Dissection 9: Pharynx, Larynx, and Ear
... equalize tympanic cavity pressure with atmospheric pressure to allow free movement of the tympanic membrane. Tube kept open by the contracted belly of the levator veli palatini pushing against one wall and the tensor veli palatini pulling on the other wall. These are muscles of the soft palate, and ...
... equalize tympanic cavity pressure with atmospheric pressure to allow free movement of the tympanic membrane. Tube kept open by the contracted belly of the levator veli palatini pushing against one wall and the tensor veli palatini pulling on the other wall. These are muscles of the soft palate, and ...
Vertebrae
... the small of the back and have an enhanced weight-bearing function • They have short, thick pedicles and laminae, flat hatchet-shaped spinous processes, and a triangular-shaped vertebral foramen • Orientation of articular facets locks the lumbar vertebrae together to provide stability ...
... the small of the back and have an enhanced weight-bearing function • They have short, thick pedicles and laminae, flat hatchet-shaped spinous processes, and a triangular-shaped vertebral foramen • Orientation of articular facets locks the lumbar vertebrae together to provide stability ...
THORACIC & WALL - University of Kansas Medical Center
... Involves contraction of intercostal muscles Results in raising of ribs Results in an increase in the lateral dimensions of the thoracic cage. ...
... Involves contraction of intercostal muscles Results in raising of ribs Results in an increase in the lateral dimensions of the thoracic cage. ...
Revista Anatomy 11
... which is in close contact with the nerves as seen in the present case, may require a careful approach by the surgeon. After its entry into the popliteal fossa, the tibial nerve gives off one or more branches to the knee joint and the medial sural cutaneous nerve to the skin of the leg and foot, whil ...
... which is in close contact with the nerves as seen in the present case, may require a careful approach by the surgeon. After its entry into the popliteal fossa, the tibial nerve gives off one or more branches to the knee joint and the medial sural cutaneous nerve to the skin of the leg and foot, whil ...
The Accessory muscles of the Axilla
... evolution muscles are redefined in humans. The process can be summarised as followed (Fig. 7) : a cranial migration of the pectoral minor muscle towards the coracoid process. Therefore the most caudal part of insertion of the pectoral major migrated to replace the minor muscle onto the superior part ...
... evolution muscles are redefined in humans. The process can be summarised as followed (Fig. 7) : a cranial migration of the pectoral minor muscle towards the coracoid process. Therefore the most caudal part of insertion of the pectoral major migrated to replace the minor muscle onto the superior part ...
Anatomy and Functional Architecture of the Anconeus Muscle
... General shape and morphometry. The shape of the anconeus bidimensional surface was nearly one of a right angle triangle, with the corner of the right angle situated at the proximal extremity of the ulna, about 1 cm distal to the olecranon. In order to identify the sides of the anconeus, we used the ...
... General shape and morphometry. The shape of the anconeus bidimensional surface was nearly one of a right angle triangle, with the corner of the right angle situated at the proximal extremity of the ulna, about 1 cm distal to the olecranon. In order to identify the sides of the anconeus, we used the ...
Close this window to return to the previous page or go
... cord as paired dorsal and ventral nerve roots and exit the vertebrae via intervertebral foramina. The dorsal nerves are composed of somatic and visceral sensory nerve fibers and may contain motor fibers as well; the ventral roots are generally composed of both somatic and visceral motor nerve fibers ...
... cord as paired dorsal and ventral nerve roots and exit the vertebrae via intervertebral foramina. The dorsal nerves are composed of somatic and visceral sensory nerve fibers and may contain motor fibers as well; the ventral roots are generally composed of both somatic and visceral motor nerve fibers ...
An Entrapment of Median Nerve and Brachial Artery Due to Double
... upward extent of the insertion cannot be seen on most bones, the muscle usually leaves no impression. The musculocutaneous nerve passes through the muscle and supplies it. Compared to the morphological interest of this muscle its action is negligible. It is a weak adductor of the shoulder joint, th ...
... upward extent of the insertion cannot be seen on most bones, the muscle usually leaves no impression. The musculocutaneous nerve passes through the muscle and supplies it. Compared to the morphological interest of this muscle its action is negligible. It is a weak adductor of the shoulder joint, th ...
Accessory origin of the piriformis muscle
... with the main tendinous part of the piriformis muscle in all the three cases. The accessory slip was found to be innervated by a small twig from the sciatic nerve. The main trunk of the sciatic nerve was found deep to the accessory slip. The average length and width of the fleshy and tendinous part ...
