PPT
... 4. How is the periodic table arranged? Be able to describe how elements are arranged in the periodic table, name the subdivisions of the periodic table, and relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its electronic structure. 5. How are electrons arranged in atoms? Be able to explain ...
... 4. How is the periodic table arranged? Be able to describe how elements are arranged in the periodic table, name the subdivisions of the periodic table, and relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its electronic structure. 5. How are electrons arranged in atoms? Be able to explain ...
WEEK
... Elements interact forming bonds in order to become more stable, The type of atoms involved determines the nature of the bond, the formula, and the name of the compound formed. Elements interact forming bonds in order to become more stable, The type of atoms involved determines the nature of the bond ...
... Elements interact forming bonds in order to become more stable, The type of atoms involved determines the nature of the bond, the formula, and the name of the compound formed. Elements interact forming bonds in order to become more stable, The type of atoms involved determines the nature of the bond ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE Democritus, ancient Greece: “All matter is
... ATOMIC STRUCTURE Democritus, ancient Greece: “All matter is made of tiny invisible particles, atoms.” Dalton’s atomic theory, 1807 ...
... ATOMIC STRUCTURE Democritus, ancient Greece: “All matter is made of tiny invisible particles, atoms.” Dalton’s atomic theory, 1807 ...
4 Atomic Structure / Quantum Mechanics
... credited with the discovery of the neutral subatomic particle - the neutron Walter Bothe obtained initial evidence nearly two years before Chadwick's experiments Neutrons have a mass nearly identical to that of the proton, but no electrical charge. ...
... credited with the discovery of the neutral subatomic particle - the neutron Walter Bothe obtained initial evidence nearly two years before Chadwick's experiments Neutrons have a mass nearly identical to that of the proton, but no electrical charge. ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE Democritus, ancient Greece: “All matter is
... ATOMIC STRUCTURE Democritus, ancient Greece: “All matter is made of tiny invisible particles, atoms.” Dalton’s atomic theory, 1807 ...
... ATOMIC STRUCTURE Democritus, ancient Greece: “All matter is made of tiny invisible particles, atoms.” Dalton’s atomic theory, 1807 ...
Unit 2 Review
... The observation of the unique line spectra of samples of elemental gases led to the belief that the atom consisted of _____. a. electrons orbiting the nucleus with discrete and quantized amounts of energy b. a positively charged center surrounded by negative electrons c. negatively charged particles ...
... The observation of the unique line spectra of samples of elemental gases led to the belief that the atom consisted of _____. a. electrons orbiting the nucleus with discrete and quantized amounts of energy b. a positively charged center surrounded by negative electrons c. negatively charged particles ...
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... • Explain the impact of de Broglie's wave article duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the current view of electrons in atoms. • Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom's energy levels, sublevels, and atomic orbitals. atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains all ...
... • Explain the impact of de Broglie's wave article duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the current view of electrons in atoms. • Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom's energy levels, sublevels, and atomic orbitals. atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains all ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... A Chemistry Helper and one 3 x 5 index card (double sided) may be used on the final. Please complete these questions on a separate sheet of paper (15 pts.) ...
... A Chemistry Helper and one 3 x 5 index card (double sided) may be used on the final. Please complete these questions on a separate sheet of paper (15 pts.) ...
Review - gbschemphys
... The observation of the unique line spectra of samples of elemental gases led to the belief that the atom consisted of _____. a. electrons orbiting the nucleus with discrete and quantized amounts of energy b. a positively charged center surrounded by negative electrons c. negatively charged particles ...
... The observation of the unique line spectra of samples of elemental gases led to the belief that the atom consisted of _____. a. electrons orbiting the nucleus with discrete and quantized amounts of energy b. a positively charged center surrounded by negative electrons c. negatively charged particles ...
Atomic Model/Theory Webquest
... This site is real good interactive site that gives some information on the Bohr model and the spectral lines that had been observed for hydrogen. Remember, as the website informs us, the only lines that we can see (visible light) are between 440 and 600nM. Just a sliver of the spectrum. Another thin ...
... This site is real good interactive site that gives some information on the Bohr model and the spectral lines that had been observed for hydrogen. Remember, as the website informs us, the only lines that we can see (visible light) are between 440 and 600nM. Just a sliver of the spectrum. Another thin ...
Atoms and Molecules
... All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, and different from all other atoms. That atoms were indivisible, and were not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. When atoms of different elements form compounds, the ratio of one type of atom to another ...
... All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, and different from all other atoms. That atoms were indivisible, and were not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. When atoms of different elements form compounds, the ratio of one type of atom to another ...
The Greek Concept of Atomos: The Indivisible Atom - Mr
... Gassendi is considered by many to be the reviver of atomism, but as you have seen, atomism never really went away, it was just on the fringes. However, Gassendi was successful in making atomism more widely known and acceptable, especially by separating a belief in atomism from athesism. Before going ...
... Gassendi is considered by many to be the reviver of atomism, but as you have seen, atomism never really went away, it was just on the fringes. However, Gassendi was successful in making atomism more widely known and acceptable, especially by separating a belief in atomism from athesism. Before going ...
