Mantovani A et al
... cause inflammation and neoplasia (such as oncogenes) (Fig. 1). The intrinsic pathway was uncovered when addressing why inflammatory cells and mediators are present in the microenvironment of most, if not all, tumours and therefore are present in cases for which there is no epidemiological basis for ...
... cause inflammation and neoplasia (such as oncogenes) (Fig. 1). The intrinsic pathway was uncovered when addressing why inflammatory cells and mediators are present in the microenvironment of most, if not all, tumours and therefore are present in cases for which there is no epidemiological basis for ...
A potential solution to the critical organ donor shortage
... 13 patients (9). Most died within days, although one survived for nine months on an immunosuppressive regimen of azathioprine, actinomycin C and steroids. More recently, two patients received liver transplants from baboons. One patient survived for more than two months, but ultimately both patients ...
... 13 patients (9). Most died within days, although one survived for nine months on an immunosuppressive regimen of azathioprine, actinomycin C and steroids. More recently, two patients received liver transplants from baboons. One patient survived for more than two months, but ultimately both patients ...
Phagocytic ability declines with age in adult Drosophila hemocytes
... immediately engulfed can be destroyed by AMPs, which are released by various cells (Lemaitre & Hoffmann, 2007; Stuart & Ezekowitz, 2008). However, transcriptionally regulated AMP production is delayed compared with phagocytosis (Ramet et al., 2002; Lemaitre & Hoffmann, 2007; Haine et al., 2008). Whi ...
... immediately engulfed can be destroyed by AMPs, which are released by various cells (Lemaitre & Hoffmann, 2007; Stuart & Ezekowitz, 2008). However, transcriptionally regulated AMP production is delayed compared with phagocytosis (Ramet et al., 2002; Lemaitre & Hoffmann, 2007; Haine et al., 2008). Whi ...
A robust, high-throughput assay to determine the phagocytic activity
... Phagocytosis can be induced via the engagement of Fcγ receptors by antibody-opsonized material. Furthermore, the efficiency of antibody-induced effector functions has been shown to be dramatically modulated by changes in antibody glycosylation. Because infection can modulate antibody glycans, which ...
... Phagocytosis can be induced via the engagement of Fcγ receptors by antibody-opsonized material. Furthermore, the efficiency of antibody-induced effector functions has been shown to be dramatically modulated by changes in antibody glycosylation. Because infection can modulate antibody glycans, which ...
immunology core notes
... relatively non-specific; it distinguishes little, for example, between the bacterial organisms Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, or between the viral agents causing polio and smallpox. A next level of defense is manifested by a variety of cells and serum molecules which may promote ingestion and kil ...
... relatively non-specific; it distinguishes little, for example, between the bacterial organisms Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, or between the viral agents causing polio and smallpox. A next level of defense is manifested by a variety of cells and serum molecules which may promote ingestion and kil ...
Kinetics of tumor-specific T-cell response development after active
... Kinetics of tumor specific immunity induced by peptides are unable to recognize the antigen processed and presented naturally [13], the vaccination strategy reported here was highly effective in generating both HER-2/neu peptide- and protein-specific T cell immunity. While generation of peptide-spe ...
... Kinetics of tumor specific immunity induced by peptides are unable to recognize the antigen processed and presented naturally [13], the vaccination strategy reported here was highly effective in generating both HER-2/neu peptide- and protein-specific T cell immunity. While generation of peptide-spe ...
Lecture_5
... • The peptide is generated from proteins in the peptidepresenting cell • The peptide is not directly identified by the TCR, but recognized in a form bound to a MHC molecule ...
... • The peptide is generated from proteins in the peptidepresenting cell • The peptide is not directly identified by the TCR, but recognized in a form bound to a MHC molecule ...
Phospho-specific antibodies Cat. No. A060
... Phospho-specific antibodies Cat. No. A060 Package Preimmune serum Aliquot of the raw serum as backup Affinity purified anti-phospho antibodies (non-phosphopeptide depleted) Phosphopeptide Non-phosphopeptide ...
... Phospho-specific antibodies Cat. No. A060 Package Preimmune serum Aliquot of the raw serum as backup Affinity purified anti-phospho antibodies (non-phosphopeptide depleted) Phosphopeptide Non-phosphopeptide ...
NK cell development, homeostasis and function: parallels
... T cell precursors18. In humans, a population of CD34+ haematopoietic precursor cells was reported to develop into CD56hi NK cells in lymph nodes19. Furthermore, a recent examination of NK cell ontogeny suggested that NK cells can also develop in the liver 20, and this perhaps explains why phenotypic ...
