Chapter 3
... Foundations of Atomic Theory, continued • Law of definite proportions: a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound • Law of multiple proportions: if two or more different compounds are composed ...
... Foundations of Atomic Theory, continued • Law of definite proportions: a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound • Law of multiple proportions: if two or more different compounds are composed ...
The atomic packing factor
... Interplaner Distance between paraalls plances The space lattice consist from many crystall plances which separated by interplaner smallest distance The distance can be calcalated by using x- ray diffraction , by using the law below :√ Where dhkl = interplanar spacing between parallel closest planes ...
... Interplaner Distance between paraalls plances The space lattice consist from many crystall plances which separated by interplaner smallest distance The distance can be calcalated by using x- ray diffraction , by using the law below :√ Where dhkl = interplanar spacing between parallel closest planes ...
Appendix - Cengage
... The electrons between two atoms in a covalent bond are not always shared equally. When the atoms sharing an electron pair are identical, such as two oxygen atoms, the electrons are attracted equally by both atoms and so are shared equally. The result is a nonpolar molecule. The term nonpolar implies ...
... The electrons between two atoms in a covalent bond are not always shared equally. When the atoms sharing an electron pair are identical, such as two oxygen atoms, the electrons are attracted equally by both atoms and so are shared equally. The result is a nonpolar molecule. The term nonpolar implies ...
Chapter 3
... Foundations of Atomic Theory, continued • Law of definite proportions: a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound • Law of multiple proportions: if two or more different compounds are composed ...
... Foundations of Atomic Theory, continued • Law of definite proportions: a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound • Law of multiple proportions: if two or more different compounds are composed ...
How many grams of oxygen are made if 3.75 moles of KClO 3
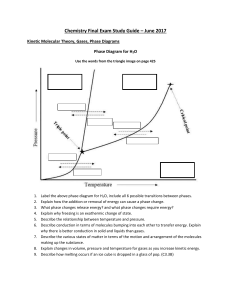
... Label the above phase diagram for H2O, include all 6 possible transitions between phases. Explain how the addition or removal of energy can cause a phase change. What phase changes release energy? and what phase changes require energy? Explain why freezing is an exothermic change of state. Describe ...
... Label the above phase diagram for H2O, include all 6 possible transitions between phases. Explain how the addition or removal of energy can cause a phase change. What phase changes release energy? and what phase changes require energy? Explain why freezing is an exothermic change of state. Describe ...
76 kJ/mole
... atomic orbitals (AO) having specific 1) shape and 2) spatial orientation. B. Most importantly, AOs can interact, combine and overlap to give more complex wave having new shape and spatial orientation. C. These new wave functions are called linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAOs) D. AOs, LCAOs ...
... atomic orbitals (AO) having specific 1) shape and 2) spatial orientation. B. Most importantly, AOs can interact, combine and overlap to give more complex wave having new shape and spatial orientation. C. These new wave functions are called linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAOs) D. AOs, LCAOs ...
atomic mass
... PreAP Chemistry Chapter 3 Chapter 3 Outlines Due to the box NOW Not later today! ...
... PreAP Chemistry Chapter 3 Chapter 3 Outlines Due to the box NOW Not later today! ...
Ions + Isotopes
... Atomic Mass • The mass of an atom is determined using the number of protons and neutrons in it. (electrons are ignored) • Since the masses of atoms are so small in conventional mass units, like grams, we use a unit that is equivalent to the mass, in grams, of a proton. ...
... Atomic Mass • The mass of an atom is determined using the number of protons and neutrons in it. (electrons are ignored) • Since the masses of atoms are so small in conventional mass units, like grams, we use a unit that is equivalent to the mass, in grams, of a proton. ...
Atomic - Chemistry R: 4(AE) 5(A,C)
... reasoned that these different colored bands of light were actually quanta of corresponding energy. These quanta were emitted as electrons of hydrogen atoms returned from their higher levels in the excited state to their lower levels in the ground state. These colors are specific and can be used to i ...
