Concept of oncolytic virotherapy- clinical implementation
... Talimogene laherparepvec is an investigational oncolytic immunotherapy designed to selectively replicate in tumor tissue and to initiate a systemic anti-tumor immune response. Talimogene laherparepvec is injected directly into tumor tissue and is intended to replicate preferentially in tumor cells c ...
... Talimogene laherparepvec is an investigational oncolytic immunotherapy designed to selectively replicate in tumor tissue and to initiate a systemic anti-tumor immune response. Talimogene laherparepvec is injected directly into tumor tissue and is intended to replicate preferentially in tumor cells c ...
An insatiable curiosity, combined with meticulous
... Mercedes Rincon, Ph.D., so good at what she does. Her laboratory investigations pinpoint the cellular activity that plays a role in immune system response, and have led to the identification of potential therapy targets for such diseases as flu infection, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis and breast canc ...
... Mercedes Rincon, Ph.D., so good at what she does. Her laboratory investigations pinpoint the cellular activity that plays a role in immune system response, and have led to the identification of potential therapy targets for such diseases as flu infection, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis and breast canc ...
APO-4: Microbes and you: who will win the war
... _____ Antigen breakdown products bind major histocompatibility complexprotein and are "displayed" on B cell surface. _____ T cell secretes cytokines which stimulate B cell. _____ Antigen-antibody complex is internalized and processed. _____ Helper T cell binds antigen via its T-cell receptor. _____ ...
... _____ Antigen breakdown products bind major histocompatibility complexprotein and are "displayed" on B cell surface. _____ T cell secretes cytokines which stimulate B cell. _____ Antigen-antibody complex is internalized and processed. _____ Helper T cell binds antigen via its T-cell receptor. _____ ...
How can your immune system malfunction?
... What happens during an Allergic reaction? • The allergen will bind to receptors on WBC’s stimulating the production of histamines. • Histamines are chemical that call trigger an inflammatory response • May experience wheezing, hives, nausea, or shock • What can we take for ANTIHISTAMINES! allergies ...
... What happens during an Allergic reaction? • The allergen will bind to receptors on WBC’s stimulating the production of histamines. • Histamines are chemical that call trigger an inflammatory response • May experience wheezing, hives, nausea, or shock • What can we take for ANTIHISTAMINES! allergies ...
Tumor immunity
... Cell-mediated reactions attack these nonself tumor cells and limit their proliferation. Such immune responses probably act as a surveillance system to detect and eliminate newly arising clones of neoplastic cells. In general, the immune response against tumor cells is weak and can be overcome experi ...
... Cell-mediated reactions attack these nonself tumor cells and limit their proliferation. Such immune responses probably act as a surveillance system to detect and eliminate newly arising clones of neoplastic cells. In general, the immune response against tumor cells is weak and can be overcome experi ...
CELLS& ORGANS OF IMMUNE MECHANISM.
... of virtually all nucleated cells. • The complete class 1 protein is highly polymorphic. • The polymorphism of these molecules is important in the recognition of self and nonself. ...
... of virtually all nucleated cells. • The complete class 1 protein is highly polymorphic. • The polymorphism of these molecules is important in the recognition of self and nonself. ...
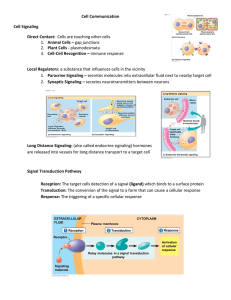
Cell Communication Cell Signaling Direct Contact: Cells are
... Ex. Steroid hormones Transduction: Relay signals from receptors to cellular responses. This is usually done by protein kinases (an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein) and includes the use of secondary ...
... Ex. Steroid hormones Transduction: Relay signals from receptors to cellular responses. This is usually done by protein kinases (an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein) and includes the use of secondary ...
immune response
... partially or completely Present some of the organism antigens on its surface ...
... partially or completely Present some of the organism antigens on its surface ...
Researchers Learn How to Turn Cancer Cells into
... arginine to either produce nitric oxide (reactive killer molecule) or ornithine (involved in repairing tissues) 2. Stimulating antibody production through antigen presentation on their cell surfaces 3. Production of cytokines to regulate the behavior of other cells as a result of the immune response ...
... arginine to either produce nitric oxide (reactive killer molecule) or ornithine (involved in repairing tissues) 2. Stimulating antibody production through antigen presentation on their cell surfaces 3. Production of cytokines to regulate the behavior of other cells as a result of the immune response ...
Genetically Engineered Multivalent Proteins for Targeted
... In this issue of Clinical Cancer Research, Vallera and colleagues (1) report the generation of a trispecific killer engager (TriKE) that incorporates single-chain variable fragments (scFV) against CD16 and CD33. This engineered protein crosslinks natural killer (NK) and myeloid tumor cells while also ...
... In this issue of Clinical Cancer Research, Vallera and colleagues (1) report the generation of a trispecific killer engager (TriKE) that incorporates single-chain variable fragments (scFV) against CD16 and CD33. This engineered protein crosslinks natural killer (NK) and myeloid tumor cells while also ...
Immune System - Dr. Annette M. Parrott
... infected and adjacent cells, thus localizing the effects. – Vertebrate immune systems have nonspecific and nonheritable defense mechanisms against pathogens. ...
