PDF Version
... approximately 7 to 9 cm3,5,7,8, but vary in length, being shorter distally compared to proximally5. The PCSA of BFlh is the second largest of the hamstring muscles (average value of 10 cm2 in cadavers) as is its muscle belly volume (average value of 76 cm3 in cadavers; 260 cm3 in healthy young men). ...
... approximately 7 to 9 cm3,5,7,8, but vary in length, being shorter distally compared to proximally5. The PCSA of BFlh is the second largest of the hamstring muscles (average value of 10 cm2 in cadavers) as is its muscle belly volume (average value of 76 cm3 in cadavers; 260 cm3 in healthy young men). ...
anatomy - Trauma Audit and Research Network
... grade being the more extensive the fracture. Usually asymmetrical, the Malar complex (‘middle third’) may be fractured at a different level on each side. A bilateral Le Fort III fracture implies that the facial skeleton has become separated from the base of the skull. This is an unstable injury usua ...
... grade being the more extensive the fracture. Usually asymmetrical, the Malar complex (‘middle third’) may be fractured at a different level on each side. A bilateral Le Fort III fracture implies that the facial skeleton has become separated from the base of the skull. This is an unstable injury usua ...
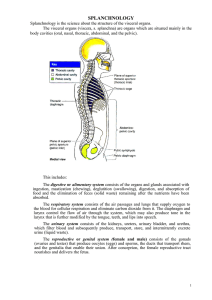
2. Splanchnology
... left lobe of the liver. It measures about 1.25 cm in length, and only its front and left aspects are covered by peritoneum. The esophagus has three anatomical constrictions, which are significant in making the diagnosis of pathological processes: 1) pharyngeal (at the origin of the esophagus), 2) br ...
... left lobe of the liver. It measures about 1.25 cm in length, and only its front and left aspects are covered by peritoneum. The esophagus has three anatomical constrictions, which are significant in making the diagnosis of pathological processes: 1) pharyngeal (at the origin of the esophagus), 2) br ...
Learning objectives
... 35. Define gas exchange and distinguish between a respiratory medium and a respiratory surface. 36. Describe the general requirements for a respiratory surface and list a variety of respiratory organs that meet these requirements. 37. Describe respiratory adaptations of aquatic animals. 38. Describe ...
... 35. Define gas exchange and distinguish between a respiratory medium and a respiratory surface. 36. Describe the general requirements for a respiratory surface and list a variety of respiratory organs that meet these requirements. 37. Describe respiratory adaptations of aquatic animals. 38. Describe ...
Animal Evolution –The Invertebrates
... 25.17 Insect Diversity and Importance It would be hard to overestimate the importance of insects, for either good or ill Insects help provide us with food crops, are food for animals, and help dispose of wastes • The four most diverse groups of insects all include pollinators of flowering plant ...
... 25.17 Insect Diversity and Importance It would be hard to overestimate the importance of insects, for either good or ill Insects help provide us with food crops, are food for animals, and help dispose of wastes • The four most diverse groups of insects all include pollinators of flowering plant ...
chapter25_part3 - OCC
... 25.17 Insect Diversity and Importance It would be hard to overestimate the importance of insects, for either good or ill Insects help provide us with food crops, are food for animals, and help dispose of wastes • The four most diverse groups of insects all include pollinators of flowering plant ...
... 25.17 Insect Diversity and Importance It would be hard to overestimate the importance of insects, for either good or ill Insects help provide us with food crops, are food for animals, and help dispose of wastes • The four most diverse groups of insects all include pollinators of flowering plant ...
intranasal anatomy of nasolacrimal sac in adult human cadaver
... Zagazig university between April 2010 and March 2011 on 10 half-heads of adult human cadavers (two female, 8 male), of which six were the left side and four were the right side. Each skull was examined endoscopically (0,30 degree) regarding the structure of the lateral nasal wall (axilla of middle t ...
... Zagazig university between April 2010 and March 2011 on 10 half-heads of adult human cadavers (two female, 8 male), of which six were the left side and four were the right side. Each skull was examined endoscopically (0,30 degree) regarding the structure of the lateral nasal wall (axilla of middle t ...
The Intervertebral Disk
... The intra-spinal course of the upper thoracic nerve root is almost horizontal (as in the cervical spine). Therefore, the nerve can only be compressed by its corresponding disk. More inferiorly in the spine though, the course of the nerve root becomes more oblique, and the lowest thoracic nerve roots ...
