
BSc/Diploma in Medical Laboratory Technology 3 BLT301
... function as T helper cells, whereas those that have CD8 glycoproteins function as T cytotoxic cells. • T cells can attack (1) host cells that have been parasitized by viruses or microorganisms, (2) tissue cells that have been transplanted from one host to another, and (3) cancer cells. Since T cells ...
... function as T helper cells, whereas those that have CD8 glycoproteins function as T cytotoxic cells. • T cells can attack (1) host cells that have been parasitized by viruses or microorganisms, (2) tissue cells that have been transplanted from one host to another, and (3) cancer cells. Since T cells ...
Immunopathology Type III: Immune Complex Disease
... have one of these conditions. If you add hypersensitivity (allergies) it could be as many as 25% of the population. As with all of disease, immunopathology depends upon three factors: ►genetics, environment, and bad luck. In 1963 Gell and Coombs tried to make sense of immunological diseases by group ...
... have one of these conditions. If you add hypersensitivity (allergies) it could be as many as 25% of the population. As with all of disease, immunopathology depends upon three factors: ►genetics, environment, and bad luck. In 1963 Gell and Coombs tried to make sense of immunological diseases by group ...
allergies - West Campus | Pima Community College, Tucson
... The organs involved with the immune system are the lymphoid organs, which affect growth, development, and the release of lymphocytes. The blood vessels and lymphatic vessels are important parts of the lymphoid organs, because they carry the lymphocytes to and from different areas in the body Each ly ...
... The organs involved with the immune system are the lymphoid organs, which affect growth, development, and the release of lymphocytes. The blood vessels and lymphatic vessels are important parts of the lymphoid organs, because they carry the lymphocytes to and from different areas in the body Each ly ...
Flea Infestations: Turn On the Light Vaccine
... mutations to help the immune system more effectively eradicate cancer cells. Based on the small sample size, there seemed to be clinical benefit when treating soft tissue sarcomas. However, most of the dogs also were treated initially with surgery, but details regarding the completeness of excision ...
... mutations to help the immune system more effectively eradicate cancer cells. Based on the small sample size, there seemed to be clinical benefit when treating soft tissue sarcomas. However, most of the dogs also were treated initially with surgery, but details regarding the completeness of excision ...
Mr. B: Health 2 Chapter 23 Lesson 3 Notes Today`s Objectives
... The lymphatic system is part of your immune system. It includes your ________________, lymph nodes, and a network of vessels, similar to blood vessels, that transport lymph, or tissue fluid. ...
... The lymphatic system is part of your immune system. It includes your ________________, lymph nodes, and a network of vessels, similar to blood vessels, that transport lymph, or tissue fluid. ...
Lymphatic System - bushelman-hap
... - T cell development: cells migrate from bone marrow and differentiate into T cells - The stroma of the thymus consists of star-shaped epithelial cells (not reticular fibers) - These star-shaped thymocytes secrete hormones that stimulate lymphocytes to become immunocompetent ...
... - T cell development: cells migrate from bone marrow and differentiate into T cells - The stroma of the thymus consists of star-shaped epithelial cells (not reticular fibers) - These star-shaped thymocytes secrete hormones that stimulate lymphocytes to become immunocompetent ...
What is an Autoimmune Disease?
... Many B cells mature into what are called plasma cells that produce antibodies (proteins) necessary to fight off infections while other B cells mature into memory B cells. B cells work in co-ordination as whilst one set may produce antigens in order to fight off infection or bacteria whilst the other ...
... Many B cells mature into what are called plasma cells that produce antibodies (proteins) necessary to fight off infections while other B cells mature into memory B cells. B cells work in co-ordination as whilst one set may produce antigens in order to fight off infection or bacteria whilst the other ...
lymphatic system
... and natural killer (NK) cells, inhibit cell growth, and suppress tumor formation; they may hold ...
... and natural killer (NK) cells, inhibit cell growth, and suppress tumor formation; they may hold ...
... 1-Does not involve production of antibodies; is effective against intracellular pathogens (such as viruses, fungi )malignant cells, and grafts of foreign tissue. 2. Helper T cells recognize the foreign antigen, are antigen specific, and begin to divide to form different groups of T cells. 3. Memory ...
