Atomic structure - Dayton Independent Schools
... they fired Helium nuclei at a piece of gold foil which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
... they fired Helium nuclei at a piece of gold foil which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
Unit 3 Notes, Practice, and Review
... 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of another. ...
... 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of another. ...
Atomic Theory
... Air – cool, light Fire – warm, light The composition of a substance could be estimated from its properties. ...
... Air – cool, light Fire – warm, light The composition of a substance could be estimated from its properties. ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... • (7) Dalton’s atomic theory stated that every element was made of atoms that could not be subdivided, atoms of the same element are alike, and atoms can join to form molecules. ...
... • (7) Dalton’s atomic theory stated that every element was made of atoms that could not be subdivided, atoms of the same element are alike, and atoms can join to form molecules. ...
Topic one midterm review
... – If the “Plum Pudding” model was correct then the α particles would pass through the foil with just a few being slightly deflected. – Some of the α particles were deflected, and some even bounced back. » Rutherford concluded that atoms have a small dense positively charged central core, and the res ...
... – If the “Plum Pudding” model was correct then the α particles would pass through the foil with just a few being slightly deflected. – Some of the α particles were deflected, and some even bounced back. » Rutherford concluded that atoms have a small dense positively charged central core, and the res ...
Atomic Theory
... particle which an element can be divided into and still be the same • The theory has been around for over 2000 years. But no one saw an atom until ...
... particle which an element can be divided into and still be the same • The theory has been around for over 2000 years. But no one saw an atom until ...
Ch 8 Bonding and Molecular Structure 06-Nov
... Because of the difference in Electronegativity for HF, the compound is polar. Nonpolar bonds form when the difference in electronegativity is less than 0.5 Polar bonds form when the difference in electronegativity is greater than 0.5 Ionic bonds form when the difference in electronegativity is great ...
... Because of the difference in Electronegativity for HF, the compound is polar. Nonpolar bonds form when the difference in electronegativity is less than 0.5 Polar bonds form when the difference in electronegativity is greater than 0.5 Ionic bonds form when the difference in electronegativity is great ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... 6. What kind of bond is NaCl? Ionic CO2 Covalent N2 Covalent 7. Which group forms acids with H+ ion? Halogens (Group 17) 8. How many valence electrons are in a Group 1 element? 1 Group 13? 3 9. How do positive and negative ions form? Positive ions form when an atom loses an electron, negative ions f ...
... 6. What kind of bond is NaCl? Ionic CO2 Covalent N2 Covalent 7. Which group forms acids with H+ ion? Halogens (Group 17) 8. How many valence electrons are in a Group 1 element? 1 Group 13? 3 9. How do positive and negative ions form? Positive ions form when an atom loses an electron, negative ions f ...
Atoms and Elements
... putting electrons into orbitals that have the same energy as each other. Put one electron into each orbital before pairing them up. Whichever way the first arrow (electron) points, the others must point the same way until they pair up, then they point in opposite directions. ...
... putting electrons into orbitals that have the same energy as each other. Put one electron into each orbital before pairing them up. Whichever way the first arrow (electron) points, the others must point the same way until they pair up, then they point in opposite directions. ...
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
... He asked: Could matter be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever, or was there a limit to the number of times a piece of matter could be divided? ...
... He asked: Could matter be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever, or was there a limit to the number of times a piece of matter could be divided? ...
Preview to Mole Activity #2 preview_to_mole_activity_21
... A long time ago chemists discovered what you just discovered by answering question 8. If they were talking about the mass of one atom of an element they talked about its mass in amu’s. This was not very helpful as most often they were dealing with many more atoms than just one or two. What they foun ...
... A long time ago chemists discovered what you just discovered by answering question 8. If they were talking about the mass of one atom of an element they talked about its mass in amu’s. This was not very helpful as most often they were dealing with many more atoms than just one or two. What they foun ...
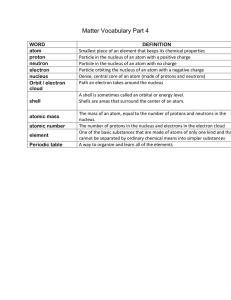
Matter Vocab Part 4
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
Click here to Ch 06.2 Covalent Bonding_Lewis Structures
... electrons, and for those that can fit more than eight electrons, into their outermost orbital. • Hydrogen forms bonds in which it is surrounded by only two electrons. • Boron has just three valence electrons, so it tends to form bonds in which it is surrounded by six electrons. ...
... electrons, and for those that can fit more than eight electrons, into their outermost orbital. • Hydrogen forms bonds in which it is surrounded by only two electrons. • Boron has just three valence electrons, so it tends to form bonds in which it is surrounded by six electrons. ...
