File - BIOLOGY Mound
... • Leukocytes: white blood cells. • Phagocytes (innate immune system) Macrophages (engulf pathogens) • B cells (produce antibodies) • Antibodies: proteins that …. • Lymphocytes (T cells and mature b cells) – Helper T cells mature after macrophage antigen presentation…. Effector T cells and Memory T c ...
... • Leukocytes: white blood cells. • Phagocytes (innate immune system) Macrophages (engulf pathogens) • B cells (produce antibodies) • Antibodies: proteins that …. • Lymphocytes (T cells and mature b cells) – Helper T cells mature after macrophage antigen presentation…. Effector T cells and Memory T c ...
Natural Killer (NK) cell “memory”
... humans) undergo antigen-driven expansion and persist over time, displaying high effector functions during secondary infection (1-3). Despite these observations, the molecular mechanisms underlying these properties have not been completely elucidated. In particular, it still needs to be clarified whe ...
... humans) undergo antigen-driven expansion and persist over time, displaying high effector functions during secondary infection (1-3). Despite these observations, the molecular mechanisms underlying these properties have not been completely elucidated. In particular, it still needs to be clarified whe ...
3D mapping of cancer metabolism using nano
... The metabolic microenvironment surrounding tumours dramatically influences their growth, proliferation, metastatic potential and response/resistance to treatment. Melanocyte transformation into cancer is associated with significant structural alterations in melanosomes, which protect the cell by sca ...
... The metabolic microenvironment surrounding tumours dramatically influences their growth, proliferation, metastatic potential and response/resistance to treatment. Melanocyte transformation into cancer is associated with significant structural alterations in melanosomes, which protect the cell by sca ...
I. Student misconceptions
... individual antigen-binding sites. False. d. T cell receptors recognize and bind with antigens with the same specificity as B cell receptors. True. ...
... individual antigen-binding sites. False. d. T cell receptors recognize and bind with antigens with the same specificity as B cell receptors. True. ...
Document
... The proliferation of lymphocyte cells due to activation by an antigen Useful in primary (first exposure to antigen) and secondary (subsequent exposure to same antigen) immune responses Results in production of many antibodies against the antigen Primary immune response – 10-17 days before maximum re ...
... The proliferation of lymphocyte cells due to activation by an antigen Useful in primary (first exposure to antigen) and secondary (subsequent exposure to same antigen) immune responses Results in production of many antibodies against the antigen Primary immune response – 10-17 days before maximum re ...
Chapter 16
... Loci most responsible for the most vigorous allograft rejection are within MHC complex ○ Test donors to get matching haplotype Mismatches with Class II are more likely to lead to rejection than mismatches with Class I ○ Also test for blood type ...
... Loci most responsible for the most vigorous allograft rejection are within MHC complex ○ Test donors to get matching haplotype Mismatches with Class II are more likely to lead to rejection than mismatches with Class I ○ Also test for blood type ...
BIOL212Test3Guide30MAY2012
... **** All quizzes and tests are cumulative!! **** For this one, the emphasis will be on Circulation, Respiration, Osmoregulation and Excretion, Immunity, some Reproduction and early Development (Chap. 42, 43, 44, 46 & Sec. 47.1 & 47.2) You should be able to define any term printed in bold in the text ...
... **** All quizzes and tests are cumulative!! **** For this one, the emphasis will be on Circulation, Respiration, Osmoregulation and Excretion, Immunity, some Reproduction and early Development (Chap. 42, 43, 44, 46 & Sec. 47.1 & 47.2) You should be able to define any term printed in bold in the text ...
TOLERANCE
... • To achieve this, the antigen receptors of T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes are generated randomly. • This repertoire will inevitably contain lymphocytes specific for self antigen. • The body must therefore distinguish between self and non-self determinants to avoid AUTOIMMUNITY, • and between dang ...
... • To achieve this, the antigen receptors of T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes are generated randomly. • This repertoire will inevitably contain lymphocytes specific for self antigen. • The body must therefore distinguish between self and non-self determinants to avoid AUTOIMMUNITY, • and between dang ...
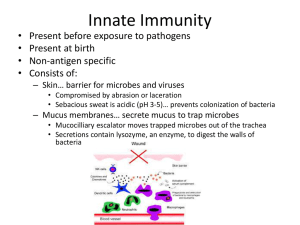
Innate Immunity - Santa Susana High School
... • Once engulfed the phagocyte fuses a lysosome to the vacuole containing the bacteria • Some bacteria evade phagocytes by hiding surface recognition via a ...
... • Once engulfed the phagocyte fuses a lysosome to the vacuole containing the bacteria • Some bacteria evade phagocytes by hiding surface recognition via a ...
Toll-like receptor structure - University of British Columbia
... • SCID--no T or B cells (severe, fatal infections) • AIDS--loss of CD4+ T cells (Intracellular pathogens, fungi, viruses, pyogenic infections, etc.) • Transplant--immunsuppression of T cells (viral, fungal) • Common Variable Immunodeficiency (decreased IgG)--generally mild increase in sinopulmonary ...
... • SCID--no T or B cells (severe, fatal infections) • AIDS--loss of CD4+ T cells (Intracellular pathogens, fungi, viruses, pyogenic infections, etc.) • Transplant--immunsuppression of T cells (viral, fungal) • Common Variable Immunodeficiency (decreased IgG)--generally mild increase in sinopulmonary ...
File
... infer that this organism was multicellular or a single cell? Generally only mulitcellular organisms are visible without a microscope. 3) Describe why cells have limits as to how big or small they can be. If cells are too small, they can’t contain all their necessary parts. If cells are too large, ox ...
... infer that this organism was multicellular or a single cell? Generally only mulitcellular organisms are visible without a microscope. 3) Describe why cells have limits as to how big or small they can be. If cells are too small, they can’t contain all their necessary parts. If cells are too large, ox ...
What causes an immune response and increase of
... 3What is the main difference between lytic and Lysogenic cycles in viruses? • Lytic is the shorter cycle that ends in cell destruction/lysed. Lysogenic is longer and leads into the lytic cycle steps. ...
... 3What is the main difference between lytic and Lysogenic cycles in viruses? • Lytic is the shorter cycle that ends in cell destruction/lysed. Lysogenic is longer and leads into the lytic cycle steps. ...
Saliva - Duplin County Schools
... The Third Line of Defense ~Antibodies~ - Most infections never make it past the first and second levels of defense - Those that do trigger the production and release of antibodies - Proteins that latch onto, damage, clump, and slow foreign particles - Each antibody binds only to one specific bindin ...
... The Third Line of Defense ~Antibodies~ - Most infections never make it past the first and second levels of defense - Those that do trigger the production and release of antibodies - Proteins that latch onto, damage, clump, and slow foreign particles - Each antibody binds only to one specific bindin ...
Innate and adaptive immunity
... • Release of soluble mediators to attract other leukocytes to site of inflammation • Removal of dead or dying cells • Transfer of infectious or toxic material to lymph nodes to initiate adaptive immune response ...
... • Release of soluble mediators to attract other leukocytes to site of inflammation • Removal of dead or dying cells • Transfer of infectious or toxic material to lymph nodes to initiate adaptive immune response ...


















![Riggs_Signal_Transduction-_PAMP_Presentation[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008651685_1-7a9da834997c5984d78c99bc734baadf-300x300.png)