DiGeorge`s syndrome
... Also known as congenital thymic aplasia/hypoplasia Associated with hypoparathyroidism, congenital heart disease, fish shaped mouth. Defects results from abnormal development of fetus during 6th-10th week of gestation when parathyroid, thymus, lips, ears and aortic arch are being formed ...
... Also known as congenital thymic aplasia/hypoplasia Associated with hypoparathyroidism, congenital heart disease, fish shaped mouth. Defects results from abnormal development of fetus during 6th-10th week of gestation when parathyroid, thymus, lips, ears and aortic arch are being formed ...
PowerPoint Presentation: Immune System
... weapons tailored just for them. These include both antibodies and cells of the immune response. The cells of the immune response include different kinds of macrophages, T-cells and B cells. Almost all antigens trigger both nonspecific and specific responses. ...
... weapons tailored just for them. These include both antibodies and cells of the immune response. The cells of the immune response include different kinds of macrophages, T-cells and B cells. Almost all antigens trigger both nonspecific and specific responses. ...
Overview Of Autoimmune Disease - American Proficiency Institute
... A basic understanding of the immune system is a prerequisite for understanding autoimmunity. The immune system has two functions. One is to protect the body from invading organisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and toxic substances. The other is to differentiate self from non-self. The immune re ...
... A basic understanding of the immune system is a prerequisite for understanding autoimmunity. The immune system has two functions. One is to protect the body from invading organisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and toxic substances. The other is to differentiate self from non-self. The immune re ...
Glossary - Immunology - TranslationDirectory.com
... immune response to allergens. Characterized by the release of pharmacological agents as a result of mast cell and basophil degranulation, which is usually mediated by antibodies of the IgE class. Also called Immediate (Type I) ...
... immune response to allergens. Characterized by the release of pharmacological agents as a result of mast cell and basophil degranulation, which is usually mediated by antibodies of the IgE class. Also called Immediate (Type I) ...
TIGIT-positive circulating follicular helper T cells
... chronic transfusions. Considering the latter question from a non-transfusion perspective, the authors propose an interesting hypothesis: if chronic stimulation induces TH1 or TFH1 cells to differentiate into TFH cells, could this process reflect an evolutionary mechanism by which TIGIT would be invo ...
... chronic transfusions. Considering the latter question from a non-transfusion perspective, the authors propose an interesting hypothesis: if chronic stimulation induces TH1 or TFH1 cells to differentiate into TFH cells, could this process reflect an evolutionary mechanism by which TIGIT would be invo ...
Blood- Chapter 18
... Neutrophils- quick responders: Lysozyme, strong oxidants, defensins- proteins that exhibit broad range antibiotic activity bacteria & fungi ...
... Neutrophils- quick responders: Lysozyme, strong oxidants, defensins- proteins that exhibit broad range antibiotic activity bacteria & fungi ...
Antibody Structure and Function
... • If complement is activated by Ag:Ab that has precipitated on a host cell or basement membrane, deposition of the complement attack complex can damage the cell or basement membrane. – A number of host factors block deposition or activation of complement on normal tissues (eg, protectin [CD59] and h ...
... • If complement is activated by Ag:Ab that has precipitated on a host cell or basement membrane, deposition of the complement attack complex can damage the cell or basement membrane. – A number of host factors block deposition or activation of complement on normal tissues (eg, protectin [CD59] and h ...
Construction of a new strain of mice that lack mast cells and set
... chest tightness and shortness of breath in susceptible individuals. Today, asthma is one of the most common chronic diseases affecting approximately 300 million people globally and about 5% ...
... chest tightness and shortness of breath in susceptible individuals. Today, asthma is one of the most common chronic diseases affecting approximately 300 million people globally and about 5% ...
Chapter 23
... Active immunoglobulin genes have V regions with sequences that are changed from the germline because of somatic mutation. The mutations occur as substitutions of individual bases. The sites of mutation are concentrated in the antigen-binding site. The process depends on the enhancer that activates t ...
... Active immunoglobulin genes have V regions with sequences that are changed from the germline because of somatic mutation. The mutations occur as substitutions of individual bases. The sites of mutation are concentrated in the antigen-binding site. The process depends on the enhancer that activates t ...
CyAn™ ADP Dendritic Cells: Rare Event Analysis E T
... In two other tubes, 400 μL of whole blood collected from a normal, healthy adult was added. To one of the tubes, the following mouse antihuman antibodies were added: 20 μL of the FITC cocktail, 40 μL of HLA-DR APC and 20 μL of CD123 RPE. In the other tube, the following mouse anti-human antibodies w ...
