hypersensitivities ppt
... • Acute graft rejection, skin test for TB, contact allergic reactions, and some autoimmune diseases ...
... • Acute graft rejection, skin test for TB, contact allergic reactions, and some autoimmune diseases ...
Chapter 6 - Psychology
... indirect B-cell attack - Assisted by "helper T-cells," B-cells differentiate into "plasma cells" which secrete antibodies. The antibodies are "invader specific" as are the T-cells. antibodies - Protein substances produced in response to a specific invader or antigen, marking it for destruction and t ...
... indirect B-cell attack - Assisted by "helper T-cells," B-cells differentiate into "plasma cells" which secrete antibodies. The antibodies are "invader specific" as are the T-cells. antibodies - Protein substances produced in response to a specific invader or antigen, marking it for destruction and t ...
Notes on Acquired Immunity
... Activation of Macrophages: Activation by TH1 cells also allows them to eliminate intracellular microbes efficiently o Macrophage presents Ag to TH1 cell on MHC class II (binds TCR + CD4) o CD40L on T cell binds CD40 on macrophage; IFNγ released from T cells binds its receptor on macrophage ...
... Activation of Macrophages: Activation by TH1 cells also allows them to eliminate intracellular microbes efficiently o Macrophage presents Ag to TH1 cell on MHC class II (binds TCR + CD4) o CD40L on T cell binds CD40 on macrophage; IFNγ released from T cells binds its receptor on macrophage ...
Immunological diagnosis
... specific Ab, they precipitate. Precipitation can be demonstrated via immunodiffusion in a semisolid medium (e.g. agar). b. Types immunonephelometry: the formation of IC in solution is monitored by spectrometry. single immunodiffusion double immunodiffusion immunoelectrophoresis ...
... specific Ab, they precipitate. Precipitation can be demonstrated via immunodiffusion in a semisolid medium (e.g. agar). b. Types immunonephelometry: the formation of IC in solution is monitored by spectrometry. single immunodiffusion double immunodiffusion immunoelectrophoresis ...
Summary of Human systems Human Body Systems Overview
... Immune cells are made in the bone marrow and mature either in the bone marrow (B cells) or in the thymus gland (T cells). These cells are very specialized, with each type capable of recognizing one specific antigen (cell identification markers) and destroying that foreign cell. Other immune cells (m ...
... Immune cells are made in the bone marrow and mature either in the bone marrow (B cells) or in the thymus gland (T cells). These cells are very specialized, with each type capable of recognizing one specific antigen (cell identification markers) and destroying that foreign cell. Other immune cells (m ...
How our body fights to keep us healthy
... • The virus is too weak to make us ill but now we have antibodies ready so if the original measles virus gets into our body we already have the weapon to attack it straight away and so we do not get ill or only feel mildly ...
... • The virus is too weak to make us ill but now we have antibodies ready so if the original measles virus gets into our body we already have the weapon to attack it straight away and so we do not get ill or only feel mildly ...
Peripheral tolerance
... The problem of self-nonself discrimination • The immune system responds to many foreign (microbial) antigens but not to self antigens • Developing lymphocytes express a large number of antigen receptors, not biased by specificity • Therefore, all individuals produce lymphocytes with the ability to ...
... The problem of self-nonself discrimination • The immune system responds to many foreign (microbial) antigens but not to self antigens • Developing lymphocytes express a large number of antigen receptors, not biased by specificity • Therefore, all individuals produce lymphocytes with the ability to ...
Ch51Immunity - Environmental
... 1° vs 2° response to disease Memory B cells allow a rapid, amplified response with future exposure to pathogen ...
... 1° vs 2° response to disease Memory B cells allow a rapid, amplified response with future exposure to pathogen ...
The Role of Leptin in the Cell-Mediated Immune Response and T
... BackgroundAlms: Dysphagia after stroke is a common problem and yet our understanding of this devastating complication remains poor. The aim of this study was to explore the central neural control of human swallowing, in order to determine the basis for the development and recovery of stroke induced ...
... BackgroundAlms: Dysphagia after stroke is a common problem and yet our understanding of this devastating complication remains poor. The aim of this study was to explore the central neural control of human swallowing, in order to determine the basis for the development and recovery of stroke induced ...
IMMUNE SYSTEM
... very specific aka acquired immune response activated after innate responses & develops more slowly ...
... very specific aka acquired immune response activated after innate responses & develops more slowly ...
Immune System Interactive Physiology Worksheets
... 6. Our bodies make approximately _________________different types of lymphocyte antigen receptors. With only 25,000 different genes in our body, how can so many antigen receptors be made? • ____________________________________________ 7. Receptors have two regions. The _____________region is the sam ...
... 6. Our bodies make approximately _________________different types of lymphocyte antigen receptors. With only 25,000 different genes in our body, how can so many antigen receptors be made? • ____________________________________________ 7. Receptors have two regions. The _____________region is the sam ...
2006 – San Diego, CA
... J. Laskin – Overview: Cytokines and Growth Factors Rich Irons – Regulation of Hematopoiesis by Cytokines Kevin Driscoll – Cytokines and Lung Inflammation and Fibrosis Debbie Laskin – The Involvement of Cytokines and Growth Factors in Hepatic Toxicity D. Heck – Chemical-Induced Injury to Skin ...
... J. Laskin – Overview: Cytokines and Growth Factors Rich Irons – Regulation of Hematopoiesis by Cytokines Kevin Driscoll – Cytokines and Lung Inflammation and Fibrosis Debbie Laskin – The Involvement of Cytokines and Growth Factors in Hepatic Toxicity D. Heck – Chemical-Induced Injury to Skin ...
