Uchanska-Ziegler, B., Loll, B., Fabian, H., Hee, CS, Saenger, W
... The possible consequences of carrying only MHC class I genes exhibiting a very low degree of polymorphism can be seen in the Tasmanian devil (Sarcophilus harrisii). The population of this carnivorous marsupial has declined by more than 50% due to the spread of a highly contagious clonal malignancy, ...
... The possible consequences of carrying only MHC class I genes exhibiting a very low degree of polymorphism can be seen in the Tasmanian devil (Sarcophilus harrisii). The population of this carnivorous marsupial has declined by more than 50% due to the spread of a highly contagious clonal malignancy, ...
Plasmacytoid predendritic cells initiate psoriasis through interferon
... onset of the lesions is commonly followed by chronic relapses of the disease triggered by infections, mechanical stress, and drugs (5). Although it is still unclear how these environmental factors drive the pathogenic T cell cascade, it has been suggested that innate immune pathways may provide the ...
... onset of the lesions is commonly followed by chronic relapses of the disease triggered by infections, mechanical stress, and drugs (5). Although it is still unclear how these environmental factors drive the pathogenic T cell cascade, it has been suggested that innate immune pathways may provide the ...
Review Article - clinicalevidence
... by gram-positive bacteria. This includes the identification of 1) components in gram-positive bacteria that initiates cytokine production, 2) receptors on host immune cells responsible for recognition of such components, and 3) signaling pathways leading to cytokine production. The discovery a decad ...
... by gram-positive bacteria. This includes the identification of 1) components in gram-positive bacteria that initiates cytokine production, 2) receptors on host immune cells responsible for recognition of such components, and 3) signaling pathways leading to cytokine production. The discovery a decad ...
2016 Annual Report
... The interest in the work of the Centre from the community is growing and a highlight for 2016 was the public lecture, the Centre put on, by Nobel Laureate, W.E Moerner. Organised by the Centre, over 400 people attended. Moerner’s work in the development of super-resolved fluorescence microscopy won ...
... The interest in the work of the Centre from the community is growing and a highlight for 2016 was the public lecture, the Centre put on, by Nobel Laureate, W.E Moerner. Organised by the Centre, over 400 people attended. Moerner’s work in the development of super-resolved fluorescence microscopy won ...
Candida Infections: An Update on Host Immune Defenses and Anti
... is a major component of the hyphal cell wall, but not for the yeast phase[22]. Deletion of C. albicans ALS3 results in striking adhesion and biofilm formation defects. ALS3 is also required for C. albicans cell binding to E-cadherin on epithelial cells, and for N-cadherin on endothelial cells and ex ...
... is a major component of the hyphal cell wall, but not for the yeast phase[22]. Deletion of C. albicans ALS3 results in striking adhesion and biofilm formation defects. ALS3 is also required for C. albicans cell binding to E-cadherin on epithelial cells, and for N-cadherin on endothelial cells and ex ...
Increased Susceptibility to Salmonella Infection in Signal Regulatory
... substrate-1), CD172a, BIT (brain Ig–like molecule with a tyrosinebased activation motif), MFR (macrophage fusion receptor), or p84 (17–21). It is expressed primarily on myeloid cells, such as macrophages, granulocytes, and myeloid dendritic cells (DCs), but is barely detectable on B or T lymphocytes ...
... substrate-1), CD172a, BIT (brain Ig–like molecule with a tyrosinebased activation motif), MFR (macrophage fusion receptor), or p84 (17–21). It is expressed primarily on myeloid cells, such as macrophages, granulocytes, and myeloid dendritic cells (DCs), but is barely detectable on B or T lymphocytes ...
Basophils: new players in the cytokine network
... cells. Indeed, basophils are the least common granulocytes in the circulation, where they usually represent less than 1% of the white blood cell population. Furthermore, the absence of specific surface markers, at least in mice, has been a drawback to their purification. Progress in basophil researc ...
