Chemistry 211 - George Mason University
... Gas:Loose StructurePlasma:Gaseous atoms or small molecules in an ionized state. • Substances and mixtures: • Substance: matter having a fixed composition and distinct properties. Can be either an element or a compound. – Element: a substance containing only one type of atom. E.g. Na, H 2. – Compound ...
... Gas:Loose StructurePlasma:Gaseous atoms or small molecules in an ionized state. • Substances and mixtures: • Substance: matter having a fixed composition and distinct properties. Can be either an element or a compound. – Element: a substance containing only one type of atom. E.g. Na, H 2. – Compound ...
The Periodic table
... A region of space within an electron subshell where an electron with a specific energy is most likely to be found. S subshell=1 orbital, p subshell=3 orbitals, d subshell=5 orbitals, f subshell=7 orbitals. Maximum number of electrons in a subshell is always 2. S orbital=spherical, p orbital ...
... A region of space within an electron subshell where an electron with a specific energy is most likely to be found. S subshell=1 orbital, p subshell=3 orbitals, d subshell=5 orbitals, f subshell=7 orbitals. Maximum number of electrons in a subshell is always 2. S orbital=spherical, p orbital ...
Introduction to Computational Chemistry
... special skills or prior knowledge. It should be suitable for students after their second year in the chemistry curriculum. In part II we have collected a number of subjects that we found interesting ...
... special skills or prior knowledge. It should be suitable for students after their second year in the chemistry curriculum. In part II we have collected a number of subjects that we found interesting ...
2003
... The extraction of aluminium from Al2O3 involves a chemical reaction… the breaking of the strong bond with oxygen. The recycling of aluminium involves melting which is a physical change requiring much less energy. ...
... The extraction of aluminium from Al2O3 involves a chemical reaction… the breaking of the strong bond with oxygen. The recycling of aluminium involves melting which is a physical change requiring much less energy. ...
4-Pres-Feb-08
... Chemical Equation • C2H5OH + 3 O2 2 CO2 + 3 H2O The equation is balanced and the reaction can be completely stated as: ...
... Chemical Equation • C2H5OH + 3 O2 2 CO2 + 3 H2O The equation is balanced and the reaction can be completely stated as: ...
CHEMISTRY PHYSICAL SETTING Thursday, PS/CHEMISTRY
... (1) The water loses heat to the block until both are at 10.0°C. (2) The block gains heat from the water until both are at 90.0°C. (3) The water loses heat and the block gains heat until both are at the same temperature that is between 10.0°C and 90.0°C. (4) The water gains heat and the block loses h ...
... (1) The water loses heat to the block until both are at 10.0°C. (2) The block gains heat from the water until both are at 90.0°C. (3) The water loses heat and the block gains heat until both are at the same temperature that is between 10.0°C and 90.0°C. (4) The water gains heat and the block loses h ...
Topic II. Chapter 9
... experiment. • In 1925, Goudsmit and Uhlenbeck proposed that the electron must have an intrinsic angular momentum. • The relativistic quantum theory proposed by Dirac in 1928 showed that the intrinsic spin of the electron required a fourth quantum number as a consequence of the theory of relativity. ...
... experiment. • In 1925, Goudsmit and Uhlenbeck proposed that the electron must have an intrinsic angular momentum. • The relativistic quantum theory proposed by Dirac in 1928 showed that the intrinsic spin of the electron required a fourth quantum number as a consequence of the theory of relativity. ...
CHEMISTRY 102A/102C Spring 2014 Hour Exam II Page _____ For
... a) Compounds that can H-bond have higher boiling points than ionic compounds. b) A compound must contain a CH, NH, OH, or FH covalent bond in the molecule in order to Hbond. c) Given two covalent compounds having about the same molar mass, the compound that can Hbond will have the higher vapor ...
... a) Compounds that can H-bond have higher boiling points than ionic compounds. b) A compound must contain a CH, NH, OH, or FH covalent bond in the molecule in order to Hbond. c) Given two covalent compounds having about the same molar mass, the compound that can Hbond will have the higher vapor ...
