10th Grade Chemistry X (TJ) GRADE(S)/LEVELS SUBJECT Power
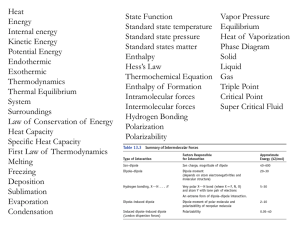
... Solutions are mixtures in which particles of one substance are evenly distributed through another substance. Liquids are limited in the amount of dissolved solid or gas that they can contain. Aqueous solutions can be described by relative quantities of the dissolved substances and acidity or alkalin ...
... Solutions are mixtures in which particles of one substance are evenly distributed through another substance. Liquids are limited in the amount of dissolved solid or gas that they can contain. Aqueous solutions can be described by relative quantities of the dissolved substances and acidity or alkalin ...
Test 1
... BUBBLE IN “1” IN THE P COLUMN TO GET YOUR GRADE POSTED!!!!! [the only way you’ll find out how you did!] ...
... BUBBLE IN “1” IN THE P COLUMN TO GET YOUR GRADE POSTED!!!!! [the only way you’ll find out how you did!] ...
Atom - Britannica
... basic building blocks of all matter. Atoms can be combined with other atoms to form molecules, but they cannot be divided into smaller parts by ordinary means. The word atom comes from the Greek word atomos, meaning “indivisible.” The ancient Greeks were the first to think of the atom as the basic u ...
... basic building blocks of all matter. Atoms can be combined with other atoms to form molecules, but they cannot be divided into smaller parts by ordinary means. The word atom comes from the Greek word atomos, meaning “indivisible.” The ancient Greeks were the first to think of the atom as the basic u ...
Structure - Britannica Encyclopedia Online
... basic building blocks of all matter. Atoms can be combined with other atoms to form molecules, but they cannot be divided into smaller parts by ordinary means. The word atom comes from the Greek word atomos, meaning “indivisible.” The ancient Greeks were the first to think of the atom as the basic u ...
... basic building blocks of all matter. Atoms can be combined with other atoms to form molecules, but they cannot be divided into smaller parts by ordinary means. The word atom comes from the Greek word atomos, meaning “indivisible.” The ancient Greeks were the first to think of the atom as the basic u ...
chapter 1 powerpoint
... divided chemically. • Nucleus: the core of the atom. Consists of protons and neutrons. • Electron: one of the particles that make up the atom. Orbits around the nucleus. Negatively ...
... divided chemically. • Nucleus: the core of the atom. Consists of protons and neutrons. • Electron: one of the particles that make up the atom. Orbits around the nucleus. Negatively ...
Chapter 2
... electrons of nitrogen are distributed into three unshared orbitals and one shared orbital. • When atoms interact to complete their valence shells, it is the __________ electrons that are involved. ...
... electrons of nitrogen are distributed into three unshared orbitals and one shared orbital. • When atoms interact to complete their valence shells, it is the __________ electrons that are involved. ...
Chem 101 notes review
... The basic assumptions of kinetic-molecular theory are: Postulate 1 – Gases consist of discrete molecules that are relatively far apart. – Gases have few intermolecular attractions. – The volume of individual molecules is very small compared to the gas’s volume. Proof - Gases are easily compressible. ...
... The basic assumptions of kinetic-molecular theory are: Postulate 1 – Gases consist of discrete molecules that are relatively far apart. – Gases have few intermolecular attractions. – The volume of individual molecules is very small compared to the gas’s volume. Proof - Gases are easily compressible. ...
History of the Atom & Atomic Structure
... Major Contribution: Atomic Theory (1808) ▪ This began the modern era of chemistry Four Principles: ▪ Elements are composed of indivisible particles called atoms. ▪ All atoms of a given element are identical. ...
... Major Contribution: Atomic Theory (1808) ▪ This began the modern era of chemistry Four Principles: ▪ Elements are composed of indivisible particles called atoms. ▪ All atoms of a given element are identical. ...
Ch. 3 - Chemical Reactions
... Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) • How many? • Of what? • In what state? ...
... Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) • How many? • Of what? • In what state? ...
Notes for Matter Packet- Balancing equations (PDF
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
Chapter 18: Atoms and Elements
... — proton (p+) = 1 amu — neutron (n0) = 1 amu — electron (e-) = 1/2000 amu ...
... — proton (p+) = 1 amu — neutron (n0) = 1 amu — electron (e-) = 1/2000 amu ...
- Science
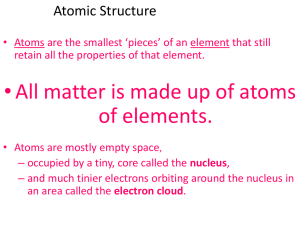
... In the case of atoms, scientists use large models to explain something that is very small Models of the atom were used to explain data or facts that were gathered experimentally. So, these models are also theories ...
... In the case of atoms, scientists use large models to explain something that is very small Models of the atom were used to explain data or facts that were gathered experimentally. So, these models are also theories ...
element - Mrs. Phillips` Physical Science Webpage
... things together in a way that makes sense, so that like are with like – makes it easier to find things if you know where to look. • The periodic table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, as a way of classifying elements according to their properties. ...
