CHEM501- Introduction to Biochemistry – Exam 1 w
... It binds at a distance from the heme groups of hemoglobin. It binds with lower affinity to fetal hemoglobin than to adult hemoglobin. It increases the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen. It is an allosteric modulator. It is normally found associated with the hemoglobin extracted from red blood cells. ...
... It binds at a distance from the heme groups of hemoglobin. It binds with lower affinity to fetal hemoglobin than to adult hemoglobin. It increases the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen. It is an allosteric modulator. It is normally found associated with the hemoglobin extracted from red blood cells. ...
Biological Response Modifiers - International Journal of ChemTech
... the body that alter immune defenses to enhance, direct or restore the body’s ability to fight disease. The body naturally produces small amounts of these substances 1. Biological response modifiers used in biological therapy include interferons, interleukins, monoclonal antibodies, erythropoietin, t ...
... the body that alter immune defenses to enhance, direct or restore the body’s ability to fight disease. The body naturally produces small amounts of these substances 1. Biological response modifiers used in biological therapy include interferons, interleukins, monoclonal antibodies, erythropoietin, t ...
Bones can be described on the basis of their overall macroscopic
... B cells remain in bone marrow for maturation T cells leave bone marrow, and migrate to thymus gland for maturation Lymphocyte Activation All lymphocytes originate in bone marrow B lymphocytes remain in bone marrow for maturation T lymphocytes leave bone marrow, and migrate to thymus gland for matura ...
... B cells remain in bone marrow for maturation T cells leave bone marrow, and migrate to thymus gland for maturation Lymphocyte Activation All lymphocytes originate in bone marrow B lymphocytes remain in bone marrow for maturation T lymphocytes leave bone marrow, and migrate to thymus gland for matura ...
Immune response of bovines stimulated by synthetic vaccine
... studies in which T-dependant antigens were used, showing that after naı̈ve B-cell activation by the antigen, they migrate to primary lymphoid follicles to start the GC which generally happens between 4 and 8 days after immunization (Liu and Arpin, 1997; Tarlinton and Smith, 2000). At the same period ...
... studies in which T-dependant antigens were used, showing that after naı̈ve B-cell activation by the antigen, they migrate to primary lymphoid follicles to start the GC which generally happens between 4 and 8 days after immunization (Liu and Arpin, 1997; Tarlinton and Smith, 2000). At the same period ...
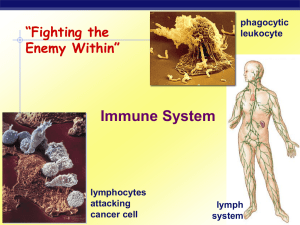
Lymphatic and Immune System
... Specific Immunity Haptens Smaller molecules that combine with larger ones to ignite an immune response IE… Penicillin and lipid toxin in poison ivy ...
... Specific Immunity Haptens Smaller molecules that combine with larger ones to ignite an immune response IE… Penicillin and lipid toxin in poison ivy ...
B1 Cell Structure and Transport
... I can apply knowledge of the function of food molecules in the body to give diet advice. ...
... I can apply knowledge of the function of food molecules in the body to give diet advice. ...
Information Packet
... POSSIBILITIES OF TRANSMEMBRANE PROGRAMMING, THE FREIBURG 2008 IGEM TEAM PROVIDES AN EXTENSIBLE SYSTEM COMPRISING AN EXTERNAL FRAMEWORK WITH SPATIAL RESOLUTION, A CONCEPT FOR MODIFYING NATURAL RECEPTORS, AND A MODULAR SET OF FUSION-BIOBRICKS FOR THE CONSTRUCTION OF SYNTHETIC RECEPTORS. SPATIAL RESOLU ...
... POSSIBILITIES OF TRANSMEMBRANE PROGRAMMING, THE FREIBURG 2008 IGEM TEAM PROVIDES AN EXTENSIBLE SYSTEM COMPRISING AN EXTERNAL FRAMEWORK WITH SPATIAL RESOLUTION, A CONCEPT FOR MODIFYING NATURAL RECEPTORS, AND A MODULAR SET OF FUSION-BIOBRICKS FOR THE CONSTRUCTION OF SYNTHETIC RECEPTORS. SPATIAL RESOLU ...
01-03-12 ALLERGY: • CORD BLOOD IMMUNE STATUS
... It is presently not possible to identify a marker that is predictive of a clinical response to allergen immunotherapy. Such a marker should be serum- or plasma-based, as it is not feasible to perform complex T cell-based assays in the context of multicenter clinical trials. Candidate markers are as ...
... It is presently not possible to identify a marker that is predictive of a clinical response to allergen immunotherapy. Such a marker should be serum- or plasma-based, as it is not feasible to perform complex T cell-based assays in the context of multicenter clinical trials. Candidate markers are as ...
Norepinephrine Inhibits Energy Metabolism of Human
... Evidence accumulated over the last two decades indicating that the autonomic nervous system influences the immune response by various pathways including activation and modulation of membrane adrenergic receptors on immunocompetent cells. However, data concerning the mechanisms of action and effects ...
... Evidence accumulated over the last two decades indicating that the autonomic nervous system influences the immune response by various pathways including activation and modulation of membrane adrenergic receptors on immunocompetent cells. However, data concerning the mechanisms of action and effects ...
Regents Biology - I Heart Science
... lots of organisms want you for lunch! we are a tasty vitamin-packed meal cells are packages of proteins, carbohydrates & fats ...