... cells. Indeed, basophils are the least common granulocytes in the circulation, where they usually represent less than 1% of the white blood cell population. Furthermore, the absence of specific surface markers, at least in mice, has been a drawback to their purification. Progress in basophil researc ...
Nutritional Strategies to Counter Stress to the Immune System In
... numbers of total lymphocytes (accounted for by an decrease in CD+ T lymphocytes and resulting in a decrease in the CD4/CD8 ratio) over the course of the season. Furthermore, significant falls in both neutrophil chemotaxis and phagocytosis and in PHA-stimulated T lymphocyte proliferation were reporte ...
... numbers of total lymphocytes (accounted for by an decrease in CD+ T lymphocytes and resulting in a decrease in the CD4/CD8 ratio) over the course of the season. Furthermore, significant falls in both neutrophil chemotaxis and phagocytosis and in PHA-stimulated T lymphocyte proliferation were reporte ...
Focus Article
... contributes significantly to chronic pain and related multisymptom disorders. Finally, we discuss factors that make the individual patient uniquely susceptible to developing a particular pattern of chronic pain. ...
... contributes significantly to chronic pain and related multisymptom disorders. Finally, we discuss factors that make the individual patient uniquely susceptible to developing a particular pattern of chronic pain. ...
Mast Cell Activation and Migration to Lymph Nodes during
... primary antibodies; goat anti–mouse MIP-1a or MIP-1b (R&D Systems), and affinity-purified polyclonal rabbit anti–mouse mast cell protease-5 (mMCP-5) (40), for 1 h at room temperature, followed by HRP-conjugated donkey anti–goat IgG (Serotec, Australian Laboratory Services, Sydney, Australia) for 1 h ...
... primary antibodies; goat anti–mouse MIP-1a or MIP-1b (R&D Systems), and affinity-purified polyclonal rabbit anti–mouse mast cell protease-5 (mMCP-5) (40), for 1 h at room temperature, followed by HRP-conjugated donkey anti–goat IgG (Serotec, Australian Laboratory Services, Sydney, Australia) for 1 h ...
Induced CD4+Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells in Immune Tolerance
... lack nTreg cells) and differentiated them to iTreg cells in vitro using TGF-β and IL-2 and two different activation stimuli, APCs plus cognate antigen or plate-bound anti-CD3 and antiCD28. They observed that 50–60% of iTreg cells differentiated in the presence of APCs plus antigen expressed Helios, ...
... lack nTreg cells) and differentiated them to iTreg cells in vitro using TGF-β and IL-2 and two different activation stimuli, APCs plus cognate antigen or plate-bound anti-CD3 and antiCD28. They observed that 50–60% of iTreg cells differentiated in the presence of APCs plus antigen expressed Helios, ...
Polyclonal Antibody Order Form
... for injection into animals. The animals injected are owned solely by PRF&L. However, all of the serum and products obtained from the animals will be the property of the undersigned (project sponsor). I assure that the information in this form is fully and accurately presented. The USDA and NIH requi ...
... for injection into animals. The animals injected are owned solely by PRF&L. However, all of the serum and products obtained from the animals will be the property of the undersigned (project sponsor). I assure that the information in this form is fully and accurately presented. The USDA and NIH requi ...
PDF
... a cytokine crucial for IFN-γ production by NK cells in the spleen but not in the liver and appears to be dispensable for resistance to MCMV infection under conditions where IL-12 and NK cells are critical [36]. In other words, IL-18 does not seem to be required for NK celldependent protection agains ...
... a cytokine crucial for IFN-γ production by NK cells in the spleen but not in the liver and appears to be dispensable for resistance to MCMV infection under conditions where IL-12 and NK cells are critical [36]. In other words, IL-18 does not seem to be required for NK celldependent protection agains ...
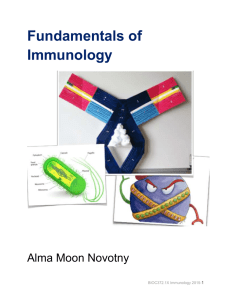
Fundamentals of Immunology
... Slower-weeks requires gene Recognizes rearrangement specific initially, 3 or proteins more days subsequently ...
