Immune System
... • Process: T cells divide and differentiate into… ▫ Killer T cells – destroy bacteria, fungi, protozoan or foreign tissue with the antigen ▫ Helper T cells – produce memory T cells ▫ Suppressor T cells – shut down killer T cells after pathogenic cells brought under control ▫ Memory T cells – cause r ...
... • Process: T cells divide and differentiate into… ▫ Killer T cells – destroy bacteria, fungi, protozoan or foreign tissue with the antigen ▫ Helper T cells – produce memory T cells ▫ Suppressor T cells – shut down killer T cells after pathogenic cells brought under control ▫ Memory T cells – cause r ...
White Blood Cell Lab
... • Leukopoiesis – pluripotent stem cells – most WBCs develop in the bone marrow – T lymphocytes complete development in thymus ...
... • Leukopoiesis – pluripotent stem cells – most WBCs develop in the bone marrow – T lymphocytes complete development in thymus ...
Document
... Helps discriminate between “self” and “nonself” Pathogen - Definition: – Any disease causing agent (microorganisms) ...
... Helps discriminate between “self” and “nonself” Pathogen - Definition: – Any disease causing agent (microorganisms) ...
introduction to the immune system
... (1) ANTIBODY MEDIATED IMMUNITY-provided by the antibodies in the body fluid--produced by lymphocytes-B CELLS Antibodies bind to bacteria and their toxins and to free viruses inactivating them temporarily and marking them for destruction by phagocytes or complement (2) CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY-provided ...
... (1) ANTIBODY MEDIATED IMMUNITY-provided by the antibodies in the body fluid--produced by lymphocytes-B CELLS Antibodies bind to bacteria and their toxins and to free viruses inactivating them temporarily and marking them for destruction by phagocytes or complement (2) CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY-provided ...
PowerPoint **
... Pyroptosis---a highly inflammatory form of cell death that lures more CD4 T cells to the area, thereby creating a vicious cycle that ultimately wreaks havoc on the immune system. IFI16, which is known to be part of the protein complex that initiates inflammatory immune responses. An existing caspas ...
... Pyroptosis---a highly inflammatory form of cell death that lures more CD4 T cells to the area, thereby creating a vicious cycle that ultimately wreaks havoc on the immune system. IFI16, which is known to be part of the protein complex that initiates inflammatory immune responses. An existing caspas ...
Tsunamis collide and grow taller
... during the early days of infection. And it seems that the more vigorous this response by CD4 T cells is, the greater an HIV-positive person’s chance is of being able to maintain a relatively low viral level and the better their disease outcome is likely to be. Hendrik Streeck at the Ragon Institute ...
... during the early days of infection. And it seems that the more vigorous this response by CD4 T cells is, the greater an HIV-positive person’s chance is of being able to maintain a relatively low viral level and the better their disease outcome is likely to be. Hendrik Streeck at the Ragon Institute ...
Aseptic Technique: Media and Equipment
... in body secretions in respiratory and GI tracts, in tears and saliva, and in the 1st milk secreted by a nursing mother – 4. IgE – monomer that is involved in ...
... in body secretions in respiratory and GI tracts, in tears and saliva, and in the 1st milk secreted by a nursing mother – 4. IgE – monomer that is involved in ...
Immune Memory and Vaccines
... • Two ways to acquire this kind of active immunity* (active because the body actively produces antibodies to trigger a quick secondary response) – Naturally acquired active immunity: example— common cold viruses – “Artificially” acquired active immunity: Vaccines… *Passive immunity: Antibodies come ...
... • Two ways to acquire this kind of active immunity* (active because the body actively produces antibodies to trigger a quick secondary response) – Naturally acquired active immunity: example— common cold viruses – “Artificially” acquired active immunity: Vaccines… *Passive immunity: Antibodies come ...
Document
... (SEB (staphylococcal enterotoxin B) -> cannot induce EAE, but relapse and exacerbate EAE) • reactivation of bacterial cell wall or collagen-induced arthritis ...
... (SEB (staphylococcal enterotoxin B) -> cannot induce EAE, but relapse and exacerbate EAE) • reactivation of bacterial cell wall or collagen-induced arthritis ...
Type of Innate immune
... antibodies; most proteins and foreign red cells are examples. Thymus-independent antigens require no T-cell cooperation for antibody production; they directly stimulate specific B lymphocytes by virtue of their ability to cross-link antigen receptors on the B-cell surface, produce predominantly IgM ...
... antibodies; most proteins and foreign red cells are examples. Thymus-independent antigens require no T-cell cooperation for antibody production; they directly stimulate specific B lymphocytes by virtue of their ability to cross-link antigen receptors on the B-cell surface, produce predominantly IgM ...
