Cell Membrane
... The Cell Cycle • Series of changes a cell undergoes from the time it forms until the time it divide ...
... The Cell Cycle • Series of changes a cell undergoes from the time it forms until the time it divide ...
Learning to tell your friends from your foes by
... The nature of mucosal friend foe information processing Immunological interactions include those of a winner-takes-all competition type. Such competitive processes at antigen presentation could link pathogenicity and commensality to microbial antigens APCs are proposed to vary with inhibitory and ex ...
... The nature of mucosal friend foe information processing Immunological interactions include those of a winner-takes-all competition type. Such competitive processes at antigen presentation could link pathogenicity and commensality to microbial antigens APCs are proposed to vary with inhibitory and ex ...
Chapter 17 Powerpoint Show
... • The process of destroying B and T cells that react to self antigens • Amount of antibody in serum called antibody titer ...
... • The process of destroying B and T cells that react to self antigens • Amount of antibody in serum called antibody titer ...
Series introduction: innate host defense of the respiratory
... pathogens are cleared from the lung without inflammation or disturbance of the local function or structure. In case this first line host-defense system fails to clear the microorganism, secondary layers of the system are activated that are accompanied by an inflammatory reaction. The devastating eff ...
... pathogens are cleared from the lung without inflammation or disturbance of the local function or structure. In case this first line host-defense system fails to clear the microorganism, secondary layers of the system are activated that are accompanied by an inflammatory reaction. The devastating eff ...
biology 377
... the College of Arts and Sciences. No make-up final examination will be given except for reasons of illness or other verified emergencies. The report will consist of a 6-8 page paper (1200-1600 words, 12 pt font, double spaced) on a topic of your choice from the Case Studies in Immunology book. To cl ...
... the College of Arts and Sciences. No make-up final examination will be given except for reasons of illness or other verified emergencies. The report will consist of a 6-8 page paper (1200-1600 words, 12 pt font, double spaced) on a topic of your choice from the Case Studies in Immunology book. To cl ...
Fingerprinting Disease
... to preventive medicine seem like too little, too late. The immune system can reveal so much because the cells that make it up are so diverse. A healthy human has millions of unique immune cells; many circulate in the blood and play major roles in the body’s response to foreign invaders. Each of thes ...
... to preventive medicine seem like too little, too late. The immune system can reveal so much because the cells that make it up are so diverse. A healthy human has millions of unique immune cells; many circulate in the blood and play major roles in the body’s response to foreign invaders. Each of thes ...
SKIN BIOLOGY - Ministry of Public Health
... • Cytokines are essential transmitters of intercellular communication • They have an inherent role in the regulation of responses of the immune system • Each cytokine has multiple functions • More than one cytokine may mediate the same, or very similar, function ...
... • Cytokines are essential transmitters of intercellular communication • They have an inherent role in the regulation of responses of the immune system • Each cytokine has multiple functions • More than one cytokine may mediate the same, or very similar, function ...
Cell organelles
... sacs. These flattened, hollow folds and sacs are called cisternae. The ER is located in the cytoplasm and is connected to the nuclear envelope. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum: smooth and rough ER. Smooth ER: does not have any ribosomes attached. It is involved in the synthesis of lipid ...
... sacs. These flattened, hollow folds and sacs are called cisternae. The ER is located in the cytoplasm and is connected to the nuclear envelope. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum: smooth and rough ER. Smooth ER: does not have any ribosomes attached. It is involved in the synthesis of lipid ...
LynchSpr15
... Mucins (shown in Fig. 1) are a class of heavily o-glycosylated proteins, most commonly found on epithelial surfaces, which provide many protective cellular functions such as the formation of mucosal barriers [1]. The range of human mucins (MUC) spreads from MUC1 to MUC21, however the specific mucin ...
... Mucins (shown in Fig. 1) are a class of heavily o-glycosylated proteins, most commonly found on epithelial surfaces, which provide many protective cellular functions such as the formation of mucosal barriers [1]. The range of human mucins (MUC) spreads from MUC1 to MUC21, however the specific mucin ...
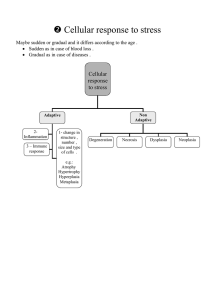
Cellular response to stress
... Compensatory : Enlargement of the remaining part of the kidney occurs after nephrectomy ...
... Compensatory : Enlargement of the remaining part of the kidney occurs after nephrectomy ...
ALPS - UMF IASI 2015
... transformation, increase in number (exponential) (cell division). • Clonal expansion: 7-8 days → specific lymphocytes can even become predominant. • *When responding to certain viruses, at the peak of the response, 50% or more of the T cell CD8+ are specific to a single MHC I – viral peptide complex ...
... transformation, increase in number (exponential) (cell division). • Clonal expansion: 7-8 days → specific lymphocytes can even become predominant. • *When responding to certain viruses, at the peak of the response, 50% or more of the T cell CD8+ are specific to a single MHC I – viral peptide complex ...
IL-1 family - Stanford Translational Medicine
... transducer of IL-6 triggering the activation of Akt and subsequently promoting survival in many cell types. • In addition to membrane-bound IL-6R, a soluble form of IL-6R (sIL-6Ra), which has been found in various human fluids, significantly enhances IL-6 tissue response by a process termed “trans-s ...
... transducer of IL-6 triggering the activation of Akt and subsequently promoting survival in many cell types. • In addition to membrane-bound IL-6R, a soluble form of IL-6R (sIL-6Ra), which has been found in various human fluids, significantly enhances IL-6 tissue response by a process termed “trans-s ...