... The intra-spinal course of the upper thoracic nerve root is almost horizontal (as in the cervical spine). Therefore, the nerve can only be compressed by its corresponding disk. More inferiorly in the spine though, the course of the nerve root becomes more oblique, and the lowest thoracic nerve roots ...
laboratory manual - learning is wild!
... before coming to class and being organized during lab will be immensely helpful in making good use of your time in lab. In addition, coming to lab outside of class time and engaging in post-lab review of the specimens and concepts, along with a spirit of inquiry on your part, will go a long way to m ...
... before coming to class and being organized during lab will be immensely helpful in making good use of your time in lab. In addition, coming to lab outside of class time and engaging in post-lab review of the specimens and concepts, along with a spirit of inquiry on your part, will go a long way to m ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... about 90% of all preganglionic parasympathetic fibers in the body. They provide fibers to the neck and to nerve plexuses (interweaving networks of nerves) that serve virtually every organ in the thoracic and abdominal cavities. The vagal nerve fibers (preganglionic axons) arise mostly from the dorsa ...
... about 90% of all preganglionic parasympathetic fibers in the body. They provide fibers to the neck and to nerve plexuses (interweaving networks of nerves) that serve virtually every organ in the thoracic and abdominal cavities. The vagal nerve fibers (preganglionic axons) arise mostly from the dorsa ...
OBJECTIVES and EXPLANATIONS:
... ligaments are the medial collateral and the lateral collateral ligament. The medial collateral is on the medial side of the elbow, and the lateral collateral is on the lateral side. Together these two ligaments connect the humerus to the ulna and keep it tightly in place as it slides through the gro ...
... ligaments are the medial collateral and the lateral collateral ligament. The medial collateral is on the medial side of the elbow, and the lateral collateral is on the lateral side. Together these two ligaments connect the humerus to the ulna and keep it tightly in place as it slides through the gro ...
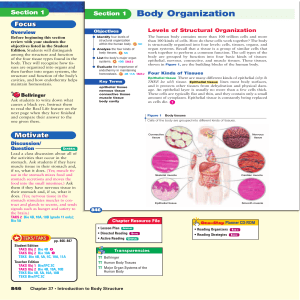
Body Organization
... Body organs are made of combinations of two or more types of tissues working together to perform a specific function. The heart, for example, contains cardiac muscle tissue and connective tissue, and the heart is stimulated by nervous tissue. Each organ belongs to at least one organ system, which is ...
... Body organs are made of combinations of two or more types of tissues working together to perform a specific function. The heart, for example, contains cardiac muscle tissue and connective tissue, and the heart is stimulated by nervous tissue. Each organ belongs to at least one organ system, which is ...
______ is the study of the body`s structure.
... Brain and pituitary gland Spinal cord One lung in each Heart Thymus gland, trachea, esophagus, bronchi, ends of the ven cavae, beginning of the aorta Stomacy, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, most of the small and large intestines, kidneys Urinary bladder, sex organs, part of the large ...
... Brain and pituitary gland Spinal cord One lung in each Heart Thymus gland, trachea, esophagus, bronchi, ends of the ven cavae, beginning of the aorta Stomacy, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, most of the small and large intestines, kidneys Urinary bladder, sex organs, part of the large ...
urinary - Wk 1-2
... The prostate parenchyma can be divided in two different ways: by zone, or by lobe. Zone classification is mostly used for pathology where as lobe classification mainly for anatomical purposes Zones - The prostate gland has four distinct glandular regions, two of which arise from different segments o ...
... The prostate parenchyma can be divided in two different ways: by zone, or by lobe. Zone classification is mostly used for pathology where as lobe classification mainly for anatomical purposes Zones - The prostate gland has four distinct glandular regions, two of which arise from different segments o ...
Anatomy of Esophagus
... • From the dense submucosal plexus the venous blood drains into the superior vena cava. The veins of the proximal and distal esophagus drain into the azygous system. Collaterals of the left gastric vein, a branch of the portal vein, receive venous drainage from the midesophagus. • The submucosal con ...
... • From the dense submucosal plexus the venous blood drains into the superior vena cava. The veins of the proximal and distal esophagus drain into the azygous system. Collaterals of the left gastric vein, a branch of the portal vein, receive venous drainage from the midesophagus. • The submucosal con ...
