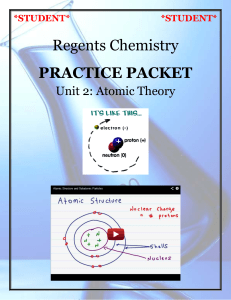
Electrons
... Describe Democritus’s ideas about atoms. Explain Dalton’s atomic theory. Identify what instrument is used to observe individual atoms. ...
... Describe Democritus’s ideas about atoms. Explain Dalton’s atomic theory. Identify what instrument is used to observe individual atoms. ...
CHEM 115 EXAM #1
... Use your periodic table to answer the following (use chemical symbols not names) a. the element expected to be chemically most similar to oxygen b. an element that exhibits properties between metals and nonmetals c. an element that is a transition metal d. a halogen ...
... Use your periodic table to answer the following (use chemical symbols not names) a. the element expected to be chemically most similar to oxygen b. an element that exhibits properties between metals and nonmetals c. an element that is a transition metal d. a halogen ...
1411_lecture_ch2
... known elements were arranged in order of atomic number, they could be placed in horizontal rows such that the elements in the vertical columns had similar properties. A tabular arrangement of elements in rows and columns, highlighting the regular repetition of properties of the elements, is called a ...
... known elements were arranged in order of atomic number, they could be placed in horizontal rows such that the elements in the vertical columns had similar properties. A tabular arrangement of elements in rows and columns, highlighting the regular repetition of properties of the elements, is called a ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and
... Unit 3 – Lessons 1-4 “ATOMS and the PERIODIC TABLE” (Pages 153-208) I. LESSON 1 A. The Atom 1. The basic UNIT of all MATTER is the __________ 2. ATOM is the SMALLEST particle of an ___________ retaining all the chemical _____________ of that ELEMENT 3. Democritus’s GREEK term “____________,” which ...
... Unit 3 – Lessons 1-4 “ATOMS and the PERIODIC TABLE” (Pages 153-208) I. LESSON 1 A. The Atom 1. The basic UNIT of all MATTER is the __________ 2. ATOM is the SMALLEST particle of an ___________ retaining all the chemical _____________ of that ELEMENT 3. Democritus’s GREEK term “____________,” which ...
effective nuclear charge
... ◦ in general, the increase in mass is greater than the increase in volume ...
... ◦ in general, the increase in mass is greater than the increase in volume ...
HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY MINI-MOCK UNIT 2
... The gases produced are a mixture of several silicon hydrides. One of the gases produced in the reaction is the silicon hydride with the formula SiH 4. The structure of this molecule is similar to methane, CH4. Draw a diagram to show the bonding in a molecule of SiH4. Represent the electrons as dots ...
... The gases produced are a mixture of several silicon hydrides. One of the gases produced in the reaction is the silicon hydride with the formula SiH 4. The structure of this molecule is similar to methane, CH4. Draw a diagram to show the bonding in a molecule of SiH4. Represent the electrons as dots ...
FirstSemesterReviewHonors
... Chapter 1 1. A characteristic of a scientific theory is that it can never ____. 2. When can a hypothesis become a theory? 3. What are the three states of matter? Define each state of matter and explain what happens to the particles that exist in each state. 4. Explain the differences between chemica ...
... Chapter 1 1. A characteristic of a scientific theory is that it can never ____. 2. When can a hypothesis become a theory? 3. What are the three states of matter? Define each state of matter and explain what happens to the particles that exist in each state. 4. Explain the differences between chemica ...
oxidation number
... Group 4A elements have four valence electrons. They form 4+ ions after losing the 4 valence electrons. They could just as easily form 4- ions after gaining four additional electrons. ...
... Group 4A elements have four valence electrons. They form 4+ ions after losing the 4 valence electrons. They could just as easily form 4- ions after gaining four additional electrons. ...
Molecular Compound
... • Other atoms can fill their outermost s and p orbitals by sharing electrons through covalent bonding. ...
... • Other atoms can fill their outermost s and p orbitals by sharing electrons through covalent bonding. ...
Atomic Structure Worksheet
... Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. The Greek philosopher Democritus coined what word for a tiny piece of matter that cannot be divided? a. element c. electron b. atom d. molecule ____ 2. According to John Dalton’s observations, when e ...
... Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. The Greek philosopher Democritus coined what word for a tiny piece of matter that cannot be divided? a. element c. electron b. atom d. molecule ____ 2. According to John Dalton’s observations, when e ...
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
... Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
... Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
How is E-M Radiation Produced?
... Because the spectra of stars are pretty close to being Planck Curves, stellar colors can be used to measure stellar temperatures. The process is: 1. Use computer models of spectra generated for stars of different temperature and calibrate a colortemperature relation 2. Measure the brightness of a st ...
... Because the spectra of stars are pretty close to being Planck Curves, stellar colors can be used to measure stellar temperatures. The process is: 1. Use computer models of spectra generated for stars of different temperature and calibrate a colortemperature relation 2. Measure the brightness of a st ...
