an intracellular protein to an antigen receptor on a nearby T cell Cytotoxic T cells (TC): bind to protei ...
... Class I MHC molecules: found on all nucleated cells Class II MHC molecules: found on macrophages, B cells, and activated T cells Antigen presentation: process by which an MHC molecule “presents’ an intracellular protein to an antigen receptor on a nearby T cell Cytotoxic T cells (TC): bind to protei ...
Cellular Communication
... • Endocrine signals are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel long distances through the blood to reach all parts of the body • The signal molecules travels throughout the body, most likely contacting nearly all cells in the organism • Only t ...
... • Endocrine signals are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel long distances through the blood to reach all parts of the body • The signal molecules travels throughout the body, most likely contacting nearly all cells in the organism • Only t ...
Specific Immunity - Austin Community College
... migrate to the lymphoid tissue, where they encounter antigens. ...
... migrate to the lymphoid tissue, where they encounter antigens. ...
The Immune System : (page 382) Recognizes and destroys
... Form the 2nd and 3rd lines of defence. To attack a pathogen, you must recognize cells that don’t belong to you ( shape of their antigens) first. Macrophages engulf them, their antigens moved to the surface of the macrophage. Then your B cells will produce shape specific antibodies that join onto the ...
... Form the 2nd and 3rd lines of defence. To attack a pathogen, you must recognize cells that don’t belong to you ( shape of their antigens) first. Macrophages engulf them, their antigens moved to the surface of the macrophage. Then your B cells will produce shape specific antibodies that join onto the ...
Slide ()
... Immune pathogenesis of apoptosis of CD34 multipotential hematopoietic cells in acquired aplastic anemia. Antigens are presented to T lymphocytes by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). This triggers T cells to activate and proliferate. T-bet, a transcription factor, binds to the interferon-γ (IFN-γ) pro ...
... Immune pathogenesis of apoptosis of CD34 multipotential hematopoietic cells in acquired aplastic anemia. Antigens are presented to T lymphocytes by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). This triggers T cells to activate and proliferate. T-bet, a transcription factor, binds to the interferon-γ (IFN-γ) pro ...
II. T cell activation
... functions of the cells. The biochemical pathways that link Ag recognition with T cell responses consist of the activation of the enzymes, ...
... functions of the cells. The biochemical pathways that link Ag recognition with T cell responses consist of the activation of the enzymes, ...
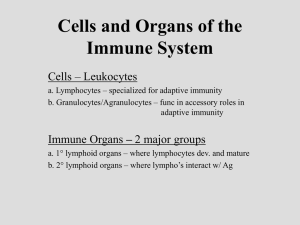
Cells and Organs of the Immune System
... balance between cells removed by cell death and those produced -for WBC’s: a human must produce ~3.7 x 1011/day ! ...
... balance between cells removed by cell death and those produced -for WBC’s: a human must produce ~3.7 x 1011/day ! ...
The Cell and Cell Division Exercises
... 12. A species has a chromosome number of 8 in a root cell. How many would you expect to find in pollen grains and why? ...
... 12. A species has a chromosome number of 8 in a root cell. How many would you expect to find in pollen grains and why? ...
Chapter 40 Review
... • What enzyme breaks down the cells walls of bacteria and can be found in mucus, saliva, ...
... • What enzyme breaks down the cells walls of bacteria and can be found in mucus, saliva, ...
Microbiology – Chapter 15
... 5. Antibodies tend to react with specific parts of an antigen – called and antigenic determinant or epitope. Size and shape; lock-key just like in enzyme substrate interactions. 6. Small molecules that are too small to cause an immune response are called haptens. Penicillin is an example. By itself, ...
... 5. Antibodies tend to react with specific parts of an antigen – called and antigenic determinant or epitope. Size and shape; lock-key just like in enzyme substrate interactions. 6. Small molecules that are too small to cause an immune response are called haptens. Penicillin is an example. By itself, ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.