Functions of the Immune System
... of being exposed to the hormone thymosin, which is secreted by the (?) • Kill the infected cells on contact – Produce interferon, which are proteins that fight viruses by slowing or stopping their multiplication memory Jogger: interferon interferes with viral ...
... of being exposed to the hormone thymosin, which is secreted by the (?) • Kill the infected cells on contact – Produce interferon, which are proteins that fight viruses by slowing or stopping their multiplication memory Jogger: interferon interferes with viral ...
What is the immune system?
... then your white blood cells (WBCs) begin their attack - WBCs normally ...
... then your white blood cells (WBCs) begin their attack - WBCs normally ...
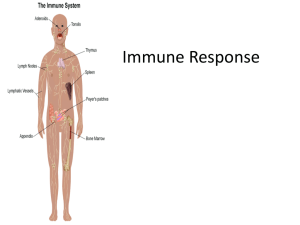
Immune Response
... • Immunology- the study of host defense mechanisms • Immunity- ability of the host to protect itself against foreign organisms. Resistance to disease. • Antigen (Ag)- is a foreign substance that can elicit specific immune response (IR) when is immunogenic • Antibody (Ab)- protein produced by the bod ...
... • Immunology- the study of host defense mechanisms • Immunity- ability of the host to protect itself against foreign organisms. Resistance to disease. • Antigen (Ag)- is a foreign substance that can elicit specific immune response (IR) when is immunogenic • Antibody (Ab)- protein produced by the bod ...
lec #1 done by Leen AbdelFattah / Slides #1
... B cells in the bone marrow move to other lymphatic organs during its maturation , it express different receptors on its surface at different stages, to specify its location we depend on the surface receptors ,BCR: B cell receptor, which are the immunoglobins on its surface. BCR could be IgM or IgD F ...
... B cells in the bone marrow move to other lymphatic organs during its maturation , it express different receptors on its surface at different stages, to specify its location we depend on the surface receptors ,BCR: B cell receptor, which are the immunoglobins on its surface. BCR could be IgM or IgD F ...
Immunology 3 – Innate Immunity
... 5. Briefly outline the events involved in a systemic acute phase response. This is a reaction that may accompany inflammation and may consist of fevers, increased leukocytosis, and production of “acute phase” proteins from the liver. These include: • C-reactive protein (CRP) – C polysaccharide of p ...
... 5. Briefly outline the events involved in a systemic acute phase response. This is a reaction that may accompany inflammation and may consist of fevers, increased leukocytosis, and production of “acute phase” proteins from the liver. These include: • C-reactive protein (CRP) – C polysaccharide of p ...
Regulatory T
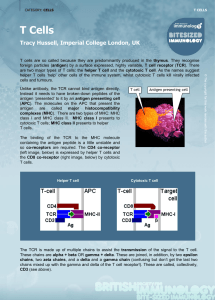
... Unlike antibody, the TCR cannot bind antigen directly. Instead it needs to have broken-down peptides of the antigen ‘presented’ to it by an antigen presenting cell (APC). The molecules on the APC that present the antigen are called major histocompatibility complexes (MHC). There are two types of MHC ...
... Unlike antibody, the TCR cannot bind antigen directly. Instead it needs to have broken-down peptides of the antigen ‘presented’ to it by an antigen presenting cell (APC). The molecules on the APC that present the antigen are called major histocompatibility complexes (MHC). There are two types of MHC ...
ONE TARGET: INFINITE HOPETM MEDICENNA BY THE NUMBERS
... Medicenna is developing a novel class of multi-targeted fusion proteins, called IL4-ECs. These proprietary, first-in-class targeted “molecular Trojan Horses” selectively and simultaneously deliver cell-killing payloads to the bulk tumor, TME and CSCs. Medicenna’s IL4-ECs have the potential to not on ...
... Medicenna is developing a novel class of multi-targeted fusion proteins, called IL4-ECs. These proprietary, first-in-class targeted “molecular Trojan Horses” selectively and simultaneously deliver cell-killing payloads to the bulk tumor, TME and CSCs. Medicenna’s IL4-ECs have the potential to not on ...