Chem-CH8-Review Guide
... where x, y, and z represent the number of atoms in one molecule of the compound (or, in the case of the empirical formula, the lowest whole-number ratio). Our problem, then, is to determine these numbers. Thus, we have been given mass-percent data for the atoms and need to determine the number of at ...
... where x, y, and z represent the number of atoms in one molecule of the compound (or, in the case of the empirical formula, the lowest whole-number ratio). Our problem, then, is to determine these numbers. Thus, we have been given mass-percent data for the atoms and need to determine the number of at ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... • Metals and nonmetals are separated by a stair-step line on the right side of the table. • Metals are found to the left of the line and nonmetals are found to the right of the line. • Elements that border the line on both sides are called semi-metals. ...
... • Metals and nonmetals are separated by a stair-step line on the right side of the table. • Metals are found to the left of the line and nonmetals are found to the right of the line. • Elements that border the line on both sides are called semi-metals. ...
Atomic mass
... Identity of each element is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons. Practice problems pg. 99 ...
... Identity of each element is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons. Practice problems pg. 99 ...
Chapter 4 Review Answers
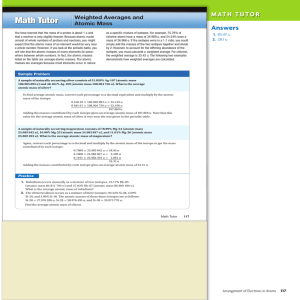
... A sample of naturally occurring silver consists of 51.839% Ag-107 (atomic mass 106.905 093 u) and 48.161% Ag-109 (atomic mass 108.904 756 u). What is the average atomic mass of silver? To find average atomic mass, convert each percentage to a decimal equivalent and multiply by the atomic mass of the ...
... A sample of naturally occurring silver consists of 51.839% Ag-107 (atomic mass 106.905 093 u) and 48.161% Ag-109 (atomic mass 108.904 756 u). What is the average atomic mass of silver? To find average atomic mass, convert each percentage to a decimal equivalent and multiply by the atomic mass of the ...
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Chemistry, a little early. We will have
... correspond with an older textbook and do not match the chapters in your book perfectly. Complete problems from Hwk 1.1 (the homework for the three chapters has been packaged as a unit) and Clwk 1.1. 2. Read the Chapter 2 notes provided. Complete problems from Hwk 1.2 and Clwk 1.2A and B (1.2B is NOT ...
... correspond with an older textbook and do not match the chapters in your book perfectly. Complete problems from Hwk 1.1 (the homework for the three chapters has been packaged as a unit) and Clwk 1.1. 2. Read the Chapter 2 notes provided. Complete problems from Hwk 1.2 and Clwk 1.2A and B (1.2B is NOT ...
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet
... Reactants are written on the left, and products are written on the right. In a balanced equation the total numbers of atoms of each kind on both sides are the same. To achieve a balance, we write coefficients in front of each chemical species, although the number 1 is never written as a coefficient. ...
... Reactants are written on the left, and products are written on the right. In a balanced equation the total numbers of atoms of each kind on both sides are the same. To achieve a balance, we write coefficients in front of each chemical species, although the number 1 is never written as a coefficient. ...
9 Chapter 1 Some History and the Mysteries of Superposition 1.1
... wave is the (vector) sum of the two individual waves.4 For example, imagine that a second device identical to the first is at work somewhere else in the pond and that a wave from the first device meets a wave from the second device. If the two waves are completely in phase (they meet crest to crest ...
... wave is the (vector) sum of the two individual waves.4 For example, imagine that a second device identical to the first is at work somewhere else in the pond and that a wave from the first device meets a wave from the second device. If the two waves are completely in phase (they meet crest to crest ...
Review Session 3 Problems
... 1) Titanium tetrachloride is an important industrial chemical. It is used for preparing the TiO2, the white pigment in paints and paper. It can be made using an impure titanium ore(often impure TiO2) with carbon and chlorine. ...
... 1) Titanium tetrachloride is an important industrial chemical. It is used for preparing the TiO2, the white pigment in paints and paper. It can be made using an impure titanium ore(often impure TiO2) with carbon and chlorine. ...
