8.3 Bonding Theories - Chemistry with Mr. Saval
... 8.3 Bonding Theories > Glossary Terms • tetrahedral angle: a bond angle of 109.5° that results when a central atom forms four bonds directed toward the center of a regular tetrahedron • VSEPR theory: valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory; because electron pairs repel, molecules adjust their ...
... 8.3 Bonding Theories > Glossary Terms • tetrahedral angle: a bond angle of 109.5° that results when a central atom forms four bonds directed toward the center of a regular tetrahedron • VSEPR theory: valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory; because electron pairs repel, molecules adjust their ...
chem learning objectives
... d. Students know the atoms and molecules in liquids move in a random pattern relative to one another because the intermolecular forces are too weak to hold the atoms or molecules in a solid form. II.I.I 9-10 e. Students know how to draw Lewis dot structures for both ions and molecules. f. *Students ...
... d. Students know the atoms and molecules in liquids move in a random pattern relative to one another because the intermolecular forces are too weak to hold the atoms or molecules in a solid form. II.I.I 9-10 e. Students know how to draw Lewis dot structures for both ions and molecules. f. *Students ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... the empirical formula for isopropyl alcohol, a task that requires us to calculate the number of moles of C, H, and O in the sample. Plan We can use the mole concept to calculate the number of grams of C present in the CO 2 and the number of grams of H present in the H2O. These amounts are the quanti ...
... the empirical formula for isopropyl alcohol, a task that requires us to calculate the number of moles of C, H, and O in the sample. Plan We can use the mole concept to calculate the number of grams of C present in the CO 2 and the number of grams of H present in the H2O. These amounts are the quanti ...
Chemistry@YIA – additional information
... Second is the quantity of material that you have to cover and sorting out what’s important. It’s useful to identify patterns that you can then ‘hang’ facts on as you need them. Third, and most importantly, getting sufficient detail into your written answers is crucial. Very often students know the f ...
... Second is the quantity of material that you have to cover and sorting out what’s important. It’s useful to identify patterns that you can then ‘hang’ facts on as you need them. Third, and most importantly, getting sufficient detail into your written answers is crucial. Very often students know the f ...
chemical equation - HCC Learning Web
... Writing and Balancing the Equation for a Chemical Reaction 1. Determine what reaction is occurring. What are the reactants, the products, and the physical states involved? 2. Write the unbalanced equation that summarizes the reaction described in step 1. 3. Balance the equation by inspection, start ...
... Writing and Balancing the Equation for a Chemical Reaction 1. Determine what reaction is occurring. What are the reactants, the products, and the physical states involved? 2. Write the unbalanced equation that summarizes the reaction described in step 1. 3. Balance the equation by inspection, start ...
2015_Final Exam Study Guide
... A bond is classified as nonpolar covalent if the difference in the electronegativities between the 2 atoms is a. 2.1 or more. c. less than 0.4. b. between 0.5 and 2. d. less than zero. Which of the following does a structural formula reveal about chemical bonds? a. their arrangement in space c. both ...
... A bond is classified as nonpolar covalent if the difference in the electronegativities between the 2 atoms is a. 2.1 or more. c. less than 0.4. b. between 0.5 and 2. d. less than zero. Which of the following does a structural formula reveal about chemical bonds? a. their arrangement in space c. both ...
Lab 1
... When adding numbers alien the numbers over the decimal, and look for the number with the least amount of accuracy to the right. In this example 2nd, 5th, and 7th numbers only have accuracy 4 places to the right, so the final number can only have 4 places past the decimal of ...
... When adding numbers alien the numbers over the decimal, and look for the number with the least amount of accuracy to the right. In this example 2nd, 5th, and 7th numbers only have accuracy 4 places to the right, so the final number can only have 4 places past the decimal of ...
Atomic Model Timeline
... they are eternal, and always moving. He made a theory on this to explain why and how atoms were so small, and what they were about. He proposed a more advance atomic theory. http://www.philosophyprofessor.com/images/philosophers/democritus.jpg ...
... they are eternal, and always moving. He made a theory on this to explain why and how atoms were so small, and what they were about. He proposed a more advance atomic theory. http://www.philosophyprofessor.com/images/philosophers/democritus.jpg ...
Unit 12 Math and Moles
... • Phases of matter for each substance. • Possibly some reference to energy changes in the reaction. ...
... • Phases of matter for each substance. • Possibly some reference to energy changes in the reaction. ...
CLASS X carbon and its compound
... 5. Other pure crystalline forms of carbon are graphite and fullerenes. In Buckminsterfullerene, each molecule has 60 atoms arranged in hexagons and pentagons. 6. Organic Chemistry : The branch of chemistry dealing with carbon compounds other than carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and carbonates is cal ...
... 5. Other pure crystalline forms of carbon are graphite and fullerenes. In Buckminsterfullerene, each molecule has 60 atoms arranged in hexagons and pentagons. 6. Organic Chemistry : The branch of chemistry dealing with carbon compounds other than carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and carbonates is cal ...
Answers to examination questions
... There is a decrease in ionic radii from P3−, S2− to Cl−: all the ions have the electron arrangement of 2,8,8 (that is, they are isoelectronic), however, there is a progressive increase in the nuclear charge due to the additional protons: the phosphide ion has 15 protons, the sulfide ion has 16 proto ...
... There is a decrease in ionic radii from P3−, S2− to Cl−: all the ions have the electron arrangement of 2,8,8 (that is, they are isoelectronic), however, there is a progressive increase in the nuclear charge due to the additional protons: the phosphide ion has 15 protons, the sulfide ion has 16 proto ...