1) if the response to an antigen
... of soluble antibodies in the body fluids, it is called: Humoral immunity. 2) if the response is through cytotoxic or killer T cells, then the immunity is known as cell-mediated. These two mechanisms complement each other. The challenge for the immune system is to be able to provide antibodies to int ...
... of soluble antibodies in the body fluids, it is called: Humoral immunity. 2) if the response is through cytotoxic or killer T cells, then the immunity is known as cell-mediated. These two mechanisms complement each other. The challenge for the immune system is to be able to provide antibodies to int ...
Immunity and Immune Response
... – Each produces a different receptor in the cell membrane – Each receptor is composed of 1 molecule each of two different proteins – Each receptor binds a specific antigen but has only one binding site – Receptor only recognizes antigens which are "presented" to it within another membrane protein of ...
... – Each produces a different receptor in the cell membrane – Each receptor is composed of 1 molecule each of two different proteins – Each receptor binds a specific antigen but has only one binding site – Receptor only recognizes antigens which are "presented" to it within another membrane protein of ...
Chapter 14 Lymphatic System Student outline
... b. An activated B-cell proliferates when stimulated by a T-cell, enlarging its clone c. Some activated B-cells specialize into antibody producing plasma cells d. Antibodies react against the antigen-bearing agent 6. Types of antibodies-these are soluble proteins called ______________. a. The five ma ...
... b. An activated B-cell proliferates when stimulated by a T-cell, enlarging its clone c. Some activated B-cells specialize into antibody producing plasma cells d. Antibodies react against the antigen-bearing agent 6. Types of antibodies-these are soluble proteins called ______________. a. The five ma ...
Topic 19 - Roslyn Public Schools
... II. Active and Passive Immunity • A. active immunity – occurs when the body makes its own antibodies against a particular antigen – can occur as a result of having a particular disease and recovering from it or from getting a vaccination for a particular disease – 1. vaccines – an injection of a we ...
... II. Active and Passive Immunity • A. active immunity – occurs when the body makes its own antibodies against a particular antigen – can occur as a result of having a particular disease and recovering from it or from getting a vaccination for a particular disease – 1. vaccines – an injection of a we ...
The Immune Response
... Have specific antigenic receptors on their surface T helper cell Also have specific receptors on their surfaces which bind to specific antigen parts on the surface of the macrophage Produces chemical that stimulates the B cells to divide repeatedly Dividing B cells produce Many plasma cells Memory B ...
... Have specific antigenic receptors on their surface T helper cell Also have specific receptors on their surfaces which bind to specific antigen parts on the surface of the macrophage Produces chemical that stimulates the B cells to divide repeatedly Dividing B cells produce Many plasma cells Memory B ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... II. State whether the following are true or false; if false give reason: (5 x 1= 5 marks) (6) Monocytes are agranulocytes. (7) An individual can inherit a maximum of 12 different MHC II molecules. (8) Autoantibodies to intrinsic factor will lead to Goodpasture’s syndrome. (9) Monoclonal antibodies a ...
... II. State whether the following are true or false; if false give reason: (5 x 1= 5 marks) (6) Monocytes are agranulocytes. (7) An individual can inherit a maximum of 12 different MHC II molecules. (8) Autoantibodies to intrinsic factor will lead to Goodpasture’s syndrome. (9) Monoclonal antibodies a ...
8_23_cancer
... • It is possible that there is some level of immune response initiated against a nascent tumor clone - as the progeny of the original tumor cells accumulate further mutations, some rare cells evolve the ability to evade host immune responses. • Some tumor cells have been seen to have lost expressi ...
... • It is possible that there is some level of immune response initiated against a nascent tumor clone - as the progeny of the original tumor cells accumulate further mutations, some rare cells evolve the ability to evade host immune responses. • Some tumor cells have been seen to have lost expressi ...
Jurkat-TIM3 Cell Line
... Cell surface receptor implicated in modulating innate and adaptive immune responses. Generally accepted to have an inhibiting function. Expressed in T-helper type 1 (Th1) lymphocytes. Expressed on regulatory T (Treg) cells after TCR stimulation. Expressed in dendritic cells and natural killer (NK) c ...