... T cell precursors18. In humans, a population of CD34+ haematopoietic precursor cells was reported to develop into CD56hi NK cells in lymph nodes19. Furthermore, a recent examination of NK cell ontogeny suggested that NK cells can also develop in the liver 20, and this perhaps explains why phenotypic ...
Document
... of genes related to cell proliferation, angiogenesis, immune responses, growth factor activities, and signal transduction, ...
... of genes related to cell proliferation, angiogenesis, immune responses, growth factor activities, and signal transduction, ...
The role of the thymus in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell
... individuals and during acute GVHD. The top panel displays a scheme for thymus function in young individuals. The HSC-derived lymphoid progenitors ( ) enter the thymic microenvironment where they are committed to the T-cell lineage. Mouse cells at early stages of this development are phenotypically c ...
... individuals and during acute GVHD. The top panel displays a scheme for thymus function in young individuals. The HSC-derived lymphoid progenitors ( ) enter the thymic microenvironment where they are committed to the T-cell lineage. Mouse cells at early stages of this development are phenotypically c ...
Immunogenicity of Pluripotent Stem Cells and Their
... Immunogenic Molecules of Pluripotent Stem Cells Major Histocompatibility Antigens The major histocompatibility complex, termed Human Leukocyte Antigen in humans, consists of glycoproteins encoded by highly polymorphic genes on chromosome 6 that are co-dominantly expressed on the surface of almost al ...
... Immunogenic Molecules of Pluripotent Stem Cells Major Histocompatibility Antigens The major histocompatibility complex, termed Human Leukocyte Antigen in humans, consists of glycoproteins encoded by highly polymorphic genes on chromosome 6 that are co-dominantly expressed on the surface of almost al ...
Positive or Negative Involvement of Heat Shock Proteins in Multiple
... extracellular vesicles that originate from the fusion of multivesicular bodies with the plasma membrane. HSPA1A, HSPA8, HSPD1, and HSPC1 have also been shown to be released through membrane vesicles, extracellular vesicles that originate directly from the plasma membrane (Tinnirello, unpublished dat ...
... extracellular vesicles that originate from the fusion of multivesicular bodies with the plasma membrane. HSPA1A, HSPA8, HSPD1, and HSPC1 have also been shown to be released through membrane vesicles, extracellular vesicles that originate directly from the plasma membrane (Tinnirello, unpublished dat ...
Downloaded - The Journal of Immunology
... (Multiscreen HA filtration; Millipore) were coated overnight with four immune prevalent recombinant B. burgdorferi proteins all generated based on the N40 sequence, 1 mg/ml DbpA and 2 mg/ml each for outer surface protein C (OspC), arthritis related protein (Arp), and Borrelia membrane protein A (Bmp ...
... (Multiscreen HA filtration; Millipore) were coated overnight with four immune prevalent recombinant B. burgdorferi proteins all generated based on the N40 sequence, 1 mg/ml DbpA and 2 mg/ml each for outer surface protein C (OspC), arthritis related protein (Arp), and Borrelia membrane protein A (Bmp ...
Is Fever Beneficial to the Host: A Clinical Perspective
... breakdown of normal control mechanisms and is therefore not comparable with fever in the setting of a "normal" host defense system. In response, the view could be expressed that over the course of evolution host defense systems have become more complicated and therefore have more ways of going wrong ...
... breakdown of normal control mechanisms and is therefore not comparable with fever in the setting of a "normal" host defense system. In response, the view could be expressed that over the course of evolution host defense systems have become more complicated and therefore have more ways of going wrong ...
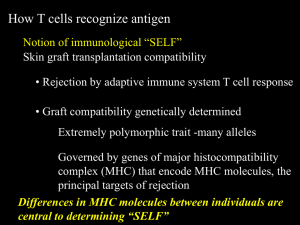
how t-cells use large deviations to recognize foreign
... The object of immunobiology is the body’s own defence against pathogens like bacteria, viruses or fungi. One distinguishes between unspecific and specific defence mechanisms. The latter form the so-called immune system, which specifically reacts to intruders. In this reaction, the T-cells play an impor ...
... The object of immunobiology is the body’s own defence against pathogens like bacteria, viruses or fungi. One distinguishes between unspecific and specific defence mechanisms. The latter form the so-called immune system, which specifically reacts to intruders. In this reaction, the T-cells play an impor ...
Molecular Innate Immunity in Teleost Fish: Review and Future Perspectives
... Innate immune response is a primitive form of defense mechanism existent in plants and animals. It is a complex system which, in vertebrates, is composed of cellular and humoral responses. The vertebrate teleost fish, which diverged from the tetrapod lineage about 450 million years ago, has an innat ...
... Innate immune response is a primitive form of defense mechanism existent in plants and animals. It is a complex system which, in vertebrates, is composed of cellular and humoral responses. The vertebrate teleost fish, which diverged from the tetrapod lineage about 450 million years ago, has an innat ...