BURNERS AND FLAMES:
... One way of viewing the energy levels in an atom is by picturing a stairway. Each stair represents an energy level. Added energy can kick an electron up to a higher level like a ball could be kicked up to a higher step on a stairway. A ball that has been kicked up the stairs will fall back down the s ...
... One way of viewing the energy levels in an atom is by picturing a stairway. Each stair represents an energy level. Added energy can kick an electron up to a higher level like a ball could be kicked up to a higher step on a stairway. A ball that has been kicked up the stairs will fall back down the s ...
What Can I Do With a Major In Chemistry
... analytical chemistry, biochemistry, inorganic chemistry, organic chemistry and physical chemistry. Analytical chemistry is the study of the physical and chemical properties of compounds and mixtures through qualitative and quantitative analyses. Biochemistry is the study of chemical processes in and ...
... analytical chemistry, biochemistry, inorganic chemistry, organic chemistry and physical chemistry. Analytical chemistry is the study of the physical and chemical properties of compounds and mixtures through qualitative and quantitative analyses. Biochemistry is the study of chemical processes in and ...
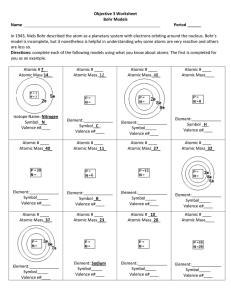
Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name Period In 1943, Niels
... Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name ...
... Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name ...
2 The Nature of Matter
... Boiling is the vigorous bubbling that occurs within the body of a liquid as it vaporizes internally. A bubble is a quantity of gas or vapour surrounded by liquid. Imagine a pot of water being heated (Figure 2.1.6). Some molecules at the bottom of the pot are receiving so much heat and consequently m ...
... Boiling is the vigorous bubbling that occurs within the body of a liquid as it vaporizes internally. A bubble is a quantity of gas or vapour surrounded by liquid. Imagine a pot of water being heated (Figure 2.1.6). Some molecules at the bottom of the pot are receiving so much heat and consequently m ...
intermediate chemistry may 2011 marking scheme
... as its molecules separate easily. (1) Since the molecules do not carry a charge, the substance does not conduct current. (1) e) Benzene molecules consist of a regular hexagon of six carbon atoms; all the carbon to carbon bonds are of equal length which is intermediate between that of a single and a ...
... as its molecules separate easily. (1) Since the molecules do not carry a charge, the substance does not conduct current. (1) e) Benzene molecules consist of a regular hexagon of six carbon atoms; all the carbon to carbon bonds are of equal length which is intermediate between that of a single and a ...
ChemistryReview
... b. twice the number of protons in one atom of the element. c. a ratio based on the mass of a carbon-12 atom. d. a weighted average of the masses of an element’s isotopes. ...
... b. twice the number of protons in one atom of the element. c. a ratio based on the mass of a carbon-12 atom. d. a weighted average of the masses of an element’s isotopes. ...
8.3 Bonding Theories
... 8.3 Bonding Theories > Glossary Terms • tetrahedral angle: a bond angle of 109.5° that results when a central atom forms four bonds directed toward the center of a regular tetrahedron • VSEPR theory: valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory; because electron pairs repel, molecules adjust their ...
... 8.3 Bonding Theories > Glossary Terms • tetrahedral angle: a bond angle of 109.5° that results when a central atom forms four bonds directed toward the center of a regular tetrahedron • VSEPR theory: valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory; because electron pairs repel, molecules adjust their ...
Chemistry 121: Topic 2 - From Atoms to Stoichiometry Topic 2
... of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass, and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. ¾ Compounds are composed of atoms of more than one element. In any compound, the ratio of the numbers of atoms of any two of the element ...
... of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass, and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. ¾ Compounds are composed of atoms of more than one element. In any compound, the ratio of the numbers of atoms of any two of the element ...
Ch08 Lesson08_3
... 8.3 Bonding Theories > Glossary Terms • tetrahedral angle: a bond angle of 109.5° that results when a central atom forms four bonds directed toward the center of a regular tetrahedron • VSEPR theory: valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory; because electron pairs repel, molecules adjust their ...
... 8.3 Bonding Theories > Glossary Terms • tetrahedral angle: a bond angle of 109.5° that results when a central atom forms four bonds directed toward the center of a regular tetrahedron • VSEPR theory: valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory; because electron pairs repel, molecules adjust their ...
System International Base Units
... Lewis structures for compounds Draw element with most unpaired electrons in center Draw other elements around center element (s) such that their unpaired electrons face each other, then connect the unpaired electrons All atoms should have eight electrons around them (remember dashes represent ...
... Lewis structures for compounds Draw element with most unpaired electrons in center Draw other elements around center element (s) such that their unpaired electrons face each other, then connect the unpaired electrons All atoms should have eight electrons around them (remember dashes represent ...
8.3 Bonding Theories - Pittsfield High School
... 8.3 Bonding Theories > Glossary Terms • tetrahedral angle: a bond angle of 109.5° that results when a central atom forms four bonds directed toward the center of a regular tetrahedron • VSEPR theory: valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory; because electron pairs repel, molecules adjust their ...
... 8.3 Bonding Theories > Glossary Terms • tetrahedral angle: a bond angle of 109.5° that results when a central atom forms four bonds directed toward the center of a regular tetrahedron • VSEPR theory: valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory; because electron pairs repel, molecules adjust their ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.