17 Unit 1 - Cloudfront.net
... • From stem cells in red bone marrow • B cells mature in bone marrow • T cells migrate to thymus • During maturation both make particular proteins in plasma membranes = antigen receptors ...
... • From stem cells in red bone marrow • B cells mature in bone marrow • T cells migrate to thymus • During maturation both make particular proteins in plasma membranes = antigen receptors ...
Biol 430 Question Bank Overview
... TCR specific for hen ovalbumin (OVA) each of which also contained a distinctive genetic sequence (“barcode”). The barcode allowed the researchers to track how many antigen-specific T-cells respond to an infection and the total number of these cells that were produced after clonal expansion (all the ...
... TCR specific for hen ovalbumin (OVA) each of which also contained a distinctive genetic sequence (“barcode”). The barcode allowed the researchers to track how many antigen-specific T-cells respond to an infection and the total number of these cells that were produced after clonal expansion (all the ...
Chapter 4 Worksheet
... Both mitochondria and chloroplasts are energy converters, but their functions are quite different. Compare them by filling in the chart below. Chloroplast Mitochondrion Found in the following organisms ...
... Both mitochondria and chloroplasts are energy converters, but their functions are quite different. Compare them by filling in the chart below. Chloroplast Mitochondrion Found in the following organisms ...
Immune System - Crestwood Local Schools
... ago. By then the vertebrate immune defense had been fully evolved. • Sharks have an immune response similar to ...
... ago. By then the vertebrate immune defense had been fully evolved. • Sharks have an immune response similar to ...
The Immune System
... • Antigen must be presented in groove of HLA molecule. • Cytotoxic T cells destroy non-self protein-bearing cells. • Helper T cells secrete cytokines that control the immune response. ...
... • Antigen must be presented in groove of HLA molecule. • Cytotoxic T cells destroy non-self protein-bearing cells. • Helper T cells secrete cytokines that control the immune response. ...
Presentation1
... • Innate Immunity: non specific, Immediate, including physical barriers such as the skin, mucous membranes of GIT, Respiratory and urogenital tracts that prevent penetration of host body. Cell involved are neutrophil, natural killer cells. • Adaptive immunity: acquired, specific, gradual, slower in ...
... • Innate Immunity: non specific, Immediate, including physical barriers such as the skin, mucous membranes of GIT, Respiratory and urogenital tracts that prevent penetration of host body. Cell involved are neutrophil, natural killer cells. • Adaptive immunity: acquired, specific, gradual, slower in ...
SCIENCE
... No copying of other peoples work. You and the person’s paper you are copying will receive a zero on the assignment. ...
... No copying of other peoples work. You and the person’s paper you are copying will receive a zero on the assignment. ...
Cell-mediated Immunity
... • A principal role of CMI is to detect and eliminate cells that harbor intracellular pathogens • The same CMI mechanisms detect and eliminate other “nonself” cells in the body, including tumor cells and cells within transplanted organs • Effector cells that mediate CMI include TH cell subsets (TH1, ...
... • A principal role of CMI is to detect and eliminate cells that harbor intracellular pathogens • The same CMI mechanisms detect and eliminate other “nonself” cells in the body, including tumor cells and cells within transplanted organs • Effector cells that mediate CMI include TH cell subsets (TH1, ...
topic 11 notes
... produces antibodies that gives it immunity. • Passive immunity is when one organism produces antibodies that benefits another organism. Ex: Newborns have passive immunity from antibodies in mothers milk (colostrum), antivenom given after snake bites. ...
... produces antibodies that gives it immunity. • Passive immunity is when one organism produces antibodies that benefits another organism. Ex: Newborns have passive immunity from antibodies in mothers milk (colostrum), antivenom given after snake bites. ...
The Innate Immune Response,
... The thymus and bone marrow are the primary (or central) lymphoid organs, where maturation of lymphocytes takes place. ...
... The thymus and bone marrow are the primary (or central) lymphoid organs, where maturation of lymphocytes takes place. ...
LU Jinhua
... Zhang H, Tay PN, Cao W, Li W and Lu J. (2002) Integrin-nucleated toll-like receptor (TLR) dimerization reveals subcellular targeting of TLRs and distinct mechanisms of TLR4 activation and signaling. FEBS Lett. 532, 171-176 Cao W, Bobryshev YV, Lord RSA, Oakley REI, Lee SH and Lu J. (2003) Dendritic ...