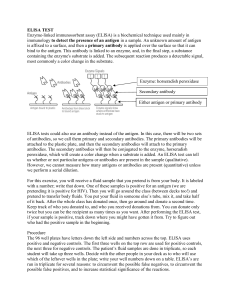
7a ELISA Test
... of antibodies, so we call them primary and secondary antibodies. The primary antibodies will be attached to the plastic plate, and then the secondary antibodies will attach to the primary antibodies. The secondary antibodies will then be conjugated to the enzyme, horseradish peroxidase, which will c ...
... of antibodies, so we call them primary and secondary antibodies. The primary antibodies will be attached to the plastic plate, and then the secondary antibodies will attach to the primary antibodies. The secondary antibodies will then be conjugated to the enzyme, horseradish peroxidase, which will c ...
Webinar Slides 3-up - Nature`s Sunshine Products
... • 100 million different kinds of white blood cells that can be stimulated to tag cells with specific characteristics for destruction • Serves as the back up for the innate immune system and is regulated by signals from it • Type os antibodies • IgG – most abundant type • IgA – involved in mucosal (i ...
... • 100 million different kinds of white blood cells that can be stimulated to tag cells with specific characteristics for destruction • Serves as the back up for the innate immune system and is regulated by signals from it • Type os antibodies • IgG – most abundant type • IgA – involved in mucosal (i ...
11.1 Antibody production and vaccination
... cells and against fungi, protozoa, and parasitic worms • Cell-mediated immunity is crucial in the body’s response against transplanted tissue and cancer cells, both of which are perceived as non-self ...
... cells and against fungi, protozoa, and parasitic worms • Cell-mediated immunity is crucial in the body’s response against transplanted tissue and cancer cells, both of which are perceived as non-self ...
PPT - Larry Smarr - California Institute for Telecommunications and
... Visualizing 5-10 Year Time Series of 150 Blood & Stool Variables Led Me to Discover a Chronic Disease ...
... Visualizing 5-10 Year Time Series of 150 Blood & Stool Variables Led Me to Discover a Chronic Disease ...
Adaptive Immunity: Activation of naive T cells
... antigen specificity; this is known as “clonal selection”. This increases the number of lymphocytes that can provide a useful response. Naïve T cells must also differentiate into effector cells in order to provide regulatory and cytolytic functions required for adaptive immunity. Limiting effector fu ...
... antigen specificity; this is known as “clonal selection”. This increases the number of lymphocytes that can provide a useful response. Naïve T cells must also differentiate into effector cells in order to provide regulatory and cytolytic functions required for adaptive immunity. Limiting effector fu ...
Fulltext PDF
... conversations in immunology, strategies that the immune system uses to identify infected cells very early during infection. In any event, the major 'effector' mechanisms or pathways that the immune system thus has to worry about generating are the production of fluid-phase 'terminator' molecules in ...
... conversations in immunology, strategies that the immune system uses to identify infected cells very early during infection. In any event, the major 'effector' mechanisms or pathways that the immune system thus has to worry about generating are the production of fluid-phase 'terminator' molecules in ...
T CELL DEFICIENCY
... • HYPER IgM SYNDROME XLHIM Genetic defect Defect of the DC40L membrane receptor gene – X-linked, disease in males ...
... • HYPER IgM SYNDROME XLHIM Genetic defect Defect of the DC40L membrane receptor gene – X-linked, disease in males ...
Cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 takes control of adult
... proliferation following LPS-induced inflammation. The authors showed that LPS reduces progenitor proliferation and neurogenesis in wild-type but not in COX-1-/- mice, pointing to an essential role for COX-1 in propagating the inflammatory response and modulating the neurogenic niche.9 Hence, COX-1 e ...
... proliferation following LPS-induced inflammation. The authors showed that LPS reduces progenitor proliferation and neurogenesis in wild-type but not in COX-1-/- mice, pointing to an essential role for COX-1 in propagating the inflammatory response and modulating the neurogenic niche.9 Hence, COX-1 e ...