Chemistry - Beck-Shop
... divided further nor destroyed, and (ii) all atoms of the same element were identical. The model had to give way to other models, as science and technology produced new evidence. This evidence could only be interpreted as atoms having other particles inside them – they have an internal structure. Sci ...
... divided further nor destroyed, and (ii) all atoms of the same element were identical. The model had to give way to other models, as science and technology produced new evidence. This evidence could only be interpreted as atoms having other particles inside them – they have an internal structure. Sci ...
Practice Packet
... 22. The lines on the visible light spectrum for the gases above represent a) electrons jumping to the same excited state or energy level. b) electrons falling back down to their ground state from the same energy level. c) electrons jumping to multiple excited states or energy levels. d) electrons fa ...
... 22. The lines on the visible light spectrum for the gases above represent a) electrons jumping to the same excited state or energy level. b) electrons falling back down to their ground state from the same energy level. c) electrons jumping to multiple excited states or energy levels. d) electrons fa ...
What are atoms?
... What is matter made of? • In 1897, J. J. Thomson performed experiments that detected smaller particles within atoms. • In the early 1900s, Ernest Rutherford and James Chadwick revealed the nature of the dense center of an atom. • Today we have the electron cloud model. ...
... What is matter made of? • In 1897, J. J. Thomson performed experiments that detected smaller particles within atoms. • In the early 1900s, Ernest Rutherford and James Chadwick revealed the nature of the dense center of an atom. • Today we have the electron cloud model. ...
Atom Basics
... 25. Choose a state of matter. Draw how particles are behaving. Create an analogy describing the particles. ...
... 25. Choose a state of matter. Draw how particles are behaving. Create an analogy describing the particles. ...
Section 2.5 The Modern View of Atomic Structure: An Introduction
... Greeks were the first to attempt to explain why chemical changes occur. Alchemy dominated for 2000 years. Several elements discovered. ...
... Greeks were the first to attempt to explain why chemical changes occur. Alchemy dominated for 2000 years. Several elements discovered. ...
CH2 Student Revision Guides pdf
... covalent and understand the way in which the electron density, distribution varies with the ionic character of the bond. ...
... covalent and understand the way in which the electron density, distribution varies with the ionic character of the bond. ...
Mass Number, A
... the four elements: • earth (cold and dry) • air (hot and moist) • fire (hot and dry) • water (cold and moist) • The differences in matter where a result of different balances of these atoms • Changing the balance could change matter • ex: what we know as ...
... the four elements: • earth (cold and dry) • air (hot and moist) • fire (hot and dry) • water (cold and moist) • The differences in matter where a result of different balances of these atoms • Changing the balance could change matter • ex: what we know as ...
9077590 Chem. Rege. Jan. 01
... (2) is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity (3) exhibits hydrogen bonding (4) exhibits metallic and nonmetallic properties ...
... (2) is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity (3) exhibits hydrogen bonding (4) exhibits metallic and nonmetallic properties ...
FREE Sample Here
... 24) A salamander relies on hydrogen bonding to stick to various surfaces. Therefore, a salamander would have the greatest difficulty clinging to a _____. A) slightly damp surface B) surface of hydrocarbons C) surface of mostly carbon-oxygen bonds D) surface of mostly carbon-nitrogen bonds Answer: B ...
... 24) A salamander relies on hydrogen bonding to stick to various surfaces. Therefore, a salamander would have the greatest difficulty clinging to a _____. A) slightly damp surface B) surface of hydrocarbons C) surface of mostly carbon-oxygen bonds D) surface of mostly carbon-nitrogen bonds Answer: B ...
File
... percentage by mass of an element in it using relative atomic mass and relative formula mass… % mass of an element in a compound = Ar x number of atoms (of element) x 100 Mr (of whole compound) ...
... percentage by mass of an element in it using relative atomic mass and relative formula mass… % mass of an element in a compound = Ar x number of atoms (of element) x 100 Mr (of whole compound) ...
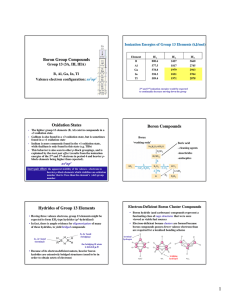
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... • How does this trend agree with electronegativities of X? • In the trigonal planar BX3 structure, π-bonding exists, most X X important for smaller elements B Rem: correct Lewis F F B structure shows all bonds and electrons F ...
... • How does this trend agree with electronegativities of X? • In the trigonal planar BX3 structure, π-bonding exists, most X X important for smaller elements B Rem: correct Lewis F F B structure shows all bonds and electrons F ...
28-2 Models of the Atom
... physicist, Niels Bohr, who incorporating ideas from Rutherford and quantum ideas. In Bohr’s model, electrons traveled in circular orbits around a central nucleus, similar to the way planets travel around the Sun. It is important to understand that the Bohr model does not reflect reality, but it prov ...
... physicist, Niels Bohr, who incorporating ideas from Rutherford and quantum ideas. In Bohr’s model, electrons traveled in circular orbits around a central nucleus, similar to the way planets travel around the Sun. It is important to understand that the Bohr model does not reflect reality, but it prov ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.