... Slower-weeks requires gene Recognizes rearrangement specific initially, 3 or proteins more days subsequently ...
Doctoral thesis from the Department of Immunology,
... the release of cytotoxic reactive oxygen intermediates (ROI) [16]. The ability of pathogenic mycobacteria to adapt to the hostile environment of macrophages has been instrumental in its success as a pathogen. Mycobacteria interfere with host trafficking pathways by modulating events in the endosoma ...
... the release of cytotoxic reactive oxygen intermediates (ROI) [16]. The ability of pathogenic mycobacteria to adapt to the hostile environment of macrophages has been instrumental in its success as a pathogen. Mycobacteria interfere with host trafficking pathways by modulating events in the endosoma ...
Homophilic Adhesion between Ig Superfamily Carcinoembryonic
... CEA, another Ig superfamily member, belongs to a subfamily of closely related cell surface glycoproteins which are found in various human tumors as well as in normal tissues (Thompson et al., 1991). The protein and mRNA levels of CEA have been found to be higher in colon tumors relative to their nor ...
... CEA, another Ig superfamily member, belongs to a subfamily of closely related cell surface glycoproteins which are found in various human tumors as well as in normal tissues (Thompson et al., 1991). The protein and mRNA levels of CEA have been found to be higher in colon tumors relative to their nor ...
S. mansoni - York College of Pennsylvania
... Schistosoma mansoni before or after BCG vaccination, and subsequently challenged with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. If clinical assessments, cellular proliferation analyses, cytokine assays, bacterial counts, and pathologic examinations indicate that helminthic infection reduces efficacy, phase two wi ...
... Schistosoma mansoni before or after BCG vaccination, and subsequently challenged with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. If clinical assessments, cellular proliferation analyses, cytokine assays, bacterial counts, and pathologic examinations indicate that helminthic infection reduces efficacy, phase two wi ...
Antiphospholipid Antibodies: Their Origin and Development
... Natural antibodies appear without prior infection or immunization. The majority is of the immunoglobulin (Ig) M isotype, but IgG or IgA have also been observed [13,14]. They are secreted mainly by B1 cells, a specific subset of B-lymphocytes. Activation of B1 cells does not depend on antigenic chall ...
... Natural antibodies appear without prior infection or immunization. The majority is of the immunoglobulin (Ig) M isotype, but IgG or IgA have also been observed [13,14]. They are secreted mainly by B1 cells, a specific subset of B-lymphocytes. Activation of B1 cells does not depend on antigenic chall ...
Activation of Innate Immune Responses by Non
... DC maturation and migration of the cells into local lymph nodes, where antigen presentation to naïve T cells and induction of adaptive immune responses takes place. During activation these cells produce cytokines, soluble mediators that regulate host immune responses. Recognition of microbes is regu ...
... DC maturation and migration of the cells into local lymph nodes, where antigen presentation to naïve T cells and induction of adaptive immune responses takes place. During activation these cells produce cytokines, soluble mediators that regulate host immune responses. Recognition of microbes is regu ...
Immune-Genetic Algorithm for Traveling Salesman Problem
... the University of Mexico, is a kind of selection Algorithms used to test data change. The algorithm embodies the ideas of the ideological principles of negative selection (Ge & Mao, 2002). The immune system works out mainly by successfully detecting abnormal changes of the system. Negative selection ...
... the University of Mexico, is a kind of selection Algorithms used to test data change. The algorithm embodies the ideas of the ideological principles of negative selection (Ge & Mao, 2002). The immune system works out mainly by successfully detecting abnormal changes of the system. Negative selection ...
Introduction to AIS
... • Computationally, the degree of interaction of an antibody-antigen or antibody-antibody can be evaluated by a distance or affinity measure • The choice of affinity measure is crucial: • It alters the shape-space topology • It will introduce an inductive bias into the algorithm • It needs to take in ...
... • Computationally, the degree of interaction of an antibody-antigen or antibody-antibody can be evaluated by a distance or affinity measure • The choice of affinity measure is crucial: • It alters the shape-space topology • It will introduce an inductive bias into the algorithm • It needs to take in ...