CHAPtER 9 Properties and reactions of organic compounds
... forces that hold the molecules of a substance together, so it is useful to compare the boiling points of related compounds to see how structural differences account for the differences in intermolecular attractions. ...
... forces that hold the molecules of a substance together, so it is useful to compare the boiling points of related compounds to see how structural differences account for the differences in intermolecular attractions. ...
Chemical bonding and structure
... of pure carbon, in which the bonding of atoms within a layer is much stronger than the forces between the layers. An understanding of bonding enables scientists to explain and predict many of the properties of materials. ...
... of pure carbon, in which the bonding of atoms within a layer is much stronger than the forces between the layers. An understanding of bonding enables scientists to explain and predict many of the properties of materials. ...
Chapter 03 - La Salle University
... blocks, of elements according to the subshells that are last to fill, s, p, d, or f. ►Beginning at the top left corner of the periodic table, the first row contains only two elements, H and He. The 1s subshell is being filled here. ►The second row begins with two s-block elements (Li and Be) and con ...
... blocks, of elements according to the subshells that are last to fill, s, p, d, or f. ►Beginning at the top left corner of the periodic table, the first row contains only two elements, H and He. The 1s subshell is being filled here. ►The second row begins with two s-block elements (Li and Be) and con ...
PPT of Notes
... Dalton also developed another law known as the Law of Multiple Proportions which states; that the ratio of a fixed mass of one element when combined with the multiple masses of another element may be expressed in small whole numbers. In simpler terms, the same element can unite in more than one way ...
... Dalton also developed another law known as the Law of Multiple Proportions which states; that the ratio of a fixed mass of one element when combined with the multiple masses of another element may be expressed in small whole numbers. In simpler terms, the same element can unite in more than one way ...
Atomic Structure
... • Radioactive isotopes are unstable (high in energy). This instability is attributed to a neutron/proton ratio that is either too high or too ...
... • Radioactive isotopes are unstable (high in energy). This instability is attributed to a neutron/proton ratio that is either too high or too ...
Science Focus 9 Matter and Chemical Change Class Notes Topic 1
... The only evidence that will guarantee a chemical change has occurred is that a new substance has been formed. Properties: Chemical or Physical? Any property that can be observed without forming a new substance is a physical property. These can include: color, texture, luster, smell, state, melting p ...
... The only evidence that will guarantee a chemical change has occurred is that a new substance has been formed. Properties: Chemical or Physical? Any property that can be observed without forming a new substance is a physical property. These can include: color, texture, luster, smell, state, melting p ...
Reviewing Chemistry: Mastering the TEKS - Student
... covered in the textbook on page 104. Reviewing Chemistry: Mastering the TEKS ...
... covered in the textbook on page 104. Reviewing Chemistry: Mastering the TEKS ...
Review Questions for 1st year chemistry
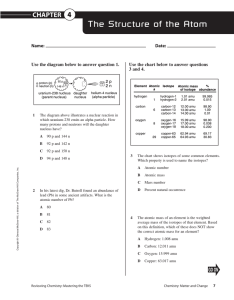
... B. Both atoms have 7 protons. C. The atoms have different atomic masses. D. Both atoms have 7 neutrons. Answer: D These isotopes have different masses (14 and 16), but the same number of protons (7). To find the neutrons, calculate mass minus protons. ...
... B. Both atoms have 7 protons. C. The atoms have different atomic masses. D. Both atoms have 7 neutrons. Answer: D These isotopes have different masses (14 and 16), but the same number of protons (7). To find the neutrons, calculate mass minus protons. ...
Chemistry Revision Guide - Mr Cartlidge`s Science Blog
... four valence electrons so needs four more to complete its outer shell, oxygen needs two more. Thus each carbon will react with two oxygens, sharing two electrons with each one. A bond involving two shared pairs is a double bond. O ...
... four valence electrons so needs four more to complete its outer shell, oxygen needs two more. Thus each carbon will react with two oxygens, sharing two electrons with each one. A bond involving two shared pairs is a double bond. O ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.