Slide 1
... well as cells infected with virus can “process” and “present” antigens on their cell membrane • MHC molecules aid in this process • By presenting antigens, the immune response is greatly accelerated • Especially important in stimulating early response to previous pathogens ...
... well as cells infected with virus can “process” and “present” antigens on their cell membrane • MHC molecules aid in this process • By presenting antigens, the immune response is greatly accelerated • Especially important in stimulating early response to previous pathogens ...
Immunity
... Respond to an organism’s own cells that have been invaded by non-self (foreign) material eg a virus or a cancer cell. ...
... Respond to an organism’s own cells that have been invaded by non-self (foreign) material eg a virus or a cancer cell. ...
dendritic cells - UCSF Immunology Program
... Immune system and chronic inflammation • Sterile inflammation (tissue injury but no infectious agent present): innate recognition of tissue damage • Chronic inflammation: if antigen persists, antigenreactive T cells can drive continued inflammation, which can cause tissue damage (autoimmune disease ...
... Immune system and chronic inflammation • Sterile inflammation (tissue injury but no infectious agent present): innate recognition of tissue damage • Chronic inflammation: if antigen persists, antigenreactive T cells can drive continued inflammation, which can cause tissue damage (autoimmune disease ...
EN90027_Imunology
... Students must acquire the basic and up-to-date concepts of immunology, in order to understand the importance of the various functions of the immune system as fundamental component of balance and maintenance of health. Students must recognize the relevance changes to such balance in the etiology of s ...
... Students must acquire the basic and up-to-date concepts of immunology, in order to understand the importance of the various functions of the immune system as fundamental component of balance and maintenance of health. Students must recognize the relevance changes to such balance in the etiology of s ...
Systemic lupus erythematosus
... The disease is characterised by the production of ‘self’ (auto) antibodies (directed against nuclear ‘self’ (auto) antigens), inflammation and organ damage. The presence of antinuclear antibodies has been detected in the serum of a majority of patients before the onset of clinical disease symptoms, ...
... The disease is characterised by the production of ‘self’ (auto) antibodies (directed against nuclear ‘self’ (auto) antigens), inflammation and organ damage. The presence of antinuclear antibodies has been detected in the serum of a majority of patients before the onset of clinical disease symptoms, ...
Chapter 1: Abstract
... inappropriate in controlling certain microbes and as a result serious infection develops. The TH1 response, on the other hand, may result in the resolution of the severe infection. In this study, we attempted to determine if leptin, cyclosporin A (CsA), and/or FK506 could switch the immune response ...
... inappropriate in controlling certain microbes and as a result serious infection develops. The TH1 response, on the other hand, may result in the resolution of the severe infection. In this study, we attempted to determine if leptin, cyclosporin A (CsA), and/or FK506 could switch the immune response ...
When a person breaks a bone, suffers infection organ damage or
... and the creation of cell processing centers. In the field of immunology, Proneuron hopes to develop drugs based on its identification of a small peptide called 'Immune Privilege Factor' (IPF), which has potent immunosuppressive and antiinflammatory properties. IPF is found in the brain and "works li ...
... and the creation of cell processing centers. In the field of immunology, Proneuron hopes to develop drugs based on its identification of a small peptide called 'Immune Privilege Factor' (IPF), which has potent immunosuppressive and antiinflammatory properties. IPF is found in the brain and "works li ...
File
... the immune system to shut down Phagocytes clean up any dead or injured B and T cells that remain ...
... the immune system to shut down Phagocytes clean up any dead or injured B and T cells that remain ...
Immune Topics - Cathedral High School
... Organ Transplants • There is a brief period before attack after a transplant where the patient feels relieved, but this is quickly disrupted by the T cell lymphocyte attacks (killer T cells) • Upon response, antirejection drugs (often toxic) are dispensed to the patient. ...
... Organ Transplants • There is a brief period before attack after a transplant where the patient feels relieved, but this is quickly disrupted by the T cell lymphocyte attacks (killer T cells) • Upon response, antirejection drugs (often toxic) are dispensed to the patient. ...
Foundation Block Lecture Two Natural defense mechanism
... 1 - Which of the following physical innate immunity ? a) Vomiting. b) saliva, c) hepcidins) d) Mucous membranes 2- serve as a link between the adaptive and innate immunity ? a) plasma cell b) neutrophile c) Monocytes d) eosinophile 3- which complement system pathway Activated by bacterial products ? ...
