Reading 2.1 A Return to Isotopes
... Notice that because the lithium atom always has protons, the atomic number for lithium is always Z = 3. The mass number, however, is A = 6 for the isotope with 3 neutrons, and A = 7 for the isotope with 4 neutrons. In nature, only certain isotopes exist. For instance, stable lithium exists as an iso ...
... Notice that because the lithium atom always has protons, the atomic number for lithium is always Z = 3. The mass number, however, is A = 6 for the isotope with 3 neutrons, and A = 7 for the isotope with 4 neutrons. In nature, only certain isotopes exist. For instance, stable lithium exists as an iso ...
2 - AQA
... find by weighing. Instead, the masses of atoms are compared and relative masses are used. This was done in the past by defining the relative atomic mass of hydrogen, the lightest element, as 1. The average mass of an atom of oxygen (for example) is 16 times heavier, to the nearest whole number, so o ...
... find by weighing. Instead, the masses of atoms are compared and relative masses are used. This was done in the past by defining the relative atomic mass of hydrogen, the lightest element, as 1. The average mass of an atom of oxygen (for example) is 16 times heavier, to the nearest whole number, so o ...
3. What is the empirical formula of a compound that is
... As you learned in health and biology, food energy typically comes from carbohydrates, proteins and fats. The amount of energy that the body can use per gram of these substances is not the same. The following balanced exothermic reaction represents combustion (respiration) of glucose (a carbohydrate) ...
... As you learned in health and biology, food energy typically comes from carbohydrates, proteins and fats. The amount of energy that the body can use per gram of these substances is not the same. The following balanced exothermic reaction represents combustion (respiration) of glucose (a carbohydrate) ...
program
... • detecting the presence of oxygen, hydrogen, water, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide. Acids and bases The candidate can sb17 recognise the following substances/solutions as an acid/acidic solution: • hydrogen chloride/hydrochloric acid; ...
... • detecting the presence of oxygen, hydrogen, water, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide. Acids and bases The candidate can sb17 recognise the following substances/solutions as an acid/acidic solution: • hydrogen chloride/hydrochloric acid; ...
Week 2
... • Four different oxides of nitrogen can be formed, by combining 28 g of nitrogen with: • 16 g oxygen, forming Compound I • 48 g oxygen, forming Compound II • 64 g oxygen, forming Compound III • 80 g oxygen, forming Compound IV ...
... • Four different oxides of nitrogen can be formed, by combining 28 g of nitrogen with: • 16 g oxygen, forming Compound I • 48 g oxygen, forming Compound II • 64 g oxygen, forming Compound III • 80 g oxygen, forming Compound IV ...
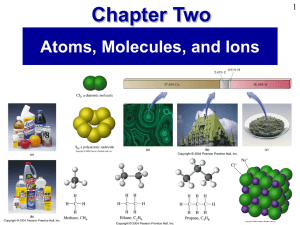
Prentice Hall Ch 02 Atoms Molecules Ions
... General Chemistry 4th edition, Hill, Petrucci, McCreary, Perry ...
... General Chemistry 4th edition, Hill, Petrucci, McCreary, Perry ...
4 - WebAssign
... Valence electrons are transferred or shared when chemical bonds form. Lewis structures of representative elements consist of the element’s symbol and one dot for each valence electron. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
... Valence electrons are transferred or shared when chemical bonds form. Lewis structures of representative elements consist of the element’s symbol and one dot for each valence electron. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
CHEM MINI-COURSE SERIES M1.2___
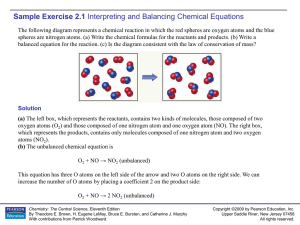
... This equation as written is unbalanced. On the left side of the arrow (reactant side), there are 2 atoms of oxygen. On the right side of the arrow (product side), there is only one atom of oxygen. A quick-and-easy attempt to balance the two sides may be to add a subscript to the H2O formula, so it a ...
... This equation as written is unbalanced. On the left side of the arrow (reactant side), there are 2 atoms of oxygen. On the right side of the arrow (product side), there is only one atom of oxygen. A quick-and-easy attempt to balance the two sides may be to add a subscript to the H2O formula, so it a ...
Introduction to Periodic Table
... Could mean a single atom of that element (Ar or H). Could mean molecules of an element (H2), which is hydrogen found in its natural state. Could mean atoms of elements are present in some form (sodium found in the human body). Look at each particular case to determine its proper use. ...
... Could mean a single atom of that element (Ar or H). Could mean molecules of an element (H2), which is hydrogen found in its natural state. Could mean atoms of elements are present in some form (sodium found in the human body). Look at each particular case to determine its proper use. ...
New Title
... Use Target Reading Skills After you read the section, reread the paragraphs that contain definitions of Key Terms. Use all of the information you have learned to write a meaningful sentence using each Key Term. a. chemical equation: ____________________________________________________ ...
... Use Target Reading Skills After you read the section, reread the paragraphs that contain definitions of Key Terms. Use all of the information you have learned to write a meaningful sentence using each Key Term. a. chemical equation: ____________________________________________________ ...
Sample Exercise 2.1
... Analyze We are given the number of moles and the name of a substance and asked to calculate the number of grams in the sample. Plan To convert moles to grams, we need the molar mass, which we can calculate using the chemical formula and atomic weights. Solve Because the calcium ion is Ca2+ and the n ...