(2) Viral and bacterial superantigens
... (SEB (staphylococcal enterotoxin B) -> cannot induce EAE, but relapse and exacerbate EAE) • reactivation of bacterial cell wall or collagen-induced arthritis ...
... (SEB (staphylococcal enterotoxin B) -> cannot induce EAE, but relapse and exacerbate EAE) • reactivation of bacterial cell wall or collagen-induced arthritis ...
No Slide Title
... lymphocytes and plasma cells What is immunity? origin and immunocompetence ...
... lymphocytes and plasma cells What is immunity? origin and immunocompetence ...
Human Health
... b) The individual has recovered from the infection. The level of plasma antibodies is raised and this protects from immediate, short term re-infection. There will be significant numbers of Bm cells present in the various lymph nodes. c) Second Infection with the same antigen d) The result is a rapid ...
... b) The individual has recovered from the infection. The level of plasma antibodies is raised and this protects from immediate, short term re-infection. There will be significant numbers of Bm cells present in the various lymph nodes. c) Second Infection with the same antigen d) The result is a rapid ...
Natural Defence - MedicalBooks.com
... antibody is designed to combat a particular antigen, or foreign protein. Two types of white blood cells are involved in this process. B cells release the antibody, which attaches to the outer covering of the antigen, marking it for destruction. T cells attack the tagged antigen and also stimulate B ...
... antibody is designed to combat a particular antigen, or foreign protein. Two types of white blood cells are involved in this process. B cells release the antibody, which attaches to the outer covering of the antigen, marking it for destruction. T cells attack the tagged antigen and also stimulate B ...
General Defence System - leavingcertbiology.net
... types of antigen and respond to them in a variety of ways – Two types: • B-cells: produced and mature in bone marrow and then migrate to lymphoid tissue – such as lymph ...
... types of antigen and respond to them in a variety of ways – Two types: • B-cells: produced and mature in bone marrow and then migrate to lymphoid tissue – such as lymph ...
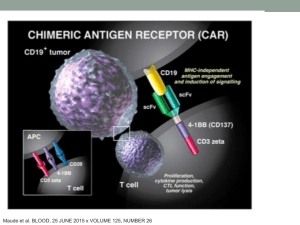
CAR T cell lecture 11.25
... Complications of CAR T cells • Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) • Typically within 5 days and CRP best predictor • Exponential T cell proliferation leads to IL2, IL6, IFN • Can lead to macrophage activation syndrome and ...
... Complications of CAR T cells • Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) • Typically within 5 days and CRP best predictor • Exponential T cell proliferation leads to IL2, IL6, IFN • Can lead to macrophage activation syndrome and ...
... leads to immune response also in other compartments of MALT. • IgA is a predominant immunoglobulin secreted through the epitelial cells. • Oral administration of antigens frequently leads to induction of immune tolerance. • Intraepitelial lymphocytes - CD8+, restricted antigenic specificity. ...
Chapter 17: Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response
... 4. An antigen is a chemical substance that causes the body to produce specific antibodies and can combine with these antibodies. A hapten is a low-molecular-weight substance that is not antigenic unless it is attached to a carrier molecule. Once an antibody has been formed against the hapten, the ha ...
... 4. An antigen is a chemical substance that causes the body to produce specific antibodies and can combine with these antibodies. A hapten is a low-molecular-weight substance that is not antigenic unless it is attached to a carrier molecule. Once an antibody has been formed against the hapten, the ha ...
Immune/Lympathic
... Capable of becoming multi drug-resistant AIDS is the final stage of the HIV infection Average incubation period for AIDS development is 10 years from point of infection Characterized by opportunistic infections There is no cure ...
... Capable of becoming multi drug-resistant AIDS is the final stage of the HIV infection Average incubation period for AIDS development is 10 years from point of infection Characterized by opportunistic infections There is no cure ...
Chapter 13: Lymphatics
... 5. Which cell types engage in nonspecific immunity? 6. Which types of cells become activated in specific (adaptive) immunity? 7. What distinguishes the humoral response from the cellular immune response? 8. What are the three recognized types of lymphocytes? 9. What are the categories of supporting ...
... 5. Which cell types engage in nonspecific immunity? 6. Which types of cells become activated in specific (adaptive) immunity? 7. What distinguishes the humoral response from the cellular immune response? 8. What are the three recognized types of lymphocytes? 9. What are the categories of supporting ...
Immunity
... • Non specific = first (skin) and second (inflammatory response) line of defenses; are effective against many different kinds of pathogens • Specific = third line (white blood cells) are effective against a specific pathogen ...
... • Non specific = first (skin) and second (inflammatory response) line of defenses; are effective against many different kinds of pathogens • Specific = third line (white blood cells) are effective against a specific pathogen ...