... Zhang H, Tay PN, Cao W, Li W and Lu J. (2002) Integrin-nucleated toll-like receptor (TLR) dimerization reveals subcellular targeting of TLRs and distinct mechanisms of TLR4 activation and signaling. FEBS Lett. 532, 171-176 Cao W, Bobryshev YV, Lord RSA, Oakley REI, Lee SH and Lu J. (2003) Dendritic ...
Specific Host Defense Mechanisms
... • Antibody (Ab) – Immunoglobulins (Ig) – glycoproteins produced by host that bind to antigens an antigenic determinant on the antigen (epitope) – ‘specific’ – recognize and bind to only the antigen that stimulate its initial production (but occasionally, they crossreact) ...
... • Antibody (Ab) – Immunoglobulins (Ig) – glycoproteins produced by host that bind to antigens an antigenic determinant on the antigen (epitope) – ‘specific’ – recognize and bind to only the antigen that stimulate its initial production (but occasionally, they crossreact) ...
Exam 3
... A. the continental shelves B. unglaciated terrain C. sedimentary rock D. igneous rock E. volcanic archipelagos such as Galapagos and Hawaiian Islands ____ 5. An adaptation is _________. A. an individual's attempt to conform to its environment B. a trait that confers a reproductive advantage on the i ...
... A. the continental shelves B. unglaciated terrain C. sedimentary rock D. igneous rock E. volcanic archipelagos such as Galapagos and Hawaiian Islands ____ 5. An adaptation is _________. A. an individual's attempt to conform to its environment B. a trait that confers a reproductive advantage on the i ...
Lecture Notes for Med. Tech. Class
... Medawar’s Experiment of Neonatal Tolerance Induction • Neonatal exposure of allogeneic blood cells causes tolerance to the skin grafts from the blood donor. Central and Peripheral Immunological Tolerance • Theoretically, most endogenous antigens can tolerize the immune cells during their maturation ...
... Medawar’s Experiment of Neonatal Tolerance Induction • Neonatal exposure of allogeneic blood cells causes tolerance to the skin grafts from the blood donor. Central and Peripheral Immunological Tolerance • Theoretically, most endogenous antigens can tolerize the immune cells during their maturation ...
The Lymphatic System
... Cellular Immunity • Types of T cells 1) helper T cells (CD4) 2) cytotoxic T cells (CD8) 3) suppressor T cells 4) memory T cells Helper T cells are involved in most aspects of immunity ...
... Cellular Immunity • Types of T cells 1) helper T cells (CD4) 2) cytotoxic T cells (CD8) 3) suppressor T cells 4) memory T cells Helper T cells are involved in most aspects of immunity ...
Lymphatic
... Cellular Immunity • Types of T cells 1) helper T cells (CD4) 2) cytotoxic T cells (CD8) 3) suppressor T cells 4) memory T cells Helper T cells are involved in most aspects of immunity ...
... Cellular Immunity • Types of T cells 1) helper T cells (CD4) 2) cytotoxic T cells (CD8) 3) suppressor T cells 4) memory T cells Helper T cells are involved in most aspects of immunity ...
Cancer- Powerpoint
... Not all mutations that lead to cancerous cells result in the cells reproducing at a faster, more uncontrolled rate. For example, a mutation may simply cause a cell to keep from self-destructing. All normal cells have surveillance mechanisms that look for damage or for problems with their own control ...
... Not all mutations that lead to cancerous cells result in the cells reproducing at a faster, more uncontrolled rate. For example, a mutation may simply cause a cell to keep from self-destructing. All normal cells have surveillance mechanisms that look for damage or for problems with their own control ...
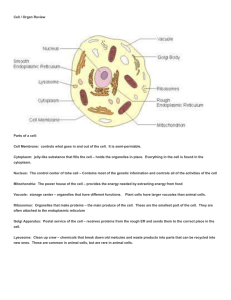
Cell / Organ Review Parts of a cell: Cell Membrane: controls what
... Mitochondria: The power house of the cell – provides the energy needed by extracting energy from food Vacuole: storage center – organelles that have different functions. ...
... Mitochondria: The power house of the cell – provides the energy needed by extracting energy from food Vacuole: storage center – organelles that have different functions. ...