... Analyze We are given the number of moles and the name of a substance and asked to calculate the number of grams in the sample. Plan To convert moles to grams, we need the molar mass, which we can calculate using the chemical formula and atomic weights. Solve Because the calcium ion is Ca2+ and the n ...
Chemical calculations review
... How many moles of oxygen are needed for the complete combustion of 3.0 moles of CH4(g)? 1. 6.0 moles ...
... How many moles of oxygen are needed for the complete combustion of 3.0 moles of CH4(g)? 1. 6.0 moles ...
Chapter 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... in living organisms, were distinctly different from inorganic compounds found in the nonliving world. Though this suggestion is now known to be incorrect, it stimulated important research into organic compounds. Who suggested this? A) Stanley Miller B) Jakob Berzelius C) Friedrich Wohler D) Hermann ...
... in living organisms, were distinctly different from inorganic compounds found in the nonliving world. Though this suggestion is now known to be incorrect, it stimulated important research into organic compounds. Who suggested this? A) Stanley Miller B) Jakob Berzelius C) Friedrich Wohler D) Hermann ...
Chapter 3
... 3.7 Chemical Equations Chemical change involves reorganization of the atoms in one or more substances. Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, or ener ...
... 3.7 Chemical Equations Chemical change involves reorganization of the atoms in one or more substances. Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, or ener ...
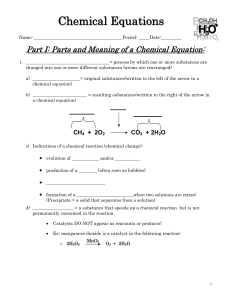
Chemical Equations
... e) remember the rules for writing formulas for molecular compounds (______________) • Only NONMETALS! f) remember the formula for water, ________ • HOH = hydrogen hydroxide 3. Write a balanced chemical equation by adding_____________________, NOT subscripts (this will require trial and error, the f ...
... e) remember the rules for writing formulas for molecular compounds (______________) • Only NONMETALS! f) remember the formula for water, ________ • HOH = hydrogen hydroxide 3. Write a balanced chemical equation by adding_____________________, NOT subscripts (this will require trial and error, the f ...
Electrons
... limitation on how precisely we can know both the location and momentum of any object. ...
... limitation on how precisely we can know both the location and momentum of any object. ...
Chemistry Transition Information
... Calcium atoms each lose two electrons to form calcium ions. Chlorine atoms each gain one electron to form chloride ions. This means that calcium atoms react with chlorine atoms in the ratio of one calcium atom for every two chlorine atoms. Complete the following diagram to show the electronic struct ...
... Calcium atoms each lose two electrons to form calcium ions. Chlorine atoms each gain one electron to form chloride ions. This means that calcium atoms react with chlorine atoms in the ratio of one calcium atom for every two chlorine atoms. Complete the following diagram to show the electronic struct ...
Unit 1 Ch. 2,3,4 notes NEW
... ratio of elements in a compound. A molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms in a molecule of a compound. Ionic compounds are always written as empirical formulas 2:29 AM ...
... ratio of elements in a compound. A molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms in a molecule of a compound. Ionic compounds are always written as empirical formulas 2:29 AM ...
mole concept and stoichiometry
... 2.5 Gay Lussac’s Law of combining Volumes Sir Gay Lussac found the relationship existing between the volumes of the gaseous reactants and their products. In 1808, he put forward a generalization known as the Gay Lussac’s Law of combining volumes. According to this Law “When gases react together, the ...
... 2.5 Gay Lussac’s Law of combining Volumes Sir Gay Lussac found the relationship existing between the volumes of the gaseous reactants and their products. In 1808, he put forward a generalization known as the Gay Lussac’s Law of combining volumes. According to this Law “When gases react together, the ...
CML738 Elias 2017 fluorine chemistry
... flooring while releasing a deadly cloud of gas containing vapours that corroded every surface it came into contact with. The Nazis who discovered this compound were interested in its military applications. They were possibly fascinated by its property of melting concrete and reacting with water. It ...
... flooring while releasing a deadly cloud of gas containing vapours that corroded every surface it came into contact with. The Nazis who discovered this compound were interested in its military applications. They were possibly fascinated by its property of melting concrete and reacting with water. It ...
3.2 MB - KFUPM Resources v3
... 100% - % mass C - % mass H = % mass O = 53.2% O (c) Assuming having 100 g of CxHyOz, there will be 40.1g C , 6.74g H, and 53.2g O. # mol of C = 40.1g C × [1 mol C / 12.01 g C] = 3.34 mol C In the same way: we get 6.67 mol H and 3.33 mol O. (d) Finding the smallest whole number ratio by dividing by 3 ...
... 100% - % mass C - % mass H = % mass O = 53.2% O (c) Assuming having 100 g of CxHyOz, there will be 40.1g C , 6.74g H, and 53.2g O. # mol of C = 40.1g C × [1 mol C / 12.01 g C] = 3.34 mol C In the same way: we get 6.67 mol H and 3.33 mol O. (d) Finding the smallest whole number ratio by dividing by 3 ...
Stoichiometry We compare all other elements to the known mass of
... 6 neutrons x 1.67 x 10-24 g/neutron 6 electrons x 9.11 x 10-27 g/electron ...
... 6 neutrons x 1.67 x 10-24 g/neutron 6 electrons x 9.11 x 10-27 g/electron ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.