A) electrons B) neutrons C) positrons D) protons 1. According to the
... 51. How do the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the third shell of an atom compare to the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the first shell of the same atom? A) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is closer to the nucleus. B) In the third ...
... 51. How do the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the third shell of an atom compare to the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the first shell of the same atom? A) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is closer to the nucleus. B) In the third ...
How Atoms Differ
... isotope from another. This is done in two ways. Hyphen notation. This gives the element name (which you can use to determine the atomic number) followed by the atomic mass which you can use to determine the number of neutrons. Hydrogen – 2 ...
... isotope from another. This is done in two ways. Hyphen notation. This gives the element name (which you can use to determine the atomic number) followed by the atomic mass which you can use to determine the number of neutrons. Hydrogen – 2 ...
Hydrogen (/ˈhaɪdrɵdʒən/ HY-drə-jən)[7] is a chemical element
... atomic number 1. With an average atomic weight of 1.00794 u (1.007825 u for hydrogen-1), hydrogen is the lightest element and its monatomic form (H1) is the most abundant chemical substance. At standard temperature and pressure, hydrogen is a colourless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, nonmetallic, ...
... atomic number 1. With an average atomic weight of 1.00794 u (1.007825 u for hydrogen-1), hydrogen is the lightest element and its monatomic form (H1) is the most abundant chemical substance. At standard temperature and pressure, hydrogen is a colourless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, nonmetallic, ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Scientists held conflicting views about the nature of the cathode rays. It was not initially clear whether the rays were an invisible stream of particles or a new form of radiation. Experiments showed that cathode rays are deflected by electric or magnetic fields in a way consistent with their being ...
... Scientists held conflicting views about the nature of the cathode rays. It was not initially clear whether the rays were an invisible stream of particles or a new form of radiation. Experiments showed that cathode rays are deflected by electric or magnetic fields in a way consistent with their being ...
CHEMISTRY: MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW SPRING 2013 Multiple
... ____ 26. Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron ____. a. falls into the nucleus b. moves within its atomic orbital c. jumps from a lower to a higher energy level d. drops from a higher to a lower energy level ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken ...
... ____ 26. Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron ____. a. falls into the nucleus b. moves within its atomic orbital c. jumps from a lower to a higher energy level d. drops from a higher to a lower energy level ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken ...
03_Worked_Examples
... required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation requires. There are eight N atoms in the eight NO molecules in the reactants box. There are also 4 2 = 8 O a ...
... required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation requires. There are eight N atoms in the eight NO molecules in the reactants box. There are also 4 2 = 8 O a ...
03_Worked_Examples
... required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation requires. There are eight N atoms in the eight NO molecules in the reactants box. There are also 4 2 = 8 O a ...
... required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation requires. There are eight N atoms in the eight NO molecules in the reactants box. There are also 4 2 = 8 O a ...
Dec. 15 , 2012, 9:00 am – noon - Dr. K. Brown
... E) No way of knowing with information given 17) A 1.00 L flask is filled with 0.160 g of unknown gas at 743 mmHg and 25 0C. Calculate the molar mass and identify the gas. The unknown gas is: A) CO2 B) O2 C) Ne D) He E) can be any of the above 18) Oxygen gas, generated by the reaction 2 KClO3 (s) → 2 ...
... E) No way of knowing with information given 17) A 1.00 L flask is filled with 0.160 g of unknown gas at 743 mmHg and 25 0C. Calculate the molar mass and identify the gas. The unknown gas is: A) CO2 B) O2 C) Ne D) He E) can be any of the above 18) Oxygen gas, generated by the reaction 2 KClO3 (s) → 2 ...
Chapter 3 - Cloudfront.net
... and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties.* • Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed.* ...
... and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties.* • Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed.* ...
atomic number
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. All matter is made of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number r ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. All matter is made of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number r ...
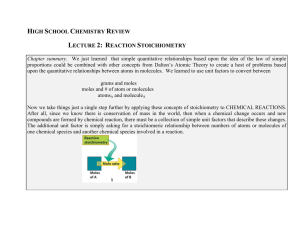
HIGH SCHOOL CHEMISTRY REVIEW LECTURE 2: REACTION
... Chapter summary. We just learned that simple quantitative relationships based upon the idea of the law of simple proportions could be combined with other concepts from Dalton’s Atomic Theory to create a host of problems based upon the quantitative relationships between atoms in molecules. We learned ...
... Chapter summary. We just learned that simple quantitative relationships based upon the idea of the law of simple proportions could be combined with other concepts from Dalton’s Atomic Theory to create a host of problems based upon the quantitative relationships between atoms in molecules. We learned ...
Name
... Copper consists of 69.15% copper-63, which has an atomic mass of 62.929 601 amu, and 30.85% copper-65, which has an atomic mass of 64.927 794 amu. The average atomic mass of copper can be calculated by multiplying the atomic mass of each isotope by its relative abundance (expressed in decimal form) ...