... lots of organisms want you for lunch! we are a tasty vitamin-packed meal cells are packages of proteins, carbohydrates & fats ...
Cell Cycle - Muncy School District
... During mitosis, the nucleus divides. One nucleus becomes two nuclei, each with an identical set of chromosomes. Mitosis is followed by cytokinesis, when the cytoplasm divides, resulting in two cells. After cytokinesis, cell division is complete. The one parent cell (the dividing cell) forms two gene ...
... During mitosis, the nucleus divides. One nucleus becomes two nuclei, each with an identical set of chromosomes. Mitosis is followed by cytokinesis, when the cytoplasm divides, resulting in two cells. After cytokinesis, cell division is complete. The one parent cell (the dividing cell) forms two gene ...
Connective tissue cells
... Ground substance: is a hydrated colorless and transparent, amorphous material, It is binding cells to the fibers of connective tissue. Ground substance is found in all cavities and clefts between the fibers and cells of connective tissues, but its main structural constituent is proteoglycans which c ...
... Ground substance: is a hydrated colorless and transparent, amorphous material, It is binding cells to the fibers of connective tissue. Ground substance is found in all cavities and clefts between the fibers and cells of connective tissues, but its main structural constituent is proteoglycans which c ...
A Naturally Healthy Immune System
... muscles and builds your natural defenses against illness and foreign invaders. We all know sleep is important. Not only can a lack of sleep affect your ability to think and reason, but recent studies have also shown that sleep deprivation can actually lower our t-cells and increase inflammatory cyto ...
... muscles and builds your natural defenses against illness and foreign invaders. We all know sleep is important. Not only can a lack of sleep affect your ability to think and reason, but recent studies have also shown that sleep deprivation can actually lower our t-cells and increase inflammatory cyto ...
Non-Specific Defense
... • Its response depends upon the ability of its cells to: – Recognize foreign substances (antigens) by binding to them – Communicate with one another so that the whole system mounts a response specific to those antigens ...
... • Its response depends upon the ability of its cells to: – Recognize foreign substances (antigens) by binding to them – Communicate with one another so that the whole system mounts a response specific to those antigens ...
Biology - H Hungary is already a member of EU system so you can
... A solute diffuses across a membrane from a region with a greater concentration of that solute to a region with a lesser concentration of that solute. Equilibrium is reached when the concentrations of the solute are identical on both sides of the membrane. The rate of simple diffusion of a solute acr ...
... A solute diffuses across a membrane from a region with a greater concentration of that solute to a region with a lesser concentration of that solute. Equilibrium is reached when the concentrations of the solute are identical on both sides of the membrane. The rate of simple diffusion of a solute acr ...
Cancers of the Immune System
... Immunodeficiencies can affect B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes, or phagocytes. The most common immunodeficiency disorder is IgA deficiency, in which the body doesn't produce enough of the antibody IgA, an immunoglobulin found primarily in the saliva and other body fluids that help guard the entrances to ...
... Immunodeficiencies can affect B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes, or phagocytes. The most common immunodeficiency disorder is IgA deficiency, in which the body doesn't produce enough of the antibody IgA, an immunoglobulin found primarily in the saliva and other body fluids that help guard the entrances to ...
Cell Biology Lecture Notes
... All reactions that occur spontaneously result in a decrease in the free energy content of the system In the cells: 1) Some reactions are thermodynamic feasible but do not occur at appreciable rates 2) The only reactions that occur at appreciable rates are those from which an enzyme is present 3) All ...
... All reactions that occur spontaneously result in a decrease in the free energy content of the system In the cells: 1) Some reactions are thermodynamic feasible but do not occur at appreciable rates 2) The only reactions that occur at appreciable rates are those from which an enzyme is present 3) All ...
06-Understanding Stress and Disease
... – Caused by the HIV virus • Human Immunodeficiency Virus • Destroys the T-cells in the immune system ...
... – Caused by the HIV virus • Human Immunodeficiency Virus • Destroys the T-cells in the immune system ...
Chapter 19
... ▫Presence or absence of the Rh (or D) factor gives the blood types a (+) or (–) ▫Blood plasma has antibodies that attack the antigens on foreign RBC’s -Type A blood has anti-B antibodies -Type B blood has anti-A antibodies -Type AB blood has no anti-A or anti-B antibodies -Type O blood has both anti ...
... ▫Presence or absence of the Rh (or D) factor gives the blood types a (+) or (–) ▫Blood plasma has antibodies that attack the antigens on foreign RBC’s -Type A blood has anti-B antibodies -Type B blood has anti-A antibodies -Type AB blood has no anti-A or anti-B antibodies -Type O blood has both anti ...
06-Understanding Stress and Disease
... • HIV destroys immune system - AIDS vulnerable to bacterial, viral, and other diseases ...
... • HIV destroys immune system - AIDS vulnerable to bacterial, viral, and other diseases ...
1986 Hohenboken et al.: Inheritance of active and passive humoral
... by other specialised white blood cells, of antibodies specific to the antigen in question. This aspect of their function will be discussed in conjunction with humoral immunity. Neutrophils and macrophages are important phagocytic cell types in ruminants. Cell Mediated Immunity Some pathogenic organi ...
... by other specialised white blood cells, of antibodies specific to the antigen in question. This aspect of their function will be discussed in conjunction with humoral immunity. Neutrophils and macrophages are important phagocytic cell types in ruminants. Cell Mediated Immunity Some pathogenic organi ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.