discovery of atomic structure
... with lots of protons would be very unstable without lots of neutrons. Strong Nuclear Force – the name for the attraction that holds a nucleus together, thus preventing it from flying apart. ...
... with lots of protons would be very unstable without lots of neutrons. Strong Nuclear Force – the name for the attraction that holds a nucleus together, thus preventing it from flying apart. ...
Instructor`s Guide - Ventura Educational Systems
... Lesson 4: Making Molecules 1… Getting Started Teacher Sheet Background Atoms are nature’s building blocks, but we very seldom see atoms by themselves in nature. More often than not, atoms bond with other atoms to form molecules and compounds. Covalent Molecules, like ...
... Lesson 4: Making Molecules 1… Getting Started Teacher Sheet Background Atoms are nature’s building blocks, but we very seldom see atoms by themselves in nature. More often than not, atoms bond with other atoms to form molecules and compounds. Covalent Molecules, like ...
History of the Atom Reading
... is, they have different masses. • Compounds are formed by the combination of atoms of different elements. Although we now know that some of Dalton's theory was not correct, it laid the important groundwork for the current concept of the atom. ...
... is, they have different masses. • Compounds are formed by the combination of atoms of different elements. Although we now know that some of Dalton's theory was not correct, it laid the important groundwork for the current concept of the atom. ...
Review Notes for Atomic Structure and Radioactivity Test on Friday
... 1. Atoms are the smallest particles of an element that retain the chemical identity (properties) of that element. Early Models of the Atom: 2. The ancient Greek philosophers, Aristotle and Plato described matter as continuous and without a definite unit. Democritus claimed that matter is discontinuo ...
... 1. Atoms are the smallest particles of an element that retain the chemical identity (properties) of that element. Early Models of the Atom: 2. The ancient Greek philosophers, Aristotle and Plato described matter as continuous and without a definite unit. Democritus claimed that matter is discontinuo ...
Know (main topic)
... Baking soda and vinegar bomb metallic bonds Demonstrations: “Chemistry show” of endothermic and -combine atoms to form exothermic reactions—student molecules by sharing electrons assistants. to form covalent or metallic Projects ...
... Baking soda and vinegar bomb metallic bonds Demonstrations: “Chemistry show” of endothermic and -combine atoms to form exothermic reactions—student molecules by sharing electrons assistants. to form covalent or metallic Projects ...
Chapter 3 - Bruder Chemistry
... Finding empirical formula from mass percent data: • We start with the mass percent of elements (i.e. empirical data) and calculate a formula. • Assume we start with 100 g of sample. • The mass percent then translates as the number of grams of each element in 100 g of sample. • From these masses, the ...
... Finding empirical formula from mass percent data: • We start with the mass percent of elements (i.e. empirical data) and calculate a formula. • Assume we start with 100 g of sample. • The mass percent then translates as the number of grams of each element in 100 g of sample. • From these masses, the ...
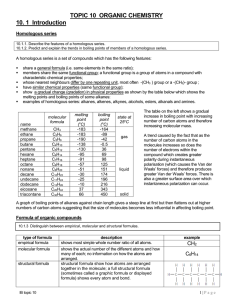
organic chemistry - Peoria Public Schools
... It is important to note that alkenes also easily combust and undergo both complete and incomplete combustion. Alkanes undergo addition reaction that means that atoms are added to the molecule at either side of the double bond so any addition reaction increases the number of atoms in the molecule. Du ...
... It is important to note that alkenes also easily combust and undergo both complete and incomplete combustion. Alkanes undergo addition reaction that means that atoms are added to the molecule at either side of the double bond so any addition reaction increases the number of atoms in the molecule. Du ...
IPC Semester Exam Review – Chemistry Topics
... 56. Proposed that electrons travel in circular orbits. 57. Draw atomic models for billiard ball through electron cloud. 58. Draw the Bohr model diagram for magnesium. 59. List the subatomic particles & isotope symbol for bromine-80. 60. Calculate the average atomic mass of lithium if 1 of 13 atoms i ...
... 56. Proposed that electrons travel in circular orbits. 57. Draw atomic models for billiard ball through electron cloud. 58. Draw the Bohr model diagram for magnesium. 59. List the subatomic particles & isotope symbol for bromine-80. 60. Calculate the average atomic mass of lithium if 1 of 13 atoms i ...
What is the main contribution of Democritus to atomic theory
... General Chemistry History of Atomic Theory ...
... General Chemistry History of Atomic Theory ...
Unit 1 Notes
... couldn’t be cut into anything smaller – used the term “atomos” (Greek for uncuttable) ...
... couldn’t be cut into anything smaller – used the term “atomos” (Greek for uncuttable) ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... 14. What are the characteristics of a covalent and ionic compound? 15. Define chemical bond. What is a lone pair of electrons? 16. What is the difference between a single, double, and triple bond? 17. Draw Lewis diagrams for PBr3, N2, CF4, HBr, SO2 18. What is a dipole? What direction does it travel ...