... Cell surface receptor implicated in modulating innate and adaptive immune responses. Generally accepted to have an inhibiting function. Expressed in T-helper type 1 (Th1) lymphocytes. Expressed on regulatory T (Treg) cells after TCR stimulation. Expressed in dendritic cells and natural killer (NK) c ...
Immune System Summmary
... One other type of non-specific cell that should be mentioned is the NK or Natural Killer cell. These cells patrol the body looking for cells that are cancerous or virus infected. They attack the cell membranes of infected cells, releasing chemicals called perforins that “punch” holes in the infected ...
... One other type of non-specific cell that should be mentioned is the NK or Natural Killer cell. These cells patrol the body looking for cells that are cancerous or virus infected. They attack the cell membranes of infected cells, releasing chemicals called perforins that “punch” holes in the infected ...
Defense Systems
... plasma cells secrete antibodies which attach to foreign particle marking them for destruction memory cells lie dormant until the next attack 3. Antigens are particles which can stimulate receptors on lymphocytes only part of the foreign invader is antigenic 4. Antibodies are proteins produced ...
... plasma cells secrete antibodies which attach to foreign particle marking them for destruction memory cells lie dormant until the next attack 3. Antigens are particles which can stimulate receptors on lymphocytes only part of the foreign invader is antigenic 4. Antibodies are proteins produced ...
Chapter 43 Power Point notes
... Help deliver antimicrobial proteins and clotting elements to the injured site ...
... Help deliver antimicrobial proteins and clotting elements to the injured site ...
1-overview
... How do immune cells communicate? Extensive cell-cell contact Membrane protein interaction Immune synapse ...
... How do immune cells communicate? Extensive cell-cell contact Membrane protein interaction Immune synapse ...
Human Body Systems
... Pathogens, cancer cells, or foreign cells have protein markers on surface (antigens) that activate the immune system because foreign to body Types of White Blood Cells - all made in the bone marrow - All called in after the non-specific WBCs B lymphocyte cells (mature in bone marrow) ...
... Pathogens, cancer cells, or foreign cells have protein markers on surface (antigens) that activate the immune system because foreign to body Types of White Blood Cells - all made in the bone marrow - All called in after the non-specific WBCs B lymphocyte cells (mature in bone marrow) ...
Cancer immunotherapy

Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncology) is the use of the immune system to treat cancer. Immunotherapies fall into three main groups: cellular, antibody and cytokine. They exploit the fact that cancer cells often have subtly different molecules on their surface that can be detected by the immune system. These molecules, known as cancer antigens, are most commonly proteins, but also include molecules such as carbohydrates. Immunotherapy is used to provoke the immune system into attacking the tumor cells by using these antigens as targets.Antibody therapies are the most successful immunotherapy, treating a wide range of cancers. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that bind to a target antigen on the cell surface. In normal physiology the immune system uses them to fight pathogens. Each antibody is specific to one or a few proteins. Those that bind to cancer antigens are used to treat cancer. Cell surface receptors are common targets for antibody therapies and include the CD20, CD274, and CD279. Once bound to a cancer antigen, antibodies can induce antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, activate the complement system, or prevent a receptor from interacting with its ligand, all of which can lead to cell death. Multiple antibodies are approved to treat cancer, including Alemtuzumab, Ipilimumab, Nivolumab, Ofatumumab, and Rituximab.Cellular therapies, also known as cancer vaccines, usually involve the removal of immune cells from the blood or from a tumor. Immune cells specific for the tumor are activated, cultured and returned to the patient where the immune cells attack the cancer. Cell types that can be used in this way are natural killer cells, lymphokine-activated killer cells, cytotoxic T cells and dendritic cells. The only cell-based therapy approved in the US is Dendreon's Provenge, for the treatment of prostate cancer.Interleukin-2 and interferon-α are examples of cytokines, proteins that regulate and coordinate the behaviour of the immune system. They have the ability to enhance anti-tumor activity and thus can be used as cancer treatments. Interferon-α is used in the treatment of hairy-cell leukaemia, AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, follicular lymphoma, chronic myeloid leukaemia and malignant melanoma. Interleukin-2 is used in the treatment of malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.