Idera Pharmaceuticals Announces Cancer Immunotherapy Regimen
... such a difference include: whether results obtained in preclinical studies and clinical trials such as the preclinical data described in this release will be indicative of the results that will be generated in future clinical trials; whether products based on Idera’s technology will advance into o ...
... such a difference include: whether results obtained in preclinical studies and clinical trials such as the preclinical data described in this release will be indicative of the results that will be generated in future clinical trials; whether products based on Idera’s technology will advance into o ...
Primary Immunodeficiencies
... - recurrent bacterial infections starting in childhood similar with XLA, but ENLARGED lymphoid tissues (particularly Peyer’s patches). 1/4 die of chronic pulmonary disease or B cell lymphomas; amyloidosis, non-caseating granulomasta of the lung, splle, skin, liver and autoimmunity are common. - IV-I ...
... - recurrent bacterial infections starting in childhood similar with XLA, but ENLARGED lymphoid tissues (particularly Peyer’s patches). 1/4 die of chronic pulmonary disease or B cell lymphomas; amyloidosis, non-caseating granulomasta of the lung, splle, skin, liver and autoimmunity are common. - IV-I ...
Lymphatic System Notes (2 of 3)
... Must take it for full 7-10 days otherwise, bacterial infection can come back and/or can cause antibiotic resistance in bacteria ...
... Must take it for full 7-10 days otherwise, bacterial infection can come back and/or can cause antibiotic resistance in bacteria ...
Immunity [M.Tevfik DORAK]
... such as viruses, are degraded by the proteasome and the resulting peptides are shuttled into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by TAP proteins. These peptides are loaded onto MHC class I molecules and the complex is delivered to the cell surface, where it stimulates cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) that ...
... such as viruses, are degraded by the proteasome and the resulting peptides are shuttled into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by TAP proteins. These peptides are loaded onto MHC class I molecules and the complex is delivered to the cell surface, where it stimulates cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) that ...
Cancer immunotherapy

Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncology) is the use of the immune system to treat cancer. Immunotherapies fall into three main groups: cellular, antibody and cytokine. They exploit the fact that cancer cells often have subtly different molecules on their surface that can be detected by the immune system. These molecules, known as cancer antigens, are most commonly proteins, but also include molecules such as carbohydrates. Immunotherapy is used to provoke the immune system into attacking the tumor cells by using these antigens as targets.Antibody therapies are the most successful immunotherapy, treating a wide range of cancers. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that bind to a target antigen on the cell surface. In normal physiology the immune system uses them to fight pathogens. Each antibody is specific to one or a few proteins. Those that bind to cancer antigens are used to treat cancer. Cell surface receptors are common targets for antibody therapies and include the CD20, CD274, and CD279. Once bound to a cancer antigen, antibodies can induce antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, activate the complement system, or prevent a receptor from interacting with its ligand, all of which can lead to cell death. Multiple antibodies are approved to treat cancer, including Alemtuzumab, Ipilimumab, Nivolumab, Ofatumumab, and Rituximab.Cellular therapies, also known as cancer vaccines, usually involve the removal of immune cells from the blood or from a tumor. Immune cells specific for the tumor are activated, cultured and returned to the patient where the immune cells attack the cancer. Cell types that can be used in this way are natural killer cells, lymphokine-activated killer cells, cytotoxic T cells and dendritic cells. The only cell-based therapy approved in the US is Dendreon's Provenge, for the treatment of prostate cancer.Interleukin-2 and interferon-α are examples of cytokines, proteins that regulate and coordinate the behaviour of the immune system. They have the ability to enhance anti-tumor activity and thus can be used as cancer treatments. Interferon-α is used in the treatment of hairy-cell leukaemia, AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, follicular lymphoma, chronic myeloid leukaemia and malignant melanoma. Interleukin-2 is used in the treatment of malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.






















![Immunity [M.Tevfik DORAK]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002972234_1-56cb2c92152ee5d44665ce30ce75baf8-300x300.png)