Microbiology 221
... The organism must be found in all animals suffering from the disease, but not in healthy animals. The organism must be isolated from a diseased animal and grown in pure culture. The cultured organism should cause disease when introduced into a healthy animal. The organism must be reisolated ...
... The organism must be found in all animals suffering from the disease, but not in healthy animals. The organism must be isolated from a diseased animal and grown in pure culture. The cultured organism should cause disease when introduced into a healthy animal. The organism must be reisolated ...
Section I Section I
... eighteenth century, and for rabies, by Pasteur and his associates in the latter half of the nineteenth century. The development by Pasteur ’s co-worker, Charles Chamberland, of the porcelain filter to produce bacteriologically-sterile water for use in culture media, eventually facilitated isolation ...
... eighteenth century, and for rabies, by Pasteur and his associates in the latter half of the nineteenth century. The development by Pasteur ’s co-worker, Charles Chamberland, of the porcelain filter to produce bacteriologically-sterile water for use in culture media, eventually facilitated isolation ...
Lyme Disease
... disease in 1833. He lived in Germany It was brought to their attention when a statistically improbable cluster of pediatric arthritis occurred in the region around Lyme, Connecticut. ...
... disease in 1833. He lived in Germany It was brought to their attention when a statistically improbable cluster of pediatric arthritis occurred in the region around Lyme, Connecticut. ...
Overview of the Second Havemeyer EHV
... identify vaccination technologies that can protect against the more important pathological sequelae to infection. For the first time there was a major discussion of the use of antiviral agents, in both experimental and clinical studies. The workshop participants agreed to participate in a multi-auth ...
... identify vaccination technologies that can protect against the more important pathological sequelae to infection. For the first time there was a major discussion of the use of antiviral agents, in both experimental and clinical studies. The workshop participants agreed to participate in a multi-auth ...
Sri Lanka - Travel Doctor
... JE is a mosquito borne viral disease prevalent in rural areas of SE Asia that can lead to serious brain infection in humans. Risk is usually greatest during the monsoon months. A vaccine is available & is particularly recommended for adults & children over 12 months of age who will be spending a mon ...
... JE is a mosquito borne viral disease prevalent in rural areas of SE Asia that can lead to serious brain infection in humans. Risk is usually greatest during the monsoon months. A vaccine is available & is particularly recommended for adults & children over 12 months of age who will be spending a mon ...
Detection and Control of Epidemic Meningococcal Disease
... Carriage and Transmission of N. Meningitidis Only humans carry N. meningitidis Bacteria live in mucosa of nose and throat Spread in oral secretions or respiratory droplets Most persons who carry N. meningitidis have no symptoms of disease Not clear why some people develop disease, but humoral immun ...
... Carriage and Transmission of N. Meningitidis Only humans carry N. meningitidis Bacteria live in mucosa of nose and throat Spread in oral secretions or respiratory droplets Most persons who carry N. meningitidis have no symptoms of disease Not clear why some people develop disease, but humoral immun ...
Human Mobility Network, Travel Restrictions and
... Panels: A,B are the probability distribution of arrival time in UK and Germany respectively. Dotted vertical line shows the observed arrival time and solid vertical line shows starting date of travel restriction. Panels C,D are the cumulative travel distribution. In this any source of infection in s ...
... Panels: A,B are the probability distribution of arrival time in UK and Germany respectively. Dotted vertical line shows the observed arrival time and solid vertical line shows starting date of travel restriction. Panels C,D are the cumulative travel distribution. In this any source of infection in s ...
Management of Hand Foot Mouth Disease (HFMD) in Health Care
... 5.1. In most mild cases, laboratory studies may not be necessary. 5.2. Viral studies for confirming the diagnosis are indicated in patients with any of the following conditions: - HFMD/ Herpangina/ suspected enterovirus infection with rapid clinical deterioration or complications; - Children w ...
... 5.1. In most mild cases, laboratory studies may not be necessary. 5.2. Viral studies for confirming the diagnosis are indicated in patients with any of the following conditions: - HFMD/ Herpangina/ suspected enterovirus infection with rapid clinical deterioration or complications; - Children w ...
BODY DEFENSES AND DISEASE
... Helper T cells are the major driving force and the main regulators of the immune defense. Their primary task is to activate B cells and killer T cells. The killer T cell is specialized in attacking cells of the body infected by viruses and sometimes also by bacteria. It can also attack ...
... Helper T cells are the major driving force and the main regulators of the immune defense. Their primary task is to activate B cells and killer T cells. The killer T cell is specialized in attacking cells of the body infected by viruses and sometimes also by bacteria. It can also attack ...
Year 11 History GCSE Pop Quiz Essay Paper) Medicine and
... explain illness and later developed by Galen? The name for the time period between of great change in medical understanding in 16th and 17th century is ... What was the name of the group set up in 1660 to enable educated people to discuss scientific ideas ... A way of giving a patient a mild do ...