... In two other tubes, 400 μL of whole blood collected from a normal, healthy adult was added. To one of the tubes, the following mouse antihuman antibodies were added: 20 μL of the FITC cocktail, 40 μL of HLA-DR APC and 20 μL of CD123 RPE. In the other tube, the following mouse anti-human antibodies w ...
2-3 Innate immunity 2016
... Cells of the innate immune system: Macrophages: Macrophages are constitutively present in tissues and recognize microbes that enter these tissues and respond rapidly to these microbes. They initiate the immune response. •These cells are phagocytes (eliminate the pathogens) •Activate the innate imm ...
... Cells of the innate immune system: Macrophages: Macrophages are constitutively present in tissues and recognize microbes that enter these tissues and respond rapidly to these microbes. They initiate the immune response. •These cells are phagocytes (eliminate the pathogens) •Activate the innate imm ...
Monoclonal antibodies
... ADCC is the least understood of the three mechanisms, it is mediated by either NK cells or CTL. The action of ADCC is dependant on the recognition of the objective cell by antibodies attached on the surface of the effector cell (terminally differentiated leukocyte). This process is part of the adapt ...
... ADCC is the least understood of the three mechanisms, it is mediated by either NK cells or CTL. The action of ADCC is dependant on the recognition of the objective cell by antibodies attached on the surface of the effector cell (terminally differentiated leukocyte). This process is part of the adapt ...
Cross‐presentation of malaria antigen by brain microvessels: why
... were much higher than those infected with non‐ECM inducing strain. It remains to be answered, however, why PbA‐infected RBCs preferentially accumulate in the brain. Is it due to the intrinsic properties of PbA or due to the immune response of the host? In addition, PbGAP50‐specific CD8þ T cells alone ...
... were much higher than those infected with non‐ECM inducing strain. It remains to be answered, however, why PbA‐infected RBCs preferentially accumulate in the brain. Is it due to the intrinsic properties of PbA or due to the immune response of the host? In addition, PbGAP50‐specific CD8þ T cells alone ...
1. dia
... Lack of T lymphocytes and adaptive immunity, (result of several gene mutations) Chains of cytokine receptor and signalling molecules are coded by 3 genes, 5 genes are required for development of antigene receptor (adenosine deaminase, purine salvage pathway, phosphatase – CD45). ...
... Lack of T lymphocytes and adaptive immunity, (result of several gene mutations) Chains of cytokine receptor and signalling molecules are coded by 3 genes, 5 genes are required for development of antigene receptor (adenosine deaminase, purine salvage pathway, phosphatase – CD45). ...
Lecture 23 - Rice University
... – Kill invaders – Signal other immune cells – Present antigen to adaptive immune system ...
... – Kill invaders – Signal other immune cells – Present antigen to adaptive immune system ...
Document
... • The alternative pathway is considered to be a primitive „bypass“ mechanism, that does not require C1, C2 and C4 • The pathway is activated through reaction of the complement system and some substances of microbial origin (polysaccharides – e.g. lipopolysaccharides of G negative bacteria, teichoic ...
... • The alternative pathway is considered to be a primitive „bypass“ mechanism, that does not require C1, C2 and C4 • The pathway is activated through reaction of the complement system and some substances of microbial origin (polysaccharides – e.g. lipopolysaccharides of G negative bacteria, teichoic ...
PPS - Jacksonville University
... Also I would like to thank Sally and Judy in the Science and Math division office, for signing me out a lab key nearly everyday of the year ...
... Also I would like to thank Sally and Judy in the Science and Math division office, for signing me out a lab key nearly everyday of the year ...
Immunity to microbes
... The major mechanisms of innate immunity in the oral cavity are inactivation and clearance of microbes from the oral mucosal epithelium and enamel surfaces as well as inflammation. The oral mucosa is an anatomical barrier that prevents entry of microbes. Oral health depends on the integrity of the mu ...
... The major mechanisms of innate immunity in the oral cavity are inactivation and clearance of microbes from the oral mucosal epithelium and enamel surfaces as well as inflammation. The oral mucosa is an anatomical barrier that prevents entry of microbes. Oral health depends on the integrity of the mu ...
HEPATITIS C VIRUS AND HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS
... In practice, the correlation of antibody with HCV clearance and outcome is controversial or lacking Patients with high levels of neutralizing antibodies nevertheless maintain chronic infection, indicating that neutralizing antibodies are not sterilizing ...
... In practice, the correlation of antibody with HCV clearance and outcome is controversial or lacking Patients with high levels of neutralizing antibodies nevertheless maintain chronic infection, indicating that neutralizing antibodies are not sterilizing ...