Lung inflammatory responses
... to invading pathogens and environmental challenges [74]. As a result, knowledge of the underlying mechanisms of inflammation is important for developing intervention strategies to reduce the impact and damage inflammation causes the host. As with most aspects of immunology, inflammation can be benef ...
... to invading pathogens and environmental challenges [74]. As a result, knowledge of the underlying mechanisms of inflammation is important for developing intervention strategies to reduce the impact and damage inflammation causes the host. As with most aspects of immunology, inflammation can be benef ...
Prescribing Information BayRho
... BayRho-D Full dose may be used to prevent isoimmunization in Rho(D) negative individuals who have been transfused with Rho(D) positive red blood cells or blood components containing red blood cells.5.13 CONTRAINDICATIONS None known. WARNINGS NEVER ADMINISTER BAYRHO-D FULL DOSE INTREVENOUSLY. INJECT ...
... BayRho-D Full dose may be used to prevent isoimmunization in Rho(D) negative individuals who have been transfused with Rho(D) positive red blood cells or blood components containing red blood cells.5.13 CONTRAINDICATIONS None known. WARNINGS NEVER ADMINISTER BAYRHO-D FULL DOSE INTREVENOUSLY. INJECT ...
Lecture 2- Immune and Lymphatic System
... immunity on the other hand directly destroys pathogens by either killing them or releasing chemicals which active inflammation and other host defense mechanisms. These 2 forms of adaptive immunity are achieved through 2 different types of lymphocytes: B-cells and Tcells. • Antigens: Before talking a ...
... immunity on the other hand directly destroys pathogens by either killing them or releasing chemicals which active inflammation and other host defense mechanisms. These 2 forms of adaptive immunity are achieved through 2 different types of lymphocytes: B-cells and Tcells. • Antigens: Before talking a ...
Adaptive immune system

The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune or, more rarely, as the specific immune system, is a subsystem of the overall immune system that is composed of highly specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate or prevent pathogen growth. The adaptive immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leads to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination. Like the innate system, the adaptive system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.Unlike the innate immune system, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to a specific pathogen. Adaptive immunity can also provide long-lasting protection: for example; someone who recovers from measles is now protected against measles for their lifetime but in other cases it does not provide lifetime protection: for example; chickenpox. The adaptive system response destroys invading pathogens and any toxic molecules they produce. Sometimes the adaptive system is unable to distinguish foreign molecules, the effects of this may be hayfever, asthma or any other allergies. Antigens are any substances that elicit the adaptive immune response. The cells that carry out the adaptive immune response are white blood cells known as lymphocytes. Two main broad classes—antibody responses and cell mediated immune response—are also carried by two different lymphocytes (B cells and T cells). In antibody responses, B cells are activated to secrete antibodies, which are proteins also known as immunoglobulins. Antibodies travel through the bloodstream and bind to the foreign antigen causing it to inactivate, which does not allow the antigen to bind to the host.In acquired immunity, pathogen-specific receptors are ""acquired"" during the lifetime of the organism (whereas in innate immunity pathogen-specific receptors are already encoded in the germline). The acquired response is called ""adaptive"" because it prepares the body's immune system for future challenges (though it can actually also be maladaptive when it results in autoimmunity).The system is highly adaptable because of somatic hypermutation (a process of accelerated somatic mutations), and V(D)J recombination (an irreversible genetic recombination of antigen receptor gene segments). This mechanism allows a small number of genes to generate a vast number of different antigen receptors, which are then uniquely expressed on each individual lymphocyte. Because the gene rearrangement leads to an irreversible change in the DNA of each cell, all progeny (offspring) of that cell inherit genes that encode the same receptor specificity, including the memory B cells and memory T cells that are the keys to long-lived specific immunity.A theoretical framework explaining the workings of the acquired immune system is provided by immune network theory. This theory, which builds on established concepts of clonal selection, is being applied in the search for an HIV vaccine.