... things together in a way that makes sense, so that like are with like – makes it easier to find things if you know where to look. • The periodic table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, as a way of classifying elements according to their properties. ...
Chapter 4 The Structure of Matter
... • 2. The same for H2O and H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) • 3. Compounds are always made up of the same elements in the same proportion. • 4. The formula can tell us what atoms a compound is made of but does not reveal how they are connected. ...
... • 2. The same for H2O and H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) • 3. Compounds are always made up of the same elements in the same proportion. • 4. The formula can tell us what atoms a compound is made of but does not reveal how they are connected. ...
Who was Democritus? How did Dalton describe atoms?
... stated that all the positive charge and the mass is concentrated in a small core in the center of the atom, AKA nucleus And that the atom is mostly empty space with electrons surrounding the ...
... stated that all the positive charge and the mass is concentrated in a small core in the center of the atom, AKA nucleus And that the atom is mostly empty space with electrons surrounding the ...
Slide 1
... Ptotal = PA + PB + PC + ..... At low temperatures and high pressures real gases do not behave ideally. The reasons for the deviations from ideality are: 1. The molecules are very close to one another, thus their volume is important. 2. The molecular interactions also become important. ...
... Ptotal = PA + PB + PC + ..... At low temperatures and high pressures real gases do not behave ideally. The reasons for the deviations from ideality are: 1. The molecules are very close to one another, thus their volume is important. 2. The molecular interactions also become important. ...
Atomic Theory - davis.k12.ut.us
... John Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. Matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms 2. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible 3. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass and chemical properties 4. Atoms of a specific element are different from those of another element 5. Diffe ...
... John Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. Matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms 2. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible 3. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass and chemical properties 4. Atoms of a specific element are different from those of another element 5. Diffe ...
Atomic Theory Development
... smaller and smaller pieces forever, or was there a limit to the number of times a piece of matter could be divided?” ...
... smaller and smaller pieces forever, or was there a limit to the number of times a piece of matter could be divided?” ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions C Kapler ` , , I 27 O//#W SELF
... a. an Fe atom must gain 3 protons. b. an Fe2+ ion must gain 1 proton. c. an Fe atom must gain 3 electrons. d. an Fe2+ ion must gain 1 electron. e. none of the above will work. 8. Consider the following statements — There are always more neutrons than protons in an atom's nucleus. — The nucleus of an ...
... a. an Fe atom must gain 3 protons. b. an Fe2+ ion must gain 1 proton. c. an Fe atom must gain 3 electrons. d. an Fe2+ ion must gain 1 electron. e. none of the above will work. 8. Consider the following statements — There are always more neutrons than protons in an atom's nucleus. — The nucleus of an ...
12-3: Lewis Structures
... Lewis structures—represent valence electrons; use dots placed around the chemical symbol All atoms want to achieve a noble gas configuration o Octet Rule—most elements will be surrounded by 8 dots, representing noble gas configuration Hydrogen is full with 2 electrons (2 dots on one side)—so i ...
... Lewis structures—represent valence electrons; use dots placed around the chemical symbol All atoms want to achieve a noble gas configuration o Octet Rule—most elements will be surrounded by 8 dots, representing noble gas configuration Hydrogen is full with 2 electrons (2 dots on one side)—so i ...
Chapter 1 Introduction: Matter and Measurement
... Laws usually precede theories because they do not have to explain Hypothesis – educated guess to explain observations or “baby” theory – followed by more experimentation Example of a theory – Kinetic Molecular Theory – atoms, molecules, ions in constant random motion unless constrained. Use Ar atom ...
... Laws usually precede theories because they do not have to explain Hypothesis – educated guess to explain observations or “baby” theory – followed by more experimentation Example of a theory – Kinetic Molecular Theory – atoms, molecules, ions in constant random motion unless constrained. Use Ar atom ...
Document
... Valence Electrons • Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of the atom. • Valence electrons are the only electrons generally involved in bond formation. • The valence electrons in the s and p orbitals are written around the element symbol. • These electrons are the ...
... Valence Electrons • Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of the atom. • Valence electrons are the only electrons generally involved in bond formation. • The valence electrons in the s and p orbitals are written around the element symbol. • These electrons are the ...
Lecture 2 - Unit 1 Part 2 Slides
... Since we know that isotopes exist, we know that not all atoms of an element are identical. All the atoms of an element will have the same number of protons, but not necessarily the same number of neutrons. This means that some atoms of an element have more mass than others! We determine the mass of ...
... Since we know that isotopes exist, we know that not all atoms of an element are identical. All the atoms of an element will have the same number of protons, but not necessarily the same number of neutrons. This means that some atoms of an element have more mass than others! We determine the mass of ...
Test revision Answers
... 2. Name the three sub-atomic particles that make up an atom. Protons, neutrons and electrons ...
... 2. Name the three sub-atomic particles that make up an atom. Protons, neutrons and electrons ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.