CXCR3+CCR5+ T cells and autoimmune diseases
... is unknown. Dysfunctional MHCII and/or T cell responses could also alter gut microbiota, subsequently influencing disease. (B) During the lymphoid phase, naive T cells differentiate into disease-associated effector and memory T cells. IFN-γ–producing Th1 cells generally express CCR5 and CXCR3, where ...
... is unknown. Dysfunctional MHCII and/or T cell responses could also alter gut microbiota, subsequently influencing disease. (B) During the lymphoid phase, naive T cells differentiate into disease-associated effector and memory T cells. IFN-γ–producing Th1 cells generally express CCR5 and CXCR3, where ...
Lesson Plan Summary Sheet
... How are protein replacement therapies used to treat various diseases? How are viruses used in gene therapy? How are non-viral delivery methods used in gene therapy? ...
... How are protein replacement therapies used to treat various diseases? How are viruses used in gene therapy? How are non-viral delivery methods used in gene therapy? ...
Chapter 16: Adaptive Immunity
... T cells (whether TH or TC) produce extremely long-lived memory cells: • activated directly upon subsequent exposure No need for activation signals from other T cells or APCs! ...
... T cells (whether TH or TC) produce extremely long-lived memory cells: • activated directly upon subsequent exposure No need for activation signals from other T cells or APCs! ...
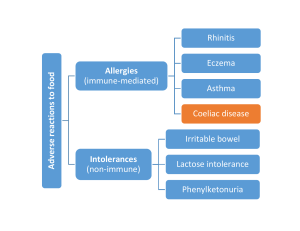
Static
... A peptide, gliadin, remains, which cannot be degraded by regular enzymes Gliadin is instead deamidated (has an amide group removed) by tissue transglutaminase (tTG). ...
... A peptide, gliadin, remains, which cannot be degraded by regular enzymes Gliadin is instead deamidated (has an amide group removed) by tissue transglutaminase (tTG). ...
File
... Principals of immunization • Active immunity – immune response in an individual upon exposure to antigen; naturally from active infection or artificially via vaccination • Passive immunity – occurs during pregnancy (natural) and when Abs are supplied from another individual or animal (artificial) ...
... Principals of immunization • Active immunity – immune response in an individual upon exposure to antigen; naturally from active infection or artificially via vaccination • Passive immunity – occurs during pregnancy (natural) and when Abs are supplied from another individual or animal (artificial) ...
Adaptive immune system

The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune or, more rarely, as the specific immune system, is a subsystem of the overall immune system that is composed of highly specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate or prevent pathogen growth. The adaptive immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leads to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination. Like the innate system, the adaptive system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.Unlike the innate immune system, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to a specific pathogen. Adaptive immunity can also provide long-lasting protection: for example; someone who recovers from measles is now protected against measles for their lifetime but in other cases it does not provide lifetime protection: for example; chickenpox. The adaptive system response destroys invading pathogens and any toxic molecules they produce. Sometimes the adaptive system is unable to distinguish foreign molecules, the effects of this may be hayfever, asthma or any other allergies. Antigens are any substances that elicit the adaptive immune response. The cells that carry out the adaptive immune response are white blood cells known as lymphocytes. Two main broad classes—antibody responses and cell mediated immune response—are also carried by two different lymphocytes (B cells and T cells). In antibody responses, B cells are activated to secrete antibodies, which are proteins also known as immunoglobulins. Antibodies travel through the bloodstream and bind to the foreign antigen causing it to inactivate, which does not allow the antigen to bind to the host.In acquired immunity, pathogen-specific receptors are ""acquired"" during the lifetime of the organism (whereas in innate immunity pathogen-specific receptors are already encoded in the germline). The acquired response is called ""adaptive"" because it prepares the body's immune system for future challenges (though it can actually also be maladaptive when it results in autoimmunity).The system is highly adaptable because of somatic hypermutation (a process of accelerated somatic mutations), and V(D)J recombination (an irreversible genetic recombination of antigen receptor gene segments). This mechanism allows a small number of genes to generate a vast number of different antigen receptors, which are then uniquely expressed on each individual lymphocyte. Because the gene rearrangement leads to an irreversible change in the DNA of each cell, all progeny (offspring) of that cell inherit genes that encode the same receptor specificity, including the memory B cells and memory T cells that are the keys to long-lived specific immunity.A theoretical framework explaining the workings of the acquired immune system is provided by immune network theory. This theory, which builds on established concepts of clonal selection, is being applied in the search for an HIV vaccine.