... 1 - Which of the following physical innate immunity ? a) Vomiting. b) saliva, c) hepcidins) d) Mucous membranes 2- serve as a link between the adaptive and innate immunity ? a) plasma cell b) neutrophile c) Monocytes d) eosinophile 3- which complement system pathway Activated by bacterial products ? ...
Powerpoint - UCSF Immunology Program
... Immune system and chronic inflammation • Sterile inflammation (tissue injury but no infectious agent present): innate recognition of tissue damage • Chronic inflammation: if antigen persists, antigenreactive T cells can drive continued inflammation, which can cause tissue damage (autoimmune disease ...
... Immune system and chronic inflammation • Sterile inflammation (tissue injury but no infectious agent present): innate recognition of tissue damage • Chronic inflammation: if antigen persists, antigenreactive T cells can drive continued inflammation, which can cause tissue damage (autoimmune disease ...
immunesystem
... AIDS – attacks cells that bear CD4 molecules on their surface, once inside a cell it reverse transcripts itself and integrates the newly formed DNA into the host cell genome. Allergies - are a result of an immune system that responds to a "false alarm." When a harmless substance such as dust, mold, ...
... AIDS – attacks cells that bear CD4 molecules on their surface, once inside a cell it reverse transcripts itself and integrates the newly formed DNA into the host cell genome. Allergies - are a result of an immune system that responds to a "false alarm." When a harmless substance such as dust, mold, ...
Chimeric Immune System
... T cells and B cells: white blood cells, more specific forms of protection ...
... T cells and B cells: white blood cells, more specific forms of protection ...
Kuby Immunology 6/e - Dr. Jennifer Capers, PhD
... ○ Early genes (1-2 hours from recognition) IL-2, IL2R, IL-6, IFN-γ ○ Late genes (more than 2 days later) Encode adhesion molecules ...
... ○ Early genes (1-2 hours from recognition) IL-2, IL2R, IL-6, IFN-γ ○ Late genes (more than 2 days later) Encode adhesion molecules ...
abstract
... The presence of DNA and aberrant RNA in the cytoplasm is a danger signal that alerts the host immune system to eliminate microbial infections and malignant cells, but inappropriate activation of these pathways can also lead to autoimmune diseases such as lupus. My talk will focus on our recent disco ...
... The presence of DNA and aberrant RNA in the cytoplasm is a danger signal that alerts the host immune system to eliminate microbial infections and malignant cells, but inappropriate activation of these pathways can also lead to autoimmune diseases such as lupus. My talk will focus on our recent disco ...
Lecture 5 T Cell-Mediated Immunity
... Polypeptides produced by a variety of cell types including T lymphocytes used for communications between cells. Cytokine production is triggered by specific receptor binding and subsequent signal transduction pathways Cytokine repertoire is dependent on cell type triggered, receptors present on that ...
... Polypeptides produced by a variety of cell types including T lymphocytes used for communications between cells. Cytokine production is triggered by specific receptor binding and subsequent signal transduction pathways Cytokine repertoire is dependent on cell type triggered, receptors present on that ...
IMMUNOLOGICAL TOLERANCE
... inducing tolerance in specific lymphocytes Induction of immunological tolerance may be exploited as a therapeutic approach for preventing harmful immune responses ...
... inducing tolerance in specific lymphocytes Induction of immunological tolerance may be exploited as a therapeutic approach for preventing harmful immune responses ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
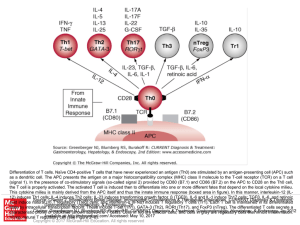
... Differentiation of T cells. Naïve CD4-positive T cells that have never experienced an antigen (Th0) are stimulated by an antigen-presenting cell (APC) such as a dendritic cell. The APC presents the antigen on a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecule to the T-cell receptor (TCR) on ...
... Differentiation of T cells. Naïve CD4-positive T cells that have never experienced an antigen (Th0) are stimulated by an antigen-presenting cell (APC) such as a dendritic cell. The APC presents the antigen on a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecule to the T-cell receptor (TCR) on ...
File - Pomp
... Innate Immunity: 5 types of Leukocytes • Eosinophils • 1.5% WBCs; destroy large parasitic invaders • Enzymatic action- no phagocytosis • Natural killer (NK) cells • destroy virus-infected body cells & abnormal cells • apoptosis ...
... Innate Immunity: 5 types of Leukocytes • Eosinophils • 1.5% WBCs; destroy large parasitic invaders • Enzymatic action- no phagocytosis • Natural killer (NK) cells • destroy virus-infected body cells & abnormal cells • apoptosis ...