
pelvic part
... • Fundus and upper part --- lumbar lymph nodes • along the round lig. --superficial inguinal lymph ...
... • Fundus and upper part --- lumbar lymph nodes • along the round lig. --superficial inguinal lymph ...
20 - PHSchool.com
... use the lymphatics to travel throughout the body. This threat to the body is partly resolved by the fact that the lymph takes “detours” through the lymph nodes, where it is cleansed of debris and “examined” by cells of the immune system. Highly specialized lymphatic capillaries called lacteals (lak⬘ ...
... use the lymphatics to travel throughout the body. This threat to the body is partly resolved by the fact that the lymph takes “detours” through the lymph nodes, where it is cleansed of debris and “examined” by cells of the immune system. Highly specialized lymphatic capillaries called lacteals (lak⬘ ...
Anatomy of the Female Reproductive System
... portion,the anterior wall of the vagina is shorter than the posterior wall.the circular cul-de-sac formed around the cervix is known as the fornix and is divided into 4 regions;the anterior fornix,the posterior fornix,and 2 lateral fornices. ...
... portion,the anterior wall of the vagina is shorter than the posterior wall.the circular cul-de-sac formed around the cervix is known as the fornix and is divided into 4 regions;the anterior fornix,the posterior fornix,and 2 lateral fornices. ...
REVIEW Invertebrates
... 3. Which three phylums have sessile species? a. Porifera, Cnidaria, and Nematoda b. Porifera, Cnidaria, and Annelida c. Porifera, Nematoda, and Platyhelminthes d. Nematoda, Platyhelminthes, and Mollusca 4. Which three phylums have only motile species? a. Porifera, Nematoda, and Mollusca b. Platyhelm ...
... 3. Which three phylums have sessile species? a. Porifera, Cnidaria, and Nematoda b. Porifera, Cnidaria, and Annelida c. Porifera, Nematoda, and Platyhelminthes d. Nematoda, Platyhelminthes, and Mollusca 4. Which three phylums have only motile species? a. Porifera, Nematoda, and Mollusca b. Platyhelm ...
Chapter 9 Gross Anatomy and Functions of Skeletal Muscles
... Gross Anatomy and Functions of Skeletal Muscles ...
... Gross Anatomy and Functions of Skeletal Muscles ...
Chapter (I) Anatomy of cervical spine
... tubercle; each is perforated by the transverse foramen, which is directed obliquely upward and laterally. The superior articular surfaces are round, slightly convex, directed upward and laterally, and are supported on the body, pedicles, and transverse processes. The inferior articular surfaces have ...
... tubercle; each is perforated by the transverse foramen, which is directed obliquely upward and laterally. The superior articular surfaces are round, slightly convex, directed upward and laterally, and are supported on the body, pedicles, and transverse processes. The inferior articular surfaces have ...
Pages 20-35
... In the mid-ventral neck area, several muscles may be seen. Use your needle probe to separate some of these narrow bands of muscle. Sternomastoid (Sternocephalic) - This is a large "V"-shaped band of muscle on the ventral and lateral surfaces of the neck. It extends from the anterior position of the ...
... In the mid-ventral neck area, several muscles may be seen. Use your needle probe to separate some of these narrow bands of muscle. Sternomastoid (Sternocephalic) - This is a large "V"-shaped band of muscle on the ventral and lateral surfaces of the neck. It extends from the anterior position of the ...
The trifid superior transverse scapular ligament
... the STSL described in this study has not yet been well documented photographically. We propose that one case of a trifid STSL studied by Ticker et al. [16] described a bifid STSL plus a singular fibrous band extending on the anterior side of the SSN, below the STSL, that Avery et al. [2] named the a ...
... the STSL described in this study has not yet been well documented photographically. We propose that one case of a trifid STSL studied by Ticker et al. [16] described a bifid STSL plus a singular fibrous band extending on the anterior side of the SSN, below the STSL, that Avery et al. [2] named the a ...
Abdominal Sonography 1 Pancreas Part 1 2017
... retroperitoneal structure that lies between the duodenal loop and the splenic hilum. The pancreas is divided into the head, uncinate process, neck, body, and tail. The EXOCRINE function of the pancreas is to secrete trypsin, lipase and amylase through the ductal system. ...