... reasoned that these different colored bands of light were actually quanta of corresponding energy. These quanta were emitted as electrons of hydrogen atoms returned from their higher levels in the excited state to their lower levels in the ground state. These colors are specific and can be used to i ...
February Valentine`s Day-10, 2010
... Each element has a name and can be abbreviated with one or two letters ...
... Each element has a name and can be abbreviated with one or two letters ...
Recherches sur la théorie des quanta
... The world of the quantum must be able to explain the classical world that we live in. To understand the quantum world we need to understand one of the major building blocks ---- the atom ...
... The world of the quantum must be able to explain the classical world that we live in. To understand the quantum world we need to understand one of the major building blocks ---- the atom ...
Chapter 4 - Development of Atomic Theory
... 1. How many protons and electrons are present in a vanadium atom? 2. How many protons and electrons are present in a nitrogen atom? 3. How many protons and electrons are present in an argon atom? 4. How many protons and electrons are present in a potassium atom? 5. How many protons and electrons are ...
... 1. How many protons and electrons are present in a vanadium atom? 2. How many protons and electrons are present in a nitrogen atom? 3. How many protons and electrons are present in an argon atom? 4. How many protons and electrons are present in a potassium atom? 5. How many protons and electrons are ...
CHAPTER #2 STRUTURE OF ATOM CLASS:9th The word atom
... electrostatic force of attraction between the nucleus and electron. This prevents the electrons from falling into nucleus. RUTHERFORD’S ATOMIC MODEL 1. Major portion of the atom is empty. 2. The whole mass of the atom is concentrated in the center of atom called nucleus. 3. The positively charged p ...
... electrostatic force of attraction between the nucleus and electron. This prevents the electrons from falling into nucleus. RUTHERFORD’S ATOMIC MODEL 1. Major portion of the atom is empty. 2. The whole mass of the atom is concentrated in the center of atom called nucleus. 3. The positively charged p ...
Packet 5
... DemocritusDemocritus (b. c. 460 BC; d. c. 370 BC) postulated the existence of invisible atoms, characterized only by quantitative properties: size, shape, and motion. Imagine these atoms as indivisible spheres, the smallest pieces of an element that still behave like the entire chunk of matter. ...
... DemocritusDemocritus (b. c. 460 BC; d. c. 370 BC) postulated the existence of invisible atoms, characterized only by quantitative properties: size, shape, and motion. Imagine these atoms as indivisible spheres, the smallest pieces of an element that still behave like the entire chunk of matter. ...
Chapter 6
... 1) Iron reacts with hydrogen sulfate to form iron (III) sulfate and hydrogen gas 2) Potassium hydroxide reacts with hydrogen phosphate to produce potassium phosphate and ...
... 1) Iron reacts with hydrogen sulfate to form iron (III) sulfate and hydrogen gas 2) Potassium hydroxide reacts with hydrogen phosphate to produce potassium phosphate and ...
Cobalt isotopes in industry 60Co is used to irradiate food sources as
... brachytherapy – the treatment of cancer, especially prostate cancer, by the insertion of radioactive implants directly into the tissue near the tumor. [return] electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric charge and a rest mass of about 9.109 × 10–31 kg. element (chemical elemen ...
... brachytherapy – the treatment of cancer, especially prostate cancer, by the insertion of radioactive implants directly into the tissue near the tumor. [return] electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric charge and a rest mass of about 9.109 × 10–31 kg. element (chemical elemen ...
Key - Seattle Central College
... CHAPTER 2: ATOMS, IONS, AND COMPOUNDS (Topics to Review) Early Models Democritus (462-370 B.C.): proposed that all matter was made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atomos (meaning “not to cut) or atoms. Empedocles (490-430 B.C.): suggested all matter was composed of four basic elements: air, ...
... CHAPTER 2: ATOMS, IONS, AND COMPOUNDS (Topics to Review) Early Models Democritus (462-370 B.C.): proposed that all matter was made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atomos (meaning “not to cut) or atoms. Empedocles (490-430 B.C.): suggested all matter was composed of four basic elements: air, ...