AP Biology Potential Essay Questions for Unit 3
... 3. After school one day you notice that you are starving and decide to go get a cheeseburger. As you are eating, you think back to all you know about the digestive process. Assuming you have protein (meat), carbohydrates (bun) and fat (meat, mayo, cheese), describe how each nutrient is processed (di ...
... 3. After school one day you notice that you are starving and decide to go get a cheeseburger. As you are eating, you think back to all you know about the digestive process. Assuming you have protein (meat), carbohydrates (bun) and fat (meat, mayo, cheese), describe how each nutrient is processed (di ...
Key Concepts in B cell Activation-I
... often seen in T cell-dependent humoral immune responses. 5. Primary & 2nd Ab responses differ qualitatively & ...
... often seen in T cell-dependent humoral immune responses. 5. Primary & 2nd Ab responses differ qualitatively & ...
10 PhD positions in the EN‐ACTI2NG H2020‐MSCA‐ITN
... are most interested in, listing the project numbers and titles in order of preference. These documents should be sent in a single pdf file to the consortium’s email address ([email protected]) mentioning in the subject line: EN‐ACTI2NG application and the numbers of the 3 projects in preferred o ...
... are most interested in, listing the project numbers and titles in order of preference. These documents should be sent in a single pdf file to the consortium’s email address ([email protected]) mentioning in the subject line: EN‐ACTI2NG application and the numbers of the 3 projects in preferred o ...
Cell Transport WS - Kenston Local Schools
... a. Hypertonic: The cell would ____________________________ because the water molecules would _____________________. b. Hypotonic: The cell would _______________________________ because the water molecules would _______________________. c. Isotonic: The cell would __________________________________ b ...
... a. Hypertonic: The cell would ____________________________ because the water molecules would _____________________. b. Hypotonic: The cell would _______________________________ because the water molecules would _______________________. c. Isotonic: The cell would __________________________________ b ...
antigen - SITH-ITB
... against any infectious agent. Innate refers to the fact that these defenses are always present and ready to function • adaptive immunity, the body’s immune cells not only recognize specific parts of a pathogen, but they also “remember” previous encounters. Innate defenses and adaptive immunity inte ...
... against any infectious agent. Innate refers to the fact that these defenses are always present and ready to function • adaptive immunity, the body’s immune cells not only recognize specific parts of a pathogen, but they also “remember” previous encounters. Innate defenses and adaptive immunity inte ...
innate adaptive - El Corte Inglés
... SLE is complex • SLE is a multigenic disease that involves loss of tolerance involving both innate and adaptive immune pathways. • Multiple triggers are likely to be involved in disease initiation and perpetuation. • Continuous exposure to excess nucleic acid containing material amplifies the diseas ...
... SLE is complex • SLE is a multigenic disease that involves loss of tolerance involving both innate and adaptive immune pathways. • Multiple triggers are likely to be involved in disease initiation and perpetuation. • Continuous exposure to excess nucleic acid containing material amplifies the diseas ...
Recombinant Human GM-CSF
... granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. It is produced by a number of different cell types (including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells and fibroblasts) in response to cytokine or immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, GM-CSF is ...
... granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. It is produced by a number of different cell types (including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, mast cells, endothelial cells and fibroblasts) in response to cytokine or immune and inflammatory stimuli. Besides granulocyte-macrophage progenitors, GM-CSF is ...
Inflammation in CNS
... membrane of gram-negative bacteria, which mimics systemic infection. LPS is one element of the “pathogen-associated molecular patterns,” which are produced by invading microorganisms and are recognized by specific receptors (TLRs) and cells of the immune system. TLRs are a family of type 1 transmemb ...
... membrane of gram-negative bacteria, which mimics systemic infection. LPS is one element of the “pathogen-associated molecular patterns,” which are produced by invading microorganisms and are recognized by specific receptors (TLRs) and cells of the immune system. TLRs are a family of type 1 transmemb ...
Immunology Lecture 1
... pathogen then responds faster and more efficiently when the same pathogen is again encountered? 4 – How to make use of all these studies: To develop vaccines and immune-therapies. ...
... pathogen then responds faster and more efficiently when the same pathogen is again encountered? 4 – How to make use of all these studies: To develop vaccines and immune-therapies. ...
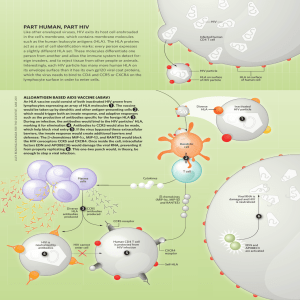
Part human, Part hIV
... Like other enveloped viruses, HIV exits its host cell enshrouded in the cell’s membrane, which contains membrane molecules such as the human leukocyte antigens (HLA). The HLA proteins act as a set of cell identification marks: every person expresses a slightly different HLA set. These molecules diff ...
... Like other enveloped viruses, HIV exits its host cell enshrouded in the cell’s membrane, which contains membrane molecules such as the human leukocyte antigens (HLA). The HLA proteins act as a set of cell identification marks: every person expresses a slightly different HLA set. These molecules diff ...
Key Concepts in B cell Activation-I
... 1. Adaptive immune responses are initiated and mediated by T-cell activation. 2. Naïve T lymphocytes migrate from Thymus to 2o Lymphoid organs, whereby encounter Ag presented by APCs (eg. DCs) and then become activated. 3. T-cell activation requires Two Signals: - Primary Signal-TCR/CD3 –Ag/MHC comp ...
... 1. Adaptive immune responses are initiated and mediated by T-cell activation. 2. Naïve T lymphocytes migrate from Thymus to 2o Lymphoid organs, whereby encounter Ag presented by APCs (eg. DCs) and then become activated. 3. T-cell activation requires Two Signals: - Primary Signal-TCR/CD3 –Ag/MHC comp ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.