Reish MAX
... Reishi provides complementary therapy to promote health and longevity • stimulates the formation of antibodies • stimulates the ability of proliferation of immune cells • modulates the function of T cells and NK cells Wang SY, et al. International Journal of Cancer 1997;70(6):699-705. Lu Z, Lin ZB. ...
... Reishi provides complementary therapy to promote health and longevity • stimulates the formation of antibodies • stimulates the ability of proliferation of immune cells • modulates the function of T cells and NK cells Wang SY, et al. International Journal of Cancer 1997;70(6):699-705. Lu Z, Lin ZB. ...
Immunological and fibrotic mechanisms in Cardiac Allograft
... recipient’s immune system recognizes the graft as foreign and attacks it. In this process there are many different immune cells involved. The main reason why a graft is rejected is because there are major antigenic differences between a donor and a host. The major histocompatibility complexes (MHC), ...
... recipient’s immune system recognizes the graft as foreign and attacks it. In this process there are many different immune cells involved. The main reason why a graft is rejected is because there are major antigenic differences between a donor and a host. The major histocompatibility complexes (MHC), ...
ReishiMax Product Training
... Reishi provides complementary therapy to promote health and longevity • stimulates the formation of antibodies • stimulates the ability of proliferation of immune cells • modulates the function of T cells and NK cells Wang SY, et al. International Journal of Cancer 1997;70(6):699-705. Lu Z, Lin ZB. ...
... Reishi provides complementary therapy to promote health and longevity • stimulates the formation of antibodies • stimulates the ability of proliferation of immune cells • modulates the function of T cells and NK cells Wang SY, et al. International Journal of Cancer 1997;70(6):699-705. Lu Z, Lin ZB. ...
Staphylococcus aureus infection induces protein A–mediated
... Figure 1. Infected patient sera responds to S. aureus antigens and infection–induced plasmablasts exhibit germinal center affinity maturation. (A) Sera from individuals infected with S. aureus (n = 18, circles) and control uninfected individuals (n = 21, triangles) were tested for recognition of th ...
... Figure 1. Infected patient sera responds to S. aureus antigens and infection–induced plasmablasts exhibit germinal center affinity maturation. (A) Sera from individuals infected with S. aureus (n = 18, circles) and control uninfected individuals (n = 21, triangles) were tested for recognition of th ...
Jeopardy - Waukee Community School District Blogs
... how they are spread, and which one do we get vaccinated for? ...
... how they are spread, and which one do we get vaccinated for? ...
Adaptive immune system

The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune or, more rarely, as the specific immune system, is a subsystem of the overall immune system that is composed of highly specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate or prevent pathogen growth. The adaptive immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leads to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination. Like the innate system, the adaptive system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.Unlike the innate immune system, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to a specific pathogen. Adaptive immunity can also provide long-lasting protection: for example; someone who recovers from measles is now protected against measles for their lifetime but in other cases it does not provide lifetime protection: for example; chickenpox. The adaptive system response destroys invading pathogens and any toxic molecules they produce. Sometimes the adaptive system is unable to distinguish foreign molecules, the effects of this may be hayfever, asthma or any other allergies. Antigens are any substances that elicit the adaptive immune response. The cells that carry out the adaptive immune response are white blood cells known as lymphocytes. Two main broad classes—antibody responses and cell mediated immune response—are also carried by two different lymphocytes (B cells and T cells). In antibody responses, B cells are activated to secrete antibodies, which are proteins also known as immunoglobulins. Antibodies travel through the bloodstream and bind to the foreign antigen causing it to inactivate, which does not allow the antigen to bind to the host.In acquired immunity, pathogen-specific receptors are ""acquired"" during the lifetime of the organism (whereas in innate immunity pathogen-specific receptors are already encoded in the germline). The acquired response is called ""adaptive"" because it prepares the body's immune system for future challenges (though it can actually also be maladaptive when it results in autoimmunity).The system is highly adaptable because of somatic hypermutation (a process of accelerated somatic mutations), and V(D)J recombination (an irreversible genetic recombination of antigen receptor gene segments). This mechanism allows a small number of genes to generate a vast number of different antigen receptors, which are then uniquely expressed on each individual lymphocyte. Because the gene rearrangement leads to an irreversible change in the DNA of each cell, all progeny (offspring) of that cell inherit genes that encode the same receptor specificity, including the memory B cells and memory T cells that are the keys to long-lived specific immunity.A theoretical framework explaining the workings of the acquired immune system is provided by immune network theory. This theory, which builds on established concepts of clonal selection, is being applied in the search for an HIV vaccine.