Chemical Bonding
... P2, you can assume that third period diatomics form valence molecular orbitals similar to second period diatomics but with n=3) and the following heteronuclear diatomic species, CO, NO and BN (assume the same energy level diagram as Be2 to N2). Determine the bond order of each species. Indicate any ...
... P2, you can assume that third period diatomics form valence molecular orbitals similar to second period diatomics but with n=3) and the following heteronuclear diatomic species, CO, NO and BN (assume the same energy level diagram as Be2 to N2). Determine the bond order of each species. Indicate any ...
Structure of Matter
... requires complex “wave equations” and higher level calculus (differential equations) than is taught in high school. But understanding the results of these wave equations can be done: ◦ Wave equations require 3 numbers, called quantum numbers, in order to reach a solution. ...
... requires complex “wave equations” and higher level calculus (differential equations) than is taught in high school. But understanding the results of these wave equations can be done: ◦ Wave equations require 3 numbers, called quantum numbers, in order to reach a solution. ...
Document
... • Complete the Reading Essentials for Lesson 9.1 on your own sheet of paper. • Then list each scientist with their specific contribution. There should be 7 scientist. ...
... • Complete the Reading Essentials for Lesson 9.1 on your own sheet of paper. • Then list each scientist with their specific contribution. There should be 7 scientist. ...
Note
... a. it takes the addition of a lot of energy to increase/decrease the temperature of water or make water evaporate/freeze i. the evaporation of sweat removes a lot of energy from an organism ii. Large bodies of water are relatively stable environments for organisms to live in iii. Land near large bod ...
... a. it takes the addition of a lot of energy to increase/decrease the temperature of water or make water evaporate/freeze i. the evaporation of sweat removes a lot of energy from an organism ii. Large bodies of water are relatively stable environments for organisms to live in iii. Land near large bod ...
Using your periodic table ppt (9/26-10/11) File
... orbitals & number of valence e-, & to know that properties are similar for elements in a group • Describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations of protons, neutrons, and electrons • Identify that protons determine an elements identity and valence electrons d ...
... orbitals & number of valence e-, & to know that properties are similar for elements in a group • Describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations of protons, neutrons, and electrons • Identify that protons determine an elements identity and valence electrons d ...
Chapte 11 Study Questions
... ____ 59. An atom of oxygen with 8 protons, 8 electrons, and 8 neutrons would have a mass number of a. 4 c. 16 b. 8 d. 24 ____ 60. ____ basic forces are at work everywhere, even within the atom. a. One c. Three b. Two d. Four ____ 61. The ____ acts between all objects all the time. a. gravitational ...
... ____ 59. An atom of oxygen with 8 protons, 8 electrons, and 8 neutrons would have a mass number of a. 4 c. 16 b. 8 d. 24 ____ 60. ____ basic forces are at work everywhere, even within the atom. a. One c. Three b. Two d. Four ____ 61. The ____ acts between all objects all the time. a. gravitational ...
2.2 The Discovery of Atomic Structure
... • Goal: find the charge on the electron to determine its mass. • Oil drops are sprayed above a positively charged plate containing a small hole. • As the oil drops fall through the hole they acquire a negative charge. • Gravity forces the drops downward. The applied electric field forces the drops u ...
... • Goal: find the charge on the electron to determine its mass. • Oil drops are sprayed above a positively charged plate containing a small hole. • As the oil drops fall through the hole they acquire a negative charge. • Gravity forces the drops downward. The applied electric field forces the drops u ...
CHEMISTRY 1
... The Born- Haber cycle uses the law of Hess to determine the Lattice Energy. The lattice energy is the enthalphy change, ∆H, associated when gaseous cations and anions from a crystal: Na+(g) + Cl-(g) NaCl(s) ∆H = - 788KJ Since heat is always evolved in these processes, all lattice energies have a n ...
... The Born- Haber cycle uses the law of Hess to determine the Lattice Energy. The lattice energy is the enthalphy change, ∆H, associated when gaseous cations and anions from a crystal: Na+(g) + Cl-(g) NaCl(s) ∆H = - 788KJ Since heat is always evolved in these processes, all lattice energies have a n ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.