... retroperitoneal structure that lies between the duodenal loop and the splenic hilum. The pancreas is divided into the head, uncinate process, neck, body, and tail. The EXOCRINE function of the pancreas is to secrete trypsin, lipase and amylase through the ductal system. ...
lower_ext_ppt.aug_o7
... 1. To teach clinically relevant gross anatomy 2. To make it easier to understand gross anatomy 3. To introduce a clinical lexicon ...
... 1. To teach clinically relevant gross anatomy 2. To make it easier to understand gross anatomy 3. To introduce a clinical lexicon ...
*Abdominal: The belly part of the body that contains all of the
... *Cervical: Having to do with any kind of neck. On which a head may rest or the neck of the cervix. ...
... *Cervical: Having to do with any kind of neck. On which a head may rest or the neck of the cervix. ...
Invertebrates 2 Cladograms Cladograms Cladograms Cladistics
... Radial – body parts are Bilateral – right half and left half are mirror images. arranged regularly Anterior/Posterior – head/tail around a central axis. (example: sea anemone) Dorsal/Ventral – back/stomach ...
... Radial – body parts are Bilateral – right half and left half are mirror images. arranged regularly Anterior/Posterior – head/tail around a central axis. (example: sea anemone) Dorsal/Ventral – back/stomach ...
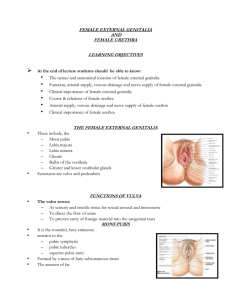
FEMALE EXTERNAL GENITALIA
... Internally labium minus consists of thin moist skin, pink in color, contains many sebaceous glands and sensory nerve endings Situated between the labia majora Extending from the clitoris obliquely downward, lateralward, and backward for about 4 cm. on either side of the orifice of the vagina Are enc ...
... Internally labium minus consists of thin moist skin, pink in color, contains many sebaceous glands and sensory nerve endings Situated between the labia majora Extending from the clitoris obliquely downward, lateralward, and backward for about 4 cm. on either side of the orifice of the vagina Are enc ...
[ PDF ] - journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences
... base of the mandible till the mastoid process and the skin flaps were raised and reflected laterally. Another horizontal incision is given along the upper border of the clavicle. Platysma a subcutaneous muscle which is also reflected along with the cutaneous nerves lying in the superficial fascia of ...
... base of the mandible till the mastoid process and the skin flaps were raised and reflected laterally. Another horizontal incision is given along the upper border of the clavicle. Platysma a subcutaneous muscle which is also reflected along with the cutaneous nerves lying in the superficial fascia of ...
case report
... ABSTRACT: Among the human endocrine glands the H Shaped Brownish Red thyroid gland is well known for its disturbed organogenesis leading to a wide variety of morphological variations ranging from commonly occurring thyroglossal duct cyst and persistence of pyramidal lobe and rarely seen hypoplasia, ...
... ABSTRACT: Among the human endocrine glands the H Shaped Brownish Red thyroid gland is well known for its disturbed organogenesis leading to a wide variety of morphological variations ranging from commonly occurring thyroglossal duct cyst and persistence of pyramidal lobe and rarely seen hypoplasia, ...
Female Ext Genitalia and urethra
... Internally labium minus consists of thin moist skin, pink in color, contains many sebaceous glands and sensory nerve endings Situated between the labia majora Extending from the clitoris obliquely downward, lateralward, and backward for about 4 cm. on either side of the orifice of the vagina Are enc ...
... Internally labium minus consists of thin moist skin, pink in color, contains many sebaceous glands and sensory nerve endings Situated between the labia majora Extending from the clitoris obliquely downward, lateralward, and backward for about 4 cm. on either side of the orifice of the vagina Are enc ...
Knee Anatomy (1)
... The angle of pull of quadriceps on the patella normal is 13 degrees male/ 18 female ...
... The angle of pull of quadriceps on the patella normal is 13 degrees male/ 18 female ...
3rd Nine Weeks 2016-2017
... Nervous System and the Autonomic Nervous System. Identify parts of the spinal cord as well as their functions. Lesson: 1. Discuss Ch. 11 “Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tisue” 2. Discuss Ch. 12 “Central Nervous System” 3. Ch. 11 Quiz ...