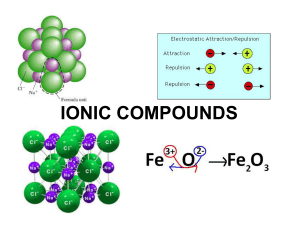
Section 8.3 Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds Formula Unit
... ion is its oxidation number. (sometimes called oxidation state) ...
... ion is its oxidation number. (sometimes called oxidation state) ...
Chemical Bonding Quiz
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
Topic 1: Quantitative Chemistry
... Solid –particles closely packed in fixed positions; forces between particles strong enough to restrict movement; have fixed shape Liquid –particles closely packed but not in fixed position; forces between particles weak enough to allow movement but fix the volume; no fixed shape Gas –forces betwe ...
... Solid –particles closely packed in fixed positions; forces between particles strong enough to restrict movement; have fixed shape Liquid –particles closely packed but not in fixed position; forces between particles weak enough to allow movement but fix the volume; no fixed shape Gas –forces betwe ...
Trends in the Periodic Table
... (protons, neutrons, and electrons), isotopes, and charged and uncharged atoms. In each case, enough information has been provided for you to fill in all of the blanks. For the far right column, if an atom has a charge, label it with the appropriate sign and number (ex. +1 ion). If an atom is neutral ...
... (protons, neutrons, and electrons), isotopes, and charged and uncharged atoms. In each case, enough information has been provided for you to fill in all of the blanks. For the far right column, if an atom has a charge, label it with the appropriate sign and number (ex. +1 ion). If an atom is neutral ...
chemistry — released form
... Energy is absorbed when excitation occurs. Excitation is when an electron goes from a low energy level to a higher energy level. ...
... Energy is absorbed when excitation occurs. Excitation is when an electron goes from a low energy level to a higher energy level. ...
Ionic Bonding
... another electron from the Na+ ion? Since the Na+ ion has a noble gas electron configuration, stripping away the next electron from this stable arrangement would take far more energy than what is released during lattice formation (Sodium I2 = 4,560 kJ/mol). Thus, sodium is present in ionic compounds ...
... another electron from the Na+ ion? Since the Na+ ion has a noble gas electron configuration, stripping away the next electron from this stable arrangement would take far more energy than what is released during lattice formation (Sodium I2 = 4,560 kJ/mol). Thus, sodium is present in ionic compounds ...
Section 1-2 Matter and Its Properties
... An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. An element is a pure substance made up of only one kind of atom. A compound is a substance that is made from the atoms of two or more elements that ...
... An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. An element is a pure substance made up of only one kind of atom. A compound is a substance that is made from the atoms of two or more elements that ...
The Atom
... compounds. Because all matter is made of elements or compounds, atoms are often called the building blocks of matter. Before the scanning tunneling microscope was invented, in 1981, no one had ever seen an atom. But the existence of atoms is not a new idea. As you will find out, our understanding of ...
... compounds. Because all matter is made of elements or compounds, atoms are often called the building blocks of matter. Before the scanning tunneling microscope was invented, in 1981, no one had ever seen an atom. But the existence of atoms is not a new idea. As you will find out, our understanding of ...
3. Chemical changes and Structure Unit Questions
... o Group 8- Noble gases o Chemical formula can be written: o From the name if there is a prefix. Di, tri, tetra etc. o Using S,V,S,D,F o The state symbols are: o (s)-solid o (l)- liquid o (g)- gas o (aq)- in solution (dissolved) o The first 20 elements can be separated into the following: o Metallic- ...
... o Group 8- Noble gases o Chemical formula can be written: o From the name if there is a prefix. Di, tri, tetra etc. o Using S,V,S,D,F o The state symbols are: o (s)-solid o (l)- liquid o (g)- gas o (aq)- in solution (dissolved) o The first 20 elements can be separated into the following: o Metallic- ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Curriculum
... ended. Sometimes, EQs can be debated. A student’s answer to an EQ will help teachers determine if he/she truly understands. Consider having only one or two EQs per Enduring Understanding.) ...
... ended. Sometimes, EQs can be debated. A student’s answer to an EQ will help teachers determine if he/she truly understands. Consider having only one or two EQs per Enduring Understanding.) ...
AP CHEMISTRY - An Incomplete List of Topics
... Example: When Na2CO3(s) is heated, it will decompose to form CO2(g). Solid Na2O will also be formed as the remainder of the original compound. The Na2O(s) will slowly re-absorb CO2(g) from the air and convert back into Na2CO3(s). Other carbonates follow this same pattern, as seen in the reaction of ...
... Example: When Na2CO3(s) is heated, it will decompose to form CO2(g). Solid Na2O will also be formed as the remainder of the original compound. The Na2O(s) will slowly re-absorb CO2(g) from the air and convert back into Na2CO3(s). Other carbonates follow this same pattern, as seen in the reaction of ...
Chemistry 211 - George Mason University
... Gas:Loose StructurePlasma:Gaseous atoms or small molecules in an ionized state. • Substances and mixtures: • Substance: matter having a fixed composition and distinct properties. Can be either an element or a compound. – Element: a substance containing only one type of atom. E.g. Na, H 2. – Compound ...
... Gas:Loose StructurePlasma:Gaseous atoms or small molecules in an ionized state. • Substances and mixtures: • Substance: matter having a fixed composition and distinct properties. Can be either an element or a compound. – Element: a substance containing only one type of atom. E.g. Na, H 2. – Compound ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.