... 14. What are the characteristics of a covalent and ionic compound? 15. Define chemical bond. What is a lone pair of electrons? 16. What is the difference between a single, double, and triple bond? 17. Draw Lewis diagrams for PBr3, N2, CF4, HBr, SO2 18. What is a dipole? What direction does it travel ...
sample paper chemistry clas xi set 3
... 9. How many grams of NaOH should be dissolved to make 100 ml of 0.15 M NaOH solution? 10. (a.) why Rutherford’s model was discarded? (b.) write the electronic configuration of S211. The reaction of NH2 CN(s) with oxygen was affected in a bomb calorimeter and ∆U was found to be -742.7 Kj/mol of cyana ...
... 9. How many grams of NaOH should be dissolved to make 100 ml of 0.15 M NaOH solution? 10. (a.) why Rutherford’s model was discarded? (b.) write the electronic configuration of S211. The reaction of NH2 CN(s) with oxygen was affected in a bomb calorimeter and ∆U was found to be -742.7 Kj/mol of cyana ...
Unit 2 Notes Atomic
... pattern called a bright line spectrum. Each element has a ____________ bright line spectrum (like a fingerprint) Bright line spectra can be used to ___________ unknown samples of elements ...
... pattern called a bright line spectrum. Each element has a ____________ bright line spectrum (like a fingerprint) Bright line spectra can be used to ___________ unknown samples of elements ...
Atoms,molecules,nomenclature.
... Atoms, Molecules and Ions The theory that atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter re-emerged in the early 19th century, championed by John Dalton. ...
... Atoms, Molecules and Ions The theory that atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter re-emerged in the early 19th century, championed by John Dalton. ...
atomic number Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
... 1 atomic mass unit (amu) =1.673x10-24 g Defined to be 1/12 of the mass of a carbon atom containing 6 protons and 6 neutrons. ...
... 1 atomic mass unit (amu) =1.673x10-24 g Defined to be 1/12 of the mass of a carbon atom containing 6 protons and 6 neutrons. ...
Honors Chemistry
... 60. Xylitol is a sweetener that has anticavity properties because it does not stick to teeth. Elemental analysis of a sample resulted in 0.5921 g carbon, 0.1184 g hydrogen and 0.7895 g oxygen. The molar mass was determined by an effusion rate comparison with oxygen gas. Oxygen was found to effuse 2. ...
... 60. Xylitol is a sweetener that has anticavity properties because it does not stick to teeth. Elemental analysis of a sample resulted in 0.5921 g carbon, 0.1184 g hydrogen and 0.7895 g oxygen. The molar mass was determined by an effusion rate comparison with oxygen gas. Oxygen was found to effuse 2. ...
Chapter 3. Stoichiometry
... Convert grams of reactant to moles of reactant (use molar mass), Convert moles of one reactant to moles of other reactants and products (use the stoichiometric ratio from the balanced chemical equation), Convert moles back into grams for desired product (use molar mass). ...
... Convert grams of reactant to moles of reactant (use molar mass), Convert moles of one reactant to moles of other reactants and products (use the stoichiometric ratio from the balanced chemical equation), Convert moles back into grams for desired product (use molar mass). ...
Unit 3 GROUP QUIZ
... c. Compounds are molecules make by uniting atoms. d. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number ratios. e. In a chemical reaction, atoms of one element are not changed into atoms of another element. ___4. Why did J.J. Thomson reason that electrons must be a part ...
... c. Compounds are molecules make by uniting atoms. d. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number ratios. e. In a chemical reaction, atoms of one element are not changed into atoms of another element. ___4. Why did J.J. Thomson reason that electrons must be a part ...
K has two shells (n=4 vs n=2) more than Li, so it
... Arrange these elements in order of increasing ionic radii: S, K, Cl K < Cl < S First you have to think about what charged ion each element will make, K+ Cl- and S2-. Between these three, there are equal numbers of electrons but different numbers of protons. Potassium has the most protons and can pul ...
... Arrange these elements in order of increasing ionic radii: S, K, Cl K < Cl < S First you have to think about what charged ion each element will make, K+ Cl- and S2-. Between these three, there are equal numbers of electrons but different numbers of protons. Potassium has the most protons and can pul ...
atomic numbers
... isotopes of that element-each with its own atomic mass ► A weighted average of the percentage of each isotope that exists versus the atomic mass of each isotope is used to calculate the atomic mass that appears on the periodic table. ...
... isotopes of that element-each with its own atomic mass ► A weighted average of the percentage of each isotope that exists versus the atomic mass of each isotope is used to calculate the atomic mass that appears on the periodic table. ...
Chapter 2 PPT - Richsingiser.com
... empirical formula that uses the smallest whole number subscripts to express the relative numbers of ions. • The relative numbers of ions in the empirical formula balances the charges to zero. • The formula of sodium chloride is NaCl, because the 1+ ions have to be present in a 1:1 ...
... empirical formula that uses the smallest whole number subscripts to express the relative numbers of ions. • The relative numbers of ions in the empirical formula balances the charges to zero. • The formula of sodium chloride is NaCl, because the 1+ ions have to be present in a 1:1 ...
Gupta 2014 Credit: Google Images for the pictures Chapter 1
... Planck’s Theory: Blackbody radiation can be explained if energy can be released or absorbed in packets of a standard size called quanta h c h = Planck’s constant = 6.63 x 10-34 J-s E h ...
... Planck’s Theory: Blackbody radiation can be explained if energy can be released or absorbed in packets of a standard size called quanta h c h = Planck’s constant = 6.63 x 10-34 J-s E h ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.