Powerpoints - Holy Cross Collegiate
... reactant reacts to make product on the ratio described by the balanced equation. • The quantity of product actually obtained by a reaction is called the experimental yield (which is also known as the actual yield). • In most reactions, the experimental yield will not match exactly with the predicted ...
... reactant reacts to make product on the ratio described by the balanced equation. • The quantity of product actually obtained by a reaction is called the experimental yield (which is also known as the actual yield). • In most reactions, the experimental yield will not match exactly with the predicted ...
practice test2
... A) The temperature of steam cannot exceed 100°C. B) The temperature of ice remains at 0°C as it melts. C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 100°C as it boils E) Both liquid water and ice are present at 0°C. ...
... A) The temperature of steam cannot exceed 100°C. B) The temperature of ice remains at 0°C as it melts. C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 100°C as it boils E) Both liquid water and ice are present at 0°C. ...
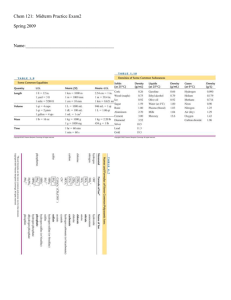
CHE 145-381 – TEST #2 SPRING 2009 CHAPTERS 6, 7, 8 NAME
... You may use the Periodic Table. Please note that all quantities needed for the successful completion of this test have been given. Feel free to ask questions for clarification. 1. Indicate to which of the following types of chemical reactions each of the statements listed applies: synthesis, decompo ...
... You may use the Periodic Table. Please note that all quantities needed for the successful completion of this test have been given. Feel free to ask questions for clarification. 1. Indicate to which of the following types of chemical reactions each of the statements listed applies: synthesis, decompo ...
Time
... -calculate rate of reactions using: r = Δc/Δt - explain the factors which effect reaction rates; predicting rate of reactions - concentration vs time graphs – instantaneous rate of reaction - use activation energy diagrams and kinetic energy diagrams to show effect of temperature and catalysts on re ...
... -calculate rate of reactions using: r = Δc/Δt - explain the factors which effect reaction rates; predicting rate of reactions - concentration vs time graphs – instantaneous rate of reaction - use activation energy diagrams and kinetic energy diagrams to show effect of temperature and catalysts on re ...
ch8 - Otterville R-VI School District
... BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) NaCl(aq) + BaSO4(s) iron sulfide and hydrochloric acid FeS(aq) + HCl(aq) FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide HCl(aq) + NaOH NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) potassium iodide and lead (II) nitrate KI(aq) + Pb(NO3)2 KNO3(aq) + PbI2(s) ...
... BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) NaCl(aq) + BaSO4(s) iron sulfide and hydrochloric acid FeS(aq) + HCl(aq) FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide HCl(aq) + NaOH NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) potassium iodide and lead (II) nitrate KI(aq) + Pb(NO3)2 KNO3(aq) + PbI2(s) ...
Chapter 1
... *Notes-The Law of Conservation of Mass dictates that chemical equations must be balanced because atoms are never _____lost__or _____gained__in a chemical reaction. ...
... *Notes-The Law of Conservation of Mass dictates that chemical equations must be balanced because atoms are never _____lost__or _____gained__in a chemical reaction. ...
Stoichiometry …like a beautiful sunset on a serene lake – NOT!
... • CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O • In a chemical reaction, atoms have been rearranged but have NOT been created or destroyed. This is why we have to balance every chemical reaction/equation. Java-Balancing! • Balance CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O • Balance HCl + NaHCO3 → CO2 + H2O + NaCl • When balancing equations, t ...
... • CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O • In a chemical reaction, atoms have been rearranged but have NOT been created or destroyed. This is why we have to balance every chemical reaction/equation. Java-Balancing! • Balance CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O • Balance HCl + NaHCO3 → CO2 + H2O + NaCl • When balancing equations, t ...
Writing And Balancing Equations
... On the left, Zn and HCl are reactants On the right, ZnCl2 and H2 are products The arrow () means “yields” The up arrow () indicated a gas product The 2 in front of HCl is a coefficient The small 2 to the right of H is a subscript ...
... On the left, Zn and HCl are reactants On the right, ZnCl2 and H2 are products The arrow () means “yields” The up arrow () indicated a gas product The 2 in front of HCl is a coefficient The small 2 to the right of H is a subscript ...
Chemical Reactions
... equation should be balanced as independent units (don’t break them down into individual elements) ...
... equation should be balanced as independent units (don’t break them down into individual elements) ...
chp0-Intro
... Gas-phase reactions with large AE are slow Radical reactions are exothermic and occur faster ...
... Gas-phase reactions with large AE are slow Radical reactions are exothermic and occur faster ...
Nuclear Astrophysics (1)
... the observing time. Then the following relation holds between the chemical potentials. ...
... the observing time. Then the following relation holds between the chemical potentials. ...
Question paper - Edexcel
... Use this space for any rough working. Anything you write in this space will gain no credit. ...
... Use this space for any rough working. Anything you write in this space will gain no credit. ...
CST REVIEW Percent Error 1. 2. What is the formula for density?
... 161. If the volume of the container that is holding the reactants is reduced, how will that affect the rate of the reaction? Explain. 162. What is activation energy? 163. What happens if reactant molecules do not have enough energy when they collide? 164. What does a catalyst do? 165. How does a cat ...
... 161. If the volume of the container that is holding the reactants is reduced, how will that affect the rate of the reaction? Explain. 162. What is activation energy? 163. What happens if reactant molecules do not have enough energy when they collide? 164. What does a catalyst do? 165. How does a cat ...
Study Guide for Test 2: Chapters 3 & 4... This is NOT a complete list of what will be... Revised March 4, 2014
... 23) Use Molarity and mole ratios in calculations with balanced reactions. 24) Know solubility rules. Identify a compound as soluble or insoluble. 25) Be able to identify, predict, and write precipitation reactions. 26) Be able to write complete Ionic equations, net ionic equations, and identify spec ...
... 23) Use Molarity and mole ratios in calculations with balanced reactions. 24) Know solubility rules. Identify a compound as soluble or insoluble. 25) Be able to identify, predict, and write precipitation reactions. 26) Be able to write complete Ionic equations, net ionic equations, and identify spec ...
Dr. Baxley`s Equilibrium Worksheet
... 12. At 450°C, ammonia gas will decompose according to the following equation: 2 NH3 (g) ⇌ N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) At 450.˚C, Kc = 6.30. An unknown quantity of NH3 is placed in a reaction flask (with no N2 or H2) and is allowed to come to equilibrium at 450. °C. The equilibrium concentration of H2 is then ...
... 12. At 450°C, ammonia gas will decompose according to the following equation: 2 NH3 (g) ⇌ N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) At 450.˚C, Kc = 6.30. An unknown quantity of NH3 is placed in a reaction flask (with no N2 or H2) and is allowed to come to equilibrium at 450. °C. The equilibrium concentration of H2 is then ...
AP Chem
... A. Determine the order of the reaction with respect to each reactant listed below. Show your work. (i) I(ii) ClOB. For the reaction, (i) Write the rate law that is consistent with the calculations in part (a); (ii) Calculate the value of the specific rate constant, k, and specify units. The catalyze ...
... A. Determine the order of the reaction with respect to each reactant listed below. Show your work. (i) I(ii) ClOB. For the reaction, (i) Write the rate law that is consistent with the calculations in part (a); (ii) Calculate the value of the specific rate constant, k, and specify units. The catalyze ...