Theories and Structure of the Atom
... Conservation of Mass (In any reaction, mass before and after the reaction will be the same) Elements can combine in different proportions (Ex: H2O and H2) Thompson’s Atomic Model (1897) Thompson’s Contributions: J.J. Thompson discovered the idea of charge in an atom His models placed the ele ...
... Conservation of Mass (In any reaction, mass before and after the reaction will be the same) Elements can combine in different proportions (Ex: H2O and H2) Thompson’s Atomic Model (1897) Thompson’s Contributions: J.J. Thompson discovered the idea of charge in an atom His models placed the ele ...
Test 2 Review Test 2 Review (15-16)_2
... table is referred to as “The PERIODIC Table” and give at least one example of a periodic trend and one example of a non-periodic trend. (see pages 126-131) ...
... table is referred to as “The PERIODIC Table” and give at least one example of a periodic trend and one example of a non-periodic trend. (see pages 126-131) ...
Chapter 4 The Structure of the Atom
... Nucleus - central core of the atom (1/100,000th diameter) • composed of p+ and n0 • contains all of the atom’s positive charge • contains 99.97 % of the atom’s mass Atomic Number • the number of protons in the nucleus • H. Moseley discovered that each element contains a unique positive charge • dete ...
... Nucleus - central core of the atom (1/100,000th diameter) • composed of p+ and n0 • contains all of the atom’s positive charge • contains 99.97 % of the atom’s mass Atomic Number • the number of protons in the nucleus • H. Moseley discovered that each element contains a unique positive charge • dete ...
Unit 16 Worksheet - Jensen Chemistry
... c increase orbital speed around the nucleus d. are released by the atom 2. Helium was discovered on the sun in 1868, almost 30 years before it was discovered here on the earth. How could that be possible? a. Investigation of light from the sun revealed a spectrum not yet found in known elements. b. ...
... c increase orbital speed around the nucleus d. are released by the atom 2. Helium was discovered on the sun in 1868, almost 30 years before it was discovered here on the earth. How could that be possible? a. Investigation of light from the sun revealed a spectrum not yet found in known elements. b. ...
Chapter 4 Cornell Notes
... ____________________ was the early (around 400BC) Greek philosopher who is credited with the concept of the atom (atomos) – which means ____________________ ____________________ (around 1800AD) is an English school teacher who proposed the law of conservation of mass, the law of definite proportions ...
... ____________________ was the early (around 400BC) Greek philosopher who is credited with the concept of the atom (atomos) – which means ____________________ ____________________ (around 1800AD) is an English school teacher who proposed the law of conservation of mass, the law of definite proportions ...
TEST REVIEW S Valence Electrons TEST REVIEW SHEET 2017
... Determine the element symbol Determine the group number and the number of valence electrons Write the symbol Draw the valence electrons around the symbol using dots to represent them ...
... Determine the element symbol Determine the group number and the number of valence electrons Write the symbol Draw the valence electrons around the symbol using dots to represent them ...
CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET
... Hydrogen is usually +1. Oxygen is usually –2. In a compound, the more electronegative element is given an oxidation number equal to its usual ionic charge. The sum of the oxidation numbers must equal the overall charge on the compound or ion. ...
... Hydrogen is usually +1. Oxygen is usually –2. In a compound, the more electronegative element is given an oxidation number equal to its usual ionic charge. The sum of the oxidation numbers must equal the overall charge on the compound or ion. ...
What do we call a substance with more than one kind of atom
... 20. Ernest Rutherford performed a famous experiment in which he used a radioactive alpha particle source and aimed the particles at a thin sheet of gold foil. . By studying photographic plates placed around the foil, he found that most particles passed straight through; some were reflected straight ...
... 20. Ernest Rutherford performed a famous experiment in which he used a radioactive alpha particle source and aimed the particles at a thin sheet of gold foil. . By studying photographic plates placed around the foil, he found that most particles passed straight through; some were reflected straight ...
Inside an Atom - Mrs. Ericka Williams
... Cannot be divided; for example, a string of beads can be cut in half again and again until you have one 2. What is chemistry? Study of matter 3. What happened in the Scientists began debating the existence of atoms once more; eighteenth century? they were learning about matter and how it changes; th ...
... Cannot be divided; for example, a string of beads can be cut in half again and again until you have one 2. What is chemistry? Study of matter 3. What happened in the Scientists began debating the existence of atoms once more; eighteenth century? they were learning about matter and how it changes; th ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... ____________________ was the early (around 400BC) Greek philosopher who is credited with the concept of the atom (atomos) – which means ____________________ ____________________ (around 1800AD) is an English school teacher who proposed the law of conservation of mass, the law of definite proportions ...
... ____________________ was the early (around 400BC) Greek philosopher who is credited with the concept of the atom (atomos) – which means ____________________ ____________________ (around 1800AD) is an English school teacher who proposed the law of conservation of mass, the law of definite proportions ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.