Practice Questions 1: Cell Membrane
... 9. A single-celled organism is represented in the diagram below. An activity is indicated by the arrow. ...
... 9. A single-celled organism is represented in the diagram below. An activity is indicated by the arrow. ...
Document
... Colorectal cancer, also known as colon cancer, rectal cancer, or bowel cancer, is a cancer from uncontrolled cell growth in the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine), or in the appendix. The symptoms and signs of colorectal cancer depend on the location of tumor in the bowel, and whet ...
... Colorectal cancer, also known as colon cancer, rectal cancer, or bowel cancer, is a cancer from uncontrolled cell growth in the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine), or in the appendix. The symptoms and signs of colorectal cancer depend on the location of tumor in the bowel, and whet ...
Nonspecific Defenses of the Host - Cal State LA
... antibody defenses against microbial infection. They function to attack and destroy invading microorganisms and to help stimulate the inflammatory response. The proteins act in an ordered sequence or cascade of reactions. In an ordered sequence of steps, the proteins activate one another usually ...
... antibody defenses against microbial infection. They function to attack and destroy invading microorganisms and to help stimulate the inflammatory response. The proteins act in an ordered sequence or cascade of reactions. In an ordered sequence of steps, the proteins activate one another usually ...
Overview of your immune system
... 1) T cells have two types of receptor; one for antigen and the other for MHC. Both receptors must be occupied to get killing. 2) T cells have one type of receptor, which recognizes a complex between the MHC molecule and the antigen. 3) Both scenarios explain the data. 4) Neither scenario explains th ...
... 1) T cells have two types of receptor; one for antigen and the other for MHC. Both receptors must be occupied to get killing. 2) T cells have one type of receptor, which recognizes a complex between the MHC molecule and the antigen. 3) Both scenarios explain the data. 4) Neither scenario explains th ...
Inhibitors of Transitions & Biofilms Cause Yeast Cells to Lose Virulence ools
... Diseases caused by Candida albicans and other fungi are often major threats to human health, especially in patients with chronic illnesses and compromised immune systems. The fungi are highly adaptive organisms, able to survive by switching their own phenotypes. This strategy allows them to resist e ...
... Diseases caused by Candida albicans and other fungi are often major threats to human health, especially in patients with chronic illnesses and compromised immune systems. The fungi are highly adaptive organisms, able to survive by switching their own phenotypes. This strategy allows them to resist e ...
Active Transport, Endocytosis, and Exocytosis
... across the cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher ...
... across the cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher ...
CXCR3+CCR5+ T cells and autoimmune diseases
... phase, naive T cells differentiate into disease-associated effector and memory T cells. IFN-γ–producing Th1 cells generally express CCR5 and CXCR3, whereas Th17 cells express CCR6 and CXCR3 to some extent. Tfh cells, which facilitate B cell antibody production, express CXCR5. Following generation in ...
... phase, naive T cells differentiate into disease-associated effector and memory T cells. IFN-γ–producing Th1 cells generally express CCR5 and CXCR3, whereas Th17 cells express CCR6 and CXCR3 to some extent. Tfh cells, which facilitate B cell antibody production, express CXCR5. Following generation in ...
T cell Metabolism–Regulating Energy
... stimulation [24]. Additionally, AMPK was shown to be required for memory T cell differentiation. Addition of the drug metformin caused an sustained activation of AMPK and subsequently led to increased numbers of memory T cells. Recent studies showing that LKB1/AMPK influences assymetric cell divisio ...
... stimulation [24]. Additionally, AMPK was shown to be required for memory T cell differentiation. Addition of the drug metformin caused an sustained activation of AMPK and subsequently led to increased numbers of memory T cells. Recent studies showing that LKB1/AMPK influences assymetric cell divisio ...
03990.001.07.04 (16-5947-03FNL) CTLA4 Fact Sheet
... Immune system—A system of biological structures and processes within the body that protects it against “foreign” threats such as bacteria or viruses. Immunodeficiency—A state in which the immune system’s ability to fight disease is compromised or entirely absent. Immunoglobulin—Large Y-shaped protei ...
... Immune system—A system of biological structures and processes within the body that protects it against “foreign” threats such as bacteria or viruses. Immunodeficiency—A state in which the immune system’s ability to fight disease is compromised or entirely absent. Immunoglobulin—Large Y-shaped protei ...
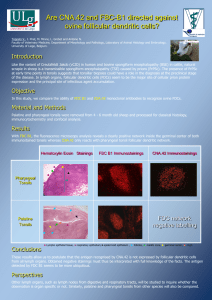
turin20064
... With FDC B1, the fluorescence microscopy analysis reveals a clearly positive network inside the germinal center of both immunostained tonsils whereas CNA.42 only reacts with pharyngeal tonsil follicular dendritic network. ...
... With FDC B1, the fluorescence microscopy analysis reveals a clearly positive network inside the germinal center of both immunostained tonsils whereas CNA.42 only reacts with pharyngeal tonsil follicular dendritic network. ...
JB Review Featured Article - Oxford Academic
... lipids, and other biomolecules. In lysosomes, these molecules are completely degraded into their building blocks, which are recycled for biosynthesis of macromolecules. An impairment in the lysosomes’ degradative function leads to the accumulation of undegraded molecules, which causes various types ...
... lipids, and other biomolecules. In lysosomes, these molecules are completely degraded into their building blocks, which are recycled for biosynthesis of macromolecules. An impairment in the lysosomes’ degradative function leads to the accumulation of undegraded molecules, which causes various types ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.