... Copper consists of 69.15% copper-63, which has an atomic mass of 62.929 601 amu, and 30.85% copper-65, which has an atomic mass of 64.927 794 amu. The average atomic mass of copper can be calculated by multiplying the atomic mass of each isotope by its relative abundance (expressed in decimal form) ...
Atomic Structure - Renton School District
... 0 If the relative mass of a protons and neutrons is 1, why is the atomic mass = 12.01? 0 Different kinds of carbon exist! 0 Average atomic mass is the average of all types of carbon ...
... 0 If the relative mass of a protons and neutrons is 1, why is the atomic mass = 12.01? 0 Different kinds of carbon exist! 0 Average atomic mass is the average of all types of carbon ...
Additional Review
... o all of matter is some combination of these four elements Alchemy [1500 AD] In the 1500’s many scientists were________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ While they were not able to create gold they did di ...
... o all of matter is some combination of these four elements Alchemy [1500 AD] In the 1500’s many scientists were________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ While they were not able to create gold they did di ...
Chapter 03
... blocks, of elements according to the subshells that are last to fill, s, p, d, or f. ►Beginning at the top left corner of the periodic table, the first row contains only two elements, H and He. The 1s subshell is being filled here. ►The second row begins with two s-block elements (Li and Be) and con ...
... blocks, of elements according to the subshells that are last to fill, s, p, d, or f. ►Beginning at the top left corner of the periodic table, the first row contains only two elements, H and He. The 1s subshell is being filled here. ►The second row begins with two s-block elements (Li and Be) and con ...
Chemistry I Accelerated StudyGuideline
... small, indivisible particles, each of which was called a(n) _____________. The theory that such particles existed was supported much later, by _____________ who proposed, in his law of _______________ _____ __________, that matter could not be created or destroyed. Then ___________ proposed, in his ...
... small, indivisible particles, each of which was called a(n) _____________. The theory that such particles existed was supported much later, by _____________ who proposed, in his law of _______________ _____ __________, that matter could not be created or destroyed. Then ___________ proposed, in his ...
Quantum Chemistry Predicts Multiply Bonded Diuranium
... of U 7s, 7p, 6d, and 5f orbitals with Cl 3p orbitals. The U-U and U-Cl bond distances and the U-U-Cl angle have been optimized at the CASPT2 level of theory. The ground state of U2Cl6 is a singlet state with the electronic configuration (σg)2(πu).4 The U-U bond distance is 2.43 Å, the U-Cl distance ...
... of U 7s, 7p, 6d, and 5f orbitals with Cl 3p orbitals. The U-U and U-Cl bond distances and the U-U-Cl angle have been optimized at the CASPT2 level of theory. The ground state of U2Cl6 is a singlet state with the electronic configuration (σg)2(πu).4 The U-U bond distance is 2.43 Å, the U-Cl distance ...
as PDF - Halbleiter.org
... The sodium atom gives off its valence electron (so it has more protons than electrons and is positively charged), while chlorine accepts one electron and thus is negatively charged. Due to the different charges the two atoms attract each other. A charged atom is known as an ion, while a positive ion ...
... The sodium atom gives off its valence electron (so it has more protons than electrons and is positively charged), while chlorine accepts one electron and thus is negatively charged. Due to the different charges the two atoms attract each other. A charged atom is known as an ion, while a positive ion ...
File
... • How many protons are there in Lithium-7? • How many neutrons are there in Lithium-7? • How many protons are there in Mg? • How many electrons are there in Mg? ...
... • How many protons are there in Lithium-7? • How many neutrons are there in Lithium-7? • How many protons are there in Mg? • How many electrons are there in Mg? ...
Chemistry(I) Final Exam 1/11/2008
... (b) According to Charles’s law, lower temperature causes smaller volume of a gas. The smallest volume of an ideal gas can have is 0. So the temperature at which an ideal gas reach zero volume is the absolute zero. ...
... (b) According to Charles’s law, lower temperature causes smaller volume of a gas. The smallest volume of an ideal gas can have is 0. So the temperature at which an ideal gas reach zero volume is the absolute zero. ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure Notes
... When an atom has the same number of protons as electrons. (+) = (-) if the atom is neutral then it has not lost or gained electrons. Atomic charge- an atom will have a charge when the protons and the electrons are not equal in number. Atoms will lose or gain electrons to ...
... When an atom has the same number of protons as electrons. (+) = (-) if the atom is neutral then it has not lost or gained electrons. Atomic charge- an atom will have a charge when the protons and the electrons are not equal in number. Atoms will lose or gain electrons to ...
04 Mass Spectrometer and Isotopes
... How easily you can change the direction of your movement is affected by how much mass you have. Isotopes have different masses! Maybe we can use this to determine the mass of different isotopes! ...
... How easily you can change the direction of your movement is affected by how much mass you have. Isotopes have different masses! Maybe we can use this to determine the mass of different isotopes! ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.



![Hydrogen (/ˈhaɪdrɵdʒən/ HY-drə-jən)[7] is a chemical element](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001197267_1-624cb7c7c4dbdb26b0769567aa77b6ad-300x300.png)