Teaching Practicum at Doherty Memorial High School Appendix
... blood leaves the heart, it moves through the body via blood vessels called arteries, veins, and capillaries. The lesson will explore what drives the blood through the vessels and how the structural features of each vessel make it suitable for its function in transport. The students, at this point, s ...
... blood leaves the heart, it moves through the body via blood vessels called arteries, veins, and capillaries. The lesson will explore what drives the blood through the vessels and how the structural features of each vessel make it suitable for its function in transport. The students, at this point, s ...
Reptiles - ABCTeach
... snakes have special pits located between their eyes and nostrils that sense small changes in temperature. These pit viper snakes usually hunt at night and this special sense helps them locate warmblooded prey. ...
... snakes have special pits located between their eyes and nostrils that sense small changes in temperature. These pit viper snakes usually hunt at night and this special sense helps them locate warmblooded prey. ...
incidence and morphology of accessory head of flexor pollicis
... AIN branches posterior from median nerve between 2 heads of PT and with anterior interosseous artery it descend anterior to interosseous membrane between and deep to FPL and Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) and supply both and terminate posterior to pronator quadratus.1Paralysis of AIN due to compre ...
... AIN branches posterior from median nerve between 2 heads of PT and with anterior interosseous artery it descend anterior to interosseous membrane between and deep to FPL and Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) and supply both and terminate posterior to pronator quadratus.1Paralysis of AIN due to compre ...
Earthworm Dissection Lab
... Pre-lab Discussion: The earthworm belongs to a group of animals called annelids (segmented worms). The body of an annelid is usually divided internally and externally into well-defined segments, which may be separated from each other by membranous partitions. Except for the tail and head regions, al ...
... Pre-lab Discussion: The earthworm belongs to a group of animals called annelids (segmented worms). The body of an annelid is usually divided internally and externally into well-defined segments, which may be separated from each other by membranous partitions. Except for the tail and head regions, al ...
Lophophorata SP
... description below? Visualize the pattern of current flow by watching the movement of the small suspended food particles in the water. b. Obtain a movie under high power of your stereoscope or low power of the light microscope of feeding in your specimen. Find the lophophore and note that its tentacl ...
... description below? Visualize the pattern of current flow by watching the movement of the small suspended food particles in the water. b. Obtain a movie under high power of your stereoscope or low power of the light microscope of feeding in your specimen. Find the lophophore and note that its tentacl ...
The Respiratory System Chapter 22
... – Blood O2 level is lowered, and any mild exercise that raises the O2 requirements of the cells leaves the patient breathless – As increasing numbers of alveolar walls are damaged, lung elastic recoil decreases due to loss of elastic fibers, and an increasing amount of air becomes trapped in the lun ...
... – Blood O2 level is lowered, and any mild exercise that raises the O2 requirements of the cells leaves the patient breathless – As increasing numbers of alveolar walls are damaged, lung elastic recoil decreases due to loss of elastic fibers, and an increasing amount of air becomes trapped in the lun ...
Urinay system - Pharmacy Fun
... The renal capsule - layer of dense fibrous connective tissue surrounding each kidney, protects kidney from trauma and infection and maintain its shape Renal adipose capsule – layer of adipose tissue surrounding the renal capsule functions as a shock absorber, cushioning the kidneys against mecha ...
... The renal capsule - layer of dense fibrous connective tissue surrounding each kidney, protects kidney from trauma and infection and maintain its shape Renal adipose capsule – layer of adipose tissue surrounding the renal capsule functions as a shock absorber, cushioning the kidneys against mecha ...
Aprob - Anatomia omului
... Human Anatomy and its role in medical fundamental and basic disciplines. Techniques of study in Anatomy. Elements of orientation in human body, anatomical terminology. Introduction to organ, system of organs, apparatuses. Individual variability of the human body, constitutional types. General notion ...
... Human Anatomy and its role in medical fundamental and basic disciplines. Techniques of study in Anatomy. Elements of orientation in human body, anatomical terminology. Introduction to organ, system of organs, apparatuses. Individual variability of the human body, constitutional types. General notion ...
1. Vertebral Column and Spinal Cord
... § Laterally, each denticulate ligament forms a series of triangular extensions that anchor through the arachnoid mater to the dura mater § They generally occur between the exit points of adjacent posterior ...
... § Laterally, each denticulate ligament forms a series of triangular extensions that anchor through the arachnoid mater to the dura mater § They generally occur between the exit points of adjacent posterior ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.