... explain illness and later developed by Galen? The name for the time period between of great change in medical understanding in 16th and 17th century is ... What was the name of the group set up in 1660 to enable educated people to discuss scientific ideas ... A way of giving a patient a mild do ...
The Impact of Urban Decay on Potential RVFV Vectors During the
... The Impact of Urban Decay on Potential RVFV Vectors During the Recent Economic Crisis ...
... The Impact of Urban Decay on Potential RVFV Vectors During the Recent Economic Crisis ...
Get
... The host-pathogen interaction determines ‘who’s in charge’. In general, if there is an infectious disease, all individuals may be exposed but only some will be infected, and of these only some will be diseased and even fewer of these will die – as genetic component to susceptibility to infection. Dr ...
... The host-pathogen interaction determines ‘who’s in charge’. In general, if there is an infectious disease, all individuals may be exposed but only some will be infected, and of these only some will be diseased and even fewer of these will die – as genetic component to susceptibility to infection. Dr ...
Oct 2-Micro Research
... 2) How is it transmitted? 3) What are the basic effects of acquiring the bacteria or virus (what does it do to the body)? 4) What is known about treatments and cures? 5) How can it be prevented? Make sure you also create a cover page that includes the title and your name. Only print the text for you ...
... 2) How is it transmitted? 3) What are the basic effects of acquiring the bacteria or virus (what does it do to the body)? 4) What is known about treatments and cures? 5) How can it be prevented? Make sure you also create a cover page that includes the title and your name. Only print the text for you ...
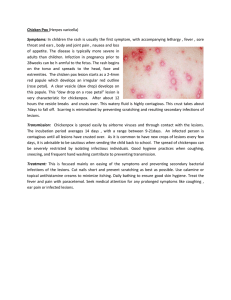
Chicken Pox (Herpes varicella) Symptoms: In children the rash is
... 7days to fall off. Scarring is minimalised by preventing scratching and resulting secondary infections of lesions. Transmission: Chickenpox is spread easily by airborne viruses and through contact with the lesions. The incubation period averages 14 days , with a range between 9-21days. An infected p ...
... 7days to fall off. Scarring is minimalised by preventing scratching and resulting secondary infections of lesions. Transmission: Chickenpox is spread easily by airborne viruses and through contact with the lesions. The incubation period averages 14 days , with a range between 9-21days. An infected p ...
Dr Paul Cotter and Professor Colin Hill
... breakthrough in Listeria research. Scientists have tried for over twenty years scientists to determine why some Listeria monocytogenes are more dangerous than others. Now, for the first time, a factor which may explain this phenomenon has been identified. These findings have even broader implication ...
... breakthrough in Listeria research. Scientists have tried for over twenty years scientists to determine why some Listeria monocytogenes are more dangerous than others. Now, for the first time, a factor which may explain this phenomenon has been identified. These findings have even broader implication ...
Introduction to Pathology
... It is a progressive development of a disease process from its initiation to conclusion in recovery or death. Disease is a dynamic process which progresses from molecular or bio-chemical alternations to structural (ultrastructural, microscopic and gross lesions) and to functional changes which are se ...
... It is a progressive development of a disease process from its initiation to conclusion in recovery or death. Disease is a dynamic process which progresses from molecular or bio-chemical alternations to structural (ultrastructural, microscopic and gross lesions) and to functional changes which are se ...
Bio07_TR__U10_CH40.QXD
... which the air passages become narrower than normal. This may cause coughing and difficulty breathing. Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system attacks the body’s own cells. For example, in Type I diabetes, the immune system attacks cells of the pancreas that make insulin. Other examples of a ...
... which the air passages become narrower than normal. This may cause coughing and difficulty breathing. Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system attacks the body’s own cells. For example, in Type I diabetes, the immune system attacks cells of the pancreas that make insulin. Other examples of a ...
Micro Pub Health Immunology
... The mycoplasmas lack a cell wall C. The mycoplasmas lack a cell membrane D. The mycoplasmas are Gram positive, yet possess an outer membrane ...
... The mycoplasmas lack a cell wall C. The mycoplasmas lack a cell membrane D. The mycoplasmas are Gram positive, yet possess an outer membrane ...
Medicine: Past and Present
... In the middle of the fourteenth century, an epidemic called the Black Plague swept across Europe, Asia and Africa. A plague that swept through the country left few people alive. plague - a disease that kills a large number of people Melissa Lape – Wilson Elementary ...
... In the middle of the fourteenth century, an epidemic called the Black Plague swept across Europe, Asia and Africa. A plague that swept through the country left few people alive. plague - a disease that kills a large number of people Melissa Lape – Wilson Elementary ...
Microbes and Human Disease
... • Invasion allows bacteria to enter safe and nutrient rich environment • Most penetrate via phagocytosis ...
... • Invasion allows bacteria to enter safe and nutrient rich environment • Most penetrate via phagocytosis ...