... with the main tendinous part of the piriformis muscle in all the three cases. The accessory slip was found to be innervated by a small twig from the sciatic nerve. The main trunk of the sciatic nerve was found deep to the accessory slip. The average length and width of the fleshy and tendinous part ...
Bones of the Thorax Bone Structure Description Notes rib the bone
... it articulates with the transverse process of a vertebra posteroinferior and lateral to the neck of the rib the shaft of the rib the body is the longest part of a typical rib the marked angulation of the angle of the rib is its most posterior part the body located just lateral to the tubercle the gr ...
... it articulates with the transverse process of a vertebra posteroinferior and lateral to the neck of the rib the shaft of the rib the body is the longest part of a typical rib the marked angulation of the angle of the rib is its most posterior part the body located just lateral to the tubercle the gr ...
21. Lymphatic System
... course, water. Lymph also contains small solutes (such as sodium and potassium) and a small amount of protein. Leukocytes and foreign particles are also found in lymph. Lymph capillaries (Fig. 21.2) are found throughout the body in most places where capillary beds are found. Notable exceptions are i ...
... course, water. Lymph also contains small solutes (such as sodium and potassium) and a small amount of protein. Leukocytes and foreign particles are also found in lymph. Lymph capillaries (Fig. 21.2) are found throughout the body in most places where capillary beds are found. Notable exceptions are i ...
Development of the Urinary System 3 Distinct Embryonic Kidney
... As the urorectal septum divides the cloaca, the caudal end of the urinary bladder narrows to form the urogenital sinus and the urethra As the body grows in length and the curvature of the body begins to straighten, the relative position of the kidney in the body changes • the kidney ascends from pel ...
... As the urorectal septum divides the cloaca, the caudal end of the urinary bladder narrows to form the urogenital sinus and the urethra As the body grows in length and the curvature of the body begins to straighten, the relative position of the kidney in the body changes • the kidney ascends from pel ...
pdf
... The inguinal ligament forms the base of the inguinal canal as it runs from the anterior superior iliac spine laterally, to the pubic tubercle medially. It is also the inguinal ligament that provides the anatomical division between the external iliac and common femoral vessels, thus splitting inguin ...
... The inguinal ligament forms the base of the inguinal canal as it runs from the anterior superior iliac spine laterally, to the pubic tubercle medially. It is also the inguinal ligament that provides the anatomical division between the external iliac and common femoral vessels, thus splitting inguin ...
Surgical anatomy of kurpara marma with special reference
... the humeral epicondyles, but in full flexion these three bony points make an equilateral triangle. 7 Stability of elbow joint: The elbow joint is stable because of the wrench shaped articular surface of the olecranon and the pully shaped trochlea of the humerus . it is also has strong medial and lat ...
... the humeral epicondyles, but in full flexion these three bony points make an equilateral triangle. 7 Stability of elbow joint: The elbow joint is stable because of the wrench shaped articular surface of the olecranon and the pully shaped trochlea of the humerus . it is also has strong medial and lat ...
Anatomy-Of-Female-Genital-System-Dr.Osman
... Histology of the Ovary The ovary is subdivided into; Cortex, Medulla, and Hilum. The Medulla: The central core of the ovary surrounded by the cortex and continuous with the hilum. It is formed of connective tissue. The Cortex: The outer active part of the ovary that produces hormones and oocyte ...
... Histology of the Ovary The ovary is subdivided into; Cortex, Medulla, and Hilum. The Medulla: The central core of the ovary surrounded by the cortex and continuous with the hilum. It is formed of connective tissue. The Cortex: The outer active part of the ovary that produces hormones and oocyte ...
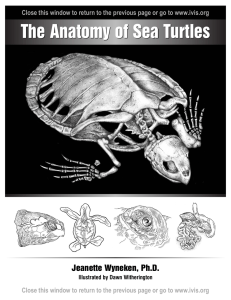
26–3 Cnidarians - cloudfront.net
... to change her into a hideous monster. Medusa had long, twisting snakes for hair. In what way are cnidarian medusas similar to the monster named Medusa? ...
... to change her into a hideous monster. Medusa had long, twisting snakes for hair. In what way are cnidarian medusas similar to the monster named Medusa? ...
MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SUPERIOR
... Compression of the oculomotor nerve manifests with symptoms involving eyeball movements and papillary size changes [8, 15]. Trochlear nerve compression with SCA trunk or branches can cause trochlear nerve palsy which manifests with superior oblique myokymia [7, 8, 16]. One of the common causes of tr ...
... Compression of the oculomotor nerve manifests with symptoms involving eyeball movements and papillary size changes [8, 15]. Trochlear nerve compression with SCA trunk or branches can cause trochlear nerve palsy which manifests with superior oblique myokymia [7, 