... Nervous System and the Autonomic Nervous System. Identify parts of the spinal cord as well as their functions. Lesson: 1. Discuss Ch. 11 “Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tisue” 2. Discuss Ch. 12 “Central Nervous System” 3. Ch. 11 Quiz ...
Presence of an articulating condylus tertius on the basilar part of the
... Radiological diagnosis of these anomalies is difficult and goes undetected due to lack of experience in identification due to rarity. It would require a high degree of suspicion and careful analysis of the radiology as also more investigations to make a diagnosis. Several radiological lines and angl ...
... Radiological diagnosis of these anomalies is difficult and goes undetected due to lack of experience in identification due to rarity. It would require a high degree of suspicion and careful analysis of the radiology as also more investigations to make a diagnosis. Several radiological lines and angl ...
Knee anatomy
... • Cruciate Ligaments from the word ‘ cross’ • Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL), extends posteriorally & laterally from the area in front of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia, to the posterior part of the medial surface of the lateral femoral condyle. • It resists forward movement of the femur ...
... • Cruciate Ligaments from the word ‘ cross’ • Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL), extends posteriorally & laterally from the area in front of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia, to the posterior part of the medial surface of the lateral femoral condyle. • It resists forward movement of the femur ...
一、程基本信息
... The bones of the skull should be viewed from front, lateral, superior, inferior aspects as whole. Please pay more attention to the base of the skull. Recognize the position of each bone, the processes which could be palpated and the foramina, through which the cranial nerves and blood vessel pass to ...
... The bones of the skull should be viewed from front, lateral, superior, inferior aspects as whole. Please pay more attention to the base of the skull. Recognize the position of each bone, the processes which could be palpated and the foramina, through which the cranial nerves and blood vessel pass to ...
An unusual popliteal vein and its clinical
... of occurrence of variation observed is 4.2%. The popliteal vein is formed proximal to the femoral condyles by a medial and lateral vein. The lateral vein received the posterior tibial vein as a direct tributary, and the diameter of the medial vein is almost double that of the lateral vein. The small ...
... of occurrence of variation observed is 4.2%. The popliteal vein is formed proximal to the femoral condyles by a medial and lateral vein. The lateral vein received the posterior tibial vein as a direct tributary, and the diameter of the medial vein is almost double that of the lateral vein. The small ...
Collagen and Collagenous Tissues
... • Collagen is a ubiquitous structural protein with many types all having a triple helix structure that is cross-linked in a staggered array. • Some of the most common collagen types are fibrillar and the collagen can be organized in 1-D, 2-D or 3-D in different tissues to confer different material p ...
... • Collagen is a ubiquitous structural protein with many types all having a triple helix structure that is cross-linked in a staggered array. • Some of the most common collagen types are fibrillar and the collagen can be organized in 1-D, 2-D or 3-D in different tissues to confer different material p ...
Anatomy of the Foot and Lower Extremity
... Anterior Tibialis (AT): Located at anterior of tibia, in front of ankle joint lateral to medial malleolus and attaches to medial cuneiform and base of first metatarsal bone, the AT is a dorsiflexor which enables the foot to move upward Posterior Tibialis (PT): Muscle begins at the top of fibula and ...
... Anterior Tibialis (AT): Located at anterior of tibia, in front of ankle joint lateral to medial malleolus and attaches to medial cuneiform and base of first metatarsal bone, the AT is a dorsiflexor which enables the foot to move upward Posterior Tibialis (PT): Muscle begins at the top of fibula and ...
anatomy - Trauma Audit and Research Network
... grade being the more extensive the fracture. Usually asymmetrical, the Malar complex (‘middle third’) may be fractured at a different level on each side. A bilateral Le Fort III fracture implies that the facial skeleton has become separated from the base of the skull. This is an unstable injury usua ...
... grade being the more extensive the fracture. Usually asymmetrical, the Malar complex (‘middle third’) may be fractured at a different level on each side. A bilateral Le Fort III fracture implies that the facial skeleton has become separated from the base of the skull. This is an unstable injury usua ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.











![[ PDF ] - journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007955894_2-e1c257efa5596d9bcec4f688fb06dda4-300x300.png)