... infected and adjacent cells, thus localizing the effects. – Vertebrate immune systems have nonspecific and nonheritable defense mechanisms against pathogens. ...
immune_system_lecture
... leucocytes with receptors for specific antigens Lymph nodes – pathogens are identified: ...
... leucocytes with receptors for specific antigens Lymph nodes – pathogens are identified: ...
Studying the Effects of Congaplex® and
... and then exposed to a substance that would provoke an immune response (antigen). The researchers then measured immune activity via the production of cytokines, proteins that regulate the action of the immune system. These chemicals are released by T cells and have a variety of different tasks. Some, ...
... and then exposed to a substance that would provoke an immune response (antigen). The researchers then measured immune activity via the production of cytokines, proteins that regulate the action of the immune system. These chemicals are released by T cells and have a variety of different tasks. Some, ...
Immunology-Uveitis
... Introduction of foreign antigens into the anterior chamber, subretinal space And vitreous cavity induces systemic tolerance to these antigens Mediated by the generation of Tregulatory cells ...
... Introduction of foreign antigens into the anterior chamber, subretinal space And vitreous cavity induces systemic tolerance to these antigens Mediated by the generation of Tregulatory cells ...
Slide - Smith Lab
... Introduction of foreign antigens into the anterior chamber, subretinal space And vitreous cavity induces systemic tolerance to these antigens Mediated by the generation of Tregulatory cells ...
... Introduction of foreign antigens into the anterior chamber, subretinal space And vitreous cavity induces systemic tolerance to these antigens Mediated by the generation of Tregulatory cells ...
General Defence System
... are called antibodies. The pathogen is identified as its surface has a chemical that is ‘foreign’ – to the body it is a ‘non-self’ chemical. This non-self chemical is called an antigen. White blood cells called lymphocytes produce antibodies to destroy cells or tissues that have these antigens. Indu ...
... are called antibodies. The pathogen is identified as its surface has a chemical that is ‘foreign’ – to the body it is a ‘non-self’ chemical. This non-self chemical is called an antigen. White blood cells called lymphocytes produce antibodies to destroy cells or tissues that have these antigens. Indu ...
Immunity
... any injurious stress is called immune system Te stress may be intrinsic (inside of the body) or extrinsic (out side of the body) Antigen: is any substance that elicits an immune response, from a virus to a sliver. Antibody: Proteins secreted by the Lymphocytes in response to antigen ...
... any injurious stress is called immune system Te stress may be intrinsic (inside of the body) or extrinsic (out side of the body) Antigen: is any substance that elicits an immune response, from a virus to a sliver. Antibody: Proteins secreted by the Lymphocytes in response to antigen ...
Chapter 24: The Immune System
... pathogens/foreign molecules nonspecifically – Phagocytes may be aided by opsonins (Usually an Ab) – NK cells use antiviral interferons ...
... pathogens/foreign molecules nonspecifically – Phagocytes may be aided by opsonins (Usually an Ab) – NK cells use antiviral interferons ...
immune system - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... Inflammation is the immune system’s response to infection. The release of chemical signals (cytokines and histamine) attracts phagocytes and other cells of the immune system to an infection site. Cytokines induce fever which stimulates immune response and reduces the growth rate of many pathogens. ...
... Inflammation is the immune system’s response to infection. The release of chemical signals (cytokines and histamine) attracts phagocytes and other cells of the immune system to an infection site. Cytokines induce fever which stimulates immune response and reduces the growth rate of many pathogens. ...
Cancer immunotherapy

Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncology) is the use of the immune system to treat cancer. Immunotherapies fall into three main groups: cellular, antibody and cytokine. They exploit the fact that cancer cells often have subtly different molecules on their surface that can be detected by the immune system. These molecules, known as cancer antigens, are most commonly proteins, but also include molecules such as carbohydrates. Immunotherapy is used to provoke the immune system into attacking the tumor cells by using these antigens as targets.Antibody therapies are the most successful immunotherapy, treating a wide range of cancers. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that bind to a target antigen on the cell surface. In normal physiology the immune system uses them to fight pathogens. Each antibody is specific to one or a few proteins. Those that bind to cancer antigens are used to treat cancer. Cell surface receptors are common targets for antibody therapies and include the CD20, CD274, and CD279. Once bound to a cancer antigen, antibodies can induce antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, activate the complement system, or prevent a receptor from interacting with its ligand, all of which can lead to cell death. Multiple antibodies are approved to treat cancer, including Alemtuzumab, Ipilimumab, Nivolumab, Ofatumumab, and Rituximab.Cellular therapies, also known as cancer vaccines, usually involve the removal of immune cells from the blood or from a tumor. Immune cells specific for the tumor are activated, cultured and returned to the patient where the immune cells attack the cancer. Cell types that can be used in this way are natural killer cells, lymphokine-activated killer cells, cytotoxic T cells and dendritic cells. The only cell-based therapy approved in the US is Dendreon's Provenge, for the treatment of prostate cancer.Interleukin-2 and interferon-α are examples of cytokines, proteins that regulate and coordinate the behaviour of the immune system. They have the ability to enhance anti-tumor activity and thus can be used as cancer treatments. Interferon-α is used in the treatment of hairy-cell leukaemia, AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, follicular lymphoma, chronic myeloid leukaemia and malignant melanoma. Interleukin-2 is used in the treatment of malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.