Answers to NHSCE 2002 Part A Page 1
... amount is assumed to be evenly distributed throughout the solution. This is initially contained in a 250.00 mL of solution, but an aliquot of only 25.00 mL is taken, so that only 0.2500 mol x 25.00 mL/250.00 mL = 0.02500 mol are taken. The answer is therefore C. Incorrect answers involve calculation ...
... amount is assumed to be evenly distributed throughout the solution. This is initially contained in a 250.00 mL of solution, but an aliquot of only 25.00 mL is taken, so that only 0.2500 mol x 25.00 mL/250.00 mL = 0.02500 mol are taken. The answer is therefore C. Incorrect answers involve calculation ...
Atoms, Elements and Compounds Home
... 1. Cut out the ‘atom people’ carefully (you will need to use each one once). 2. For each compound, put the correct ‘atom people’ together so that they have no ‘empty’ hands. Once you’re happy with all the molecules stick them in. ...
... 1. Cut out the ‘atom people’ carefully (you will need to use each one once). 2. For each compound, put the correct ‘atom people’ together so that they have no ‘empty’ hands. Once you’re happy with all the molecules stick them in. ...
1 | Page Chemistry Lecture #19: Atomic Number, Isotopes, and
... The periodic chart can be used to find the atomic number of all elements. ...
... The periodic chart can be used to find the atomic number of all elements. ...
3. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... 3.2 Atomic Number and Mass Number Atomic number (Z): Number of protons in a nucleus of an atom is called atomic number (Z). Z is characteristic of an element. An atom of oxygen always has eight protons and atomic number equal to eight. Mass Numbers (A): Number of neutrons and protons together in a n ...
... 3.2 Atomic Number and Mass Number Atomic number (Z): Number of protons in a nucleus of an atom is called atomic number (Z). Z is characteristic of an element. An atom of oxygen always has eight protons and atomic number equal to eight. Mass Numbers (A): Number of neutrons and protons together in a n ...
GOOD NOTES CH3
... 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles. 2. Atoms of the same element are chemically alike. Atoms of different elements are chemically different. 3. Atoms cannot be divided, created, nor destroyed. 4. Atoms combine in whole # ratios to form compounds. 5. Atoms are combined, separated, ...
... 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles. 2. Atoms of the same element are chemically alike. Atoms of different elements are chemically different. 3. Atoms cannot be divided, created, nor destroyed. 4. Atoms combine in whole # ratios to form compounds. 5. Atoms are combined, separated, ...
An Introduction to Redox
... individual quiz (labeled Quiz 4.3 at the end of the lesson plan) so that their progress can be assessed more formally by the instructor in the event that additional review or follow‐up activities are necessary. ...
... individual quiz (labeled Quiz 4.3 at the end of the lesson plan) so that their progress can be assessed more formally by the instructor in the event that additional review or follow‐up activities are necessary. ...
Practice EXAM I
... indicates that the empirical formula contains four C, four H and one O. Thus, the empirical formula is written as C4H4O as 1 is usually not written in the formula. 20. Chemical analysis shows the composition of a compound containing carbon and hydrogen, to be 80.00% carbon and 20% hydrogen and the ...
... indicates that the empirical formula contains four C, four H and one O. Thus, the empirical formula is written as C4H4O as 1 is usually not written in the formula. 20. Chemical analysis shows the composition of a compound containing carbon and hydrogen, to be 80.00% carbon and 20% hydrogen and the ...
Organic Chemistry
... combinations of drawings and chemical symbols. The line-angle formula is simple and unambiguous. In this system, the endpoints and intersections of each line represent one carbon, and hydrogen atoms can either be notated explicitly or assumed to be present as implied by tetravalent carbon. The depic ...
... combinations of drawings and chemical symbols. The line-angle formula is simple and unambiguous. In this system, the endpoints and intersections of each line represent one carbon, and hydrogen atoms can either be notated explicitly or assumed to be present as implied by tetravalent carbon. The depic ...
Topic 1 - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... Many reactions produce solid precipitates and go cloudy but most do so immediately. If, however, the reaction is slow enough, we can use a simple technique involving a cross drawn on a piece of paper to measure the rate of the reaction. ...
... Many reactions produce solid precipitates and go cloudy but most do so immediately. If, however, the reaction is slow enough, we can use a simple technique involving a cross drawn on a piece of paper to measure the rate of the reaction. ...
The average atomic mass of an element is the sum of the
... of protons in the nucleus of one atom. For example, the element hydrogen (the lightest element) will always have one proton in its nucleus. The element helium will always have two ...
... of protons in the nucleus of one atom. For example, the element hydrogen (the lightest element) will always have one proton in its nucleus. The element helium will always have two ...
Topic 1 - Rates of Reaction
... Many reactions produce solid precipitates and go cloudy but most do so immediately. If, however, the reaction is slow enough, we can use a simple technique involving a cross drawn on a piece of paper to measure the rate of the reaction. ...
... Many reactions produce solid precipitates and go cloudy but most do so immediately. If, however, the reaction is slow enough, we can use a simple technique involving a cross drawn on a piece of paper to measure the rate of the reaction. ...
Rutherford confirmed that the atom had a concentrated center of
... The Rutherford model is a model of the atom named after Ernest Rutherford. Rutherford directed the famous GeigerMarsden experiment in 1909, which suggested, according to Rutherford's 1911 analysis, that J. J. Thomson's socalled "plum pudding model" of the atom was incorrect. Rutherford's new model ...
