Dating the Earth Power Point
... history of Earth and determine evolutionary pathways. Radioactive dating is an important tool scientists use to do this. To find a radioactive date, the object being dated must contain a radioactive element such as uranium-235 or carbon 14. These elements are decaying by emitting a small part of the ...
... history of Earth and determine evolutionary pathways. Radioactive dating is an important tool scientists use to do this. To find a radioactive date, the object being dated must contain a radioactive element such as uranium-235 or carbon 14. These elements are decaying by emitting a small part of the ...
Slide 1
... • Mass number is used to describe the nuclear content of one isotope (usually the most abundant) of an element. • Atomic mass is the weighted average of all of the isotopes of an element. • Atomic masses on the periodic table are not whole numbers because they contain the mass numbers all of the is ...
... • Mass number is used to describe the nuclear content of one isotope (usually the most abundant) of an element. • Atomic mass is the weighted average of all of the isotopes of an element. • Atomic masses on the periodic table are not whole numbers because they contain the mass numbers all of the is ...
atomic - SandersScienceStuff
... d. Atoms cannot be created, divided* or destroyed. e. Atoms could combine to make compounds only in whole number ratios f. In a chemical reaction, atoms are separated, combined or rearranged. *later shown to be incorrect (Make sure you marked them!) ...
... d. Atoms cannot be created, divided* or destroyed. e. Atoms could combine to make compounds only in whole number ratios f. In a chemical reaction, atoms are separated, combined or rearranged. *later shown to be incorrect (Make sure you marked them!) ...
Oxidation numbers
... The behavior of the Transition metals is similar to that of the Representative metals. They are also oxidized by nonmetals, losing their electrons to the nonmetal and forming ionic compounds. However, many Transition metals exhibit multiple oxidation states, forming cations with different positive c ...
... The behavior of the Transition metals is similar to that of the Representative metals. They are also oxidized by nonmetals, losing their electrons to the nonmetal and forming ionic compounds. However, many Transition metals exhibit multiple oxidation states, forming cations with different positive c ...
15anespp
... • leaded petrol must not pass through the catalyst as the lead deposits on the catalyst’s surface and “poisons” it, thus blocking sites for reactions to take place. ...
... • leaded petrol must not pass through the catalyst as the lead deposits on the catalyst’s surface and “poisons” it, thus blocking sites for reactions to take place. ...
File
... Law of multiple proportions-When two elements form more than one compound, the different masses of one element are combined with the same mass of the other element are in a ratio of small whole numbers. (e.g. If 2.66g of oxygen combine with 1.0g of carbon to form CO2, then 1.33g of oxygen combine wi ...
... Law of multiple proportions-When two elements form more than one compound, the different masses of one element are combined with the same mass of the other element are in a ratio of small whole numbers. (e.g. If 2.66g of oxygen combine with 1.0g of carbon to form CO2, then 1.33g of oxygen combine wi ...
The Mole
... chemical reactions in which the amounts of elements or compounds being added are represented in moles. Yet if we are adding a solid we must convert from moles to grams to add the correct amount of reactant so that a successful reaction takes place. Likewise, if we are adding a liquid we must convert ...
... chemical reactions in which the amounts of elements or compounds being added are represented in moles. Yet if we are adding a solid we must convert from moles to grams to add the correct amount of reactant so that a successful reaction takes place. Likewise, if we are adding a liquid we must convert ...
Unit2 PPT 3 Atomic Structure
... Electron: the subatomic particle with a negative charge and relatively no mass ...
... Electron: the subatomic particle with a negative charge and relatively no mass ...
Priority Standards Covered
... C5.5A Predict if the bonding between two atoms of different elements will be primarily ionic or covalent. C5.5c Draw Lewis structures for simple compounds. C4.4a Explain why at room temperature different compounds can exist in different phases. C4.4b Identify if a molecule is polar or nonpolar given ...