... The Rutherford model is a model of the atom named after Ernest Rutherford. Rutherford directed the famous GeigerMarsden experiment in 1909, which suggested, according to Rutherford's 1911 analysis, that J. J. Thomson's socalled "plum pudding model" of the atom was incorrect. Rutherford's new model ...
Chapter 5 - apel slice
... The search for a description of matter began with the Greek philosopher Democritus (dihMAHK-ruh-tuhs) more than 2000 years ago. He and many other philosophers had puzzled over this question: Could matter be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever, or was there a limit to the number of times ...
... The search for a description of matter began with the Greek philosopher Democritus (dihMAHK-ruh-tuhs) more than 2000 years ago. He and many other philosophers had puzzled over this question: Could matter be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever, or was there a limit to the number of times ...
Atomic Theory - Valhalla High School
... Basic building block of matter Cannot be broken down chemically A single unit of an element ...
... Basic building block of matter Cannot be broken down chemically A single unit of an element ...
Chemistry Unit 2: Atomic Structure Unit Assignment #1 1. State the
... 1. State the five parts of Dalton’s Atomic Theory. 2. State the law of conservation of mass. 3. Compound Z is made by chemically combining elements X and Y. If only 4 grams of element Y were used to make 12 grams of compound Z, how many grams of element X were required? 4. According to the law of co ...
... 1. State the five parts of Dalton’s Atomic Theory. 2. State the law of conservation of mass. 3. Compound Z is made by chemically combining elements X and Y. If only 4 grams of element Y were used to make 12 grams of compound Z, how many grams of element X were required? 4. According to the law of co ...
Do Now: (5 min) - Schurz High School
... One formula unit of KF has how many charged particles? K has 19 + 19 = 38 charged particles F has 9 + 9 = 18 charged particles KF has 38 + 18 = 56 charged particles! ...
... One formula unit of KF has how many charged particles? K has 19 + 19 = 38 charged particles F has 9 + 9 = 18 charged particles KF has 38 + 18 = 56 charged particles! ...
OCR_AS_Level_Chemistry_Unit_F321_Atoms
... The first energy level (or shell) only contains an s orbital, labelled 1s The first shell can hold up to 2 electrons The second energy level contains an s orbital (labelled 2s) and three p orbitals (labelled 2p) The second shell can hold up to 8 electrons The third energy level contains an s orbital ...
... The first energy level (or shell) only contains an s orbital, labelled 1s The first shell can hold up to 2 electrons The second energy level contains an s orbital (labelled 2s) and three p orbitals (labelled 2p) The second shell can hold up to 8 electrons The third energy level contains an s orbital ...
Chapter 17 Thermodynamics: Directionality of Chemical Reactions
... “Energy will spread out (disperse) unless it is hindered from doing so”. ...
... “Energy will spread out (disperse) unless it is hindered from doing so”. ...
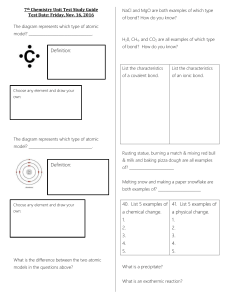
7th Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide Test Date: Friday, Nov. 16
... In the following equation, which substances The Pilgrims were researching chemical reactions. They read that if you heat a small amount of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), it will produce calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon ...
... In the following equation, which substances The Pilgrims were researching chemical reactions. They read that if you heat a small amount of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), it will produce calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon ...
Matter
... OR Isotopes are atoms of the same element with equal atomic number but different mass number. Isotopes have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of outermost shell electrons. Isotopes have different physical properties because their atomic masses are different. ...
... OR Isotopes are atoms of the same element with equal atomic number but different mass number. Isotopes have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of outermost shell electrons. Isotopes have different physical properties because their atomic masses are different. ...
Chemistry Syllabus
... from the lab. All work must be shown with equations for credit. You will get an automatic revisit for this section if your work is not shown. 1) Write all calculations in this section. One sample calculation is needed where the same calculation is repeated. Make sure the equation is written, numbers ...
... from the lab. All work must be shown with equations for credit. You will get an automatic revisit for this section if your work is not shown. 1) Write all calculations in this section. One sample calculation is needed where the same calculation is repeated. Make sure the equation is written, numbers ...
Some basic concepts of chemistry
... The three basic units, i.e., units of mass, length and time are independent units and cannot be derived from any other units, hence they are called fundamental units. The three fundamental units cannot describe all the physical quantities such as temperature, intensity of luminosity, electric curren ...
... The three basic units, i.e., units of mass, length and time are independent units and cannot be derived from any other units, hence they are called fundamental units. The three fundamental units cannot describe all the physical quantities such as temperature, intensity of luminosity, electric curren ...
1 CHAPTER 3. INSIDE THE ATOM What Is an Atom? A Closer View
... investigations she learned that the element thorium was also radioactive. Pitchblende ore, however, was so highly radioactive that neither radium not thorium could account for its activity. Was it possible that there was an element, as yet undiscovered, which was so highly radioactive that it could ...
... investigations she learned that the element thorium was also radioactive. Pitchblende ore, however, was so highly radioactive that neither radium not thorium could account for its activity. Was it possible that there was an element, as yet undiscovered, which was so highly radioactive that it could ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.