... C5.5A Predict if the bonding between two atoms of different elements will be primarily ionic or covalent. C5.5c Draw Lewis structures for simple compounds. C4.4a Explain why at room temperature different compounds can exist in different phases. C4.4b Identify if a molecule is polar or nonpolar given ...
The Structure of Atoms
... • When two protons are extremely close to each other, there is a strong attraction between them. • A similar attraction exists when neutrons are very close to each other or when protons and neutrons are very close together. • The short-range proton-neutron, proton-proton, and neutron-neutron forces ...
... • When two protons are extremely close to each other, there is a strong attraction between them. • A similar attraction exists when neutrons are very close to each other or when protons and neutrons are very close together. • The short-range proton-neutron, proton-proton, and neutron-neutron forces ...
Chapter 6
... • This quantum number defines the shape of the orbital. • Allowed values of l are integers ranging from 0 to n − 1. • We use letter designations to communicate the different values of l and, therefore, the shapes and types of orbitals. Electronic Structure of Atoms © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • This quantum number defines the shape of the orbital. • Allowed values of l are integers ranging from 0 to n − 1. • We use letter designations to communicate the different values of l and, therefore, the shapes and types of orbitals. Electronic Structure of Atoms © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Cool Chemistry
... anything that has mass and takes up space There are four types of matter: solid, liquid, gas, plasma Solids – have definite shape and volume What equipment would you use to measure the shape and volume of a solid? Why are solids “solid”? Inside a solid, the molecules are packed together very tightly ...
... anything that has mass and takes up space There are four types of matter: solid, liquid, gas, plasma Solids – have definite shape and volume What equipment would you use to measure the shape and volume of a solid? Why are solids “solid”? Inside a solid, the molecules are packed together very tightly ...
Unit #3: Atomic Structure Exam Review
... 31) An element’s ______Average Atomic Mass_________ is an average mass of the different isotopes of an element. 32) _______Isotopes________ are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. 33) ______Atomic Number_____ refers to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. 34) De ...
... 31) An element’s ______Average Atomic Mass_________ is an average mass of the different isotopes of an element. 32) _______Isotopes________ are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. 33) ______Atomic Number_____ refers to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. 34) De ...
Goal 4.01
... The arrangement of electrons within their orbits can be shown using electron dot diagrams. Start by drawing a nucleus containing the correct number of protons and neutrons. Then determine the number of electrons within the atom. Draw the 1st orbit and fill that orbit with electrons. Electrons are dr ...
... The arrangement of electrons within their orbits can be shown using electron dot diagrams. Start by drawing a nucleus containing the correct number of protons and neutrons. Then determine the number of electrons within the atom. Draw the 1st orbit and fill that orbit with electrons. Electrons are dr ...
Chemical Periodicity
... “shield” the valence electrons from the force of attraction exerted by the positive charge in the nucleus. ...
... “shield” the valence electrons from the force of attraction exerted by the positive charge in the nucleus. ...
Masterton and Hurley - Chapter 6
... • It is impossible to specify the exact position of an electron at a given instant • We can only specify the probability of finding an electron in a particular region of space ...
... • It is impossible to specify the exact position of an electron at a given instant • We can only specify the probability of finding an electron in a particular region of space ...
atom
... All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine ...
... All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine ...
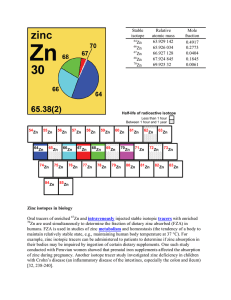
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... or CAT scan) – a computerized tomography (CT) scan combines a series of X-ray images taken from different angles and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images, or slices, of the bones, blood vessels and soft tissues inside your body [702]. cyclotron – an apparatus in which charged at ...
... or CAT scan) – a computerized tomography (CT) scan combines a series of X-ray images taken from different angles and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images, or slices, of the bones, blood vessels and soft tissues inside your body [702]. cyclotron – an apparatus in which charged at ...
Distinguishing Among Atoms
... different numbers of neutrons, they also have different mass numbers. ...
... different numbers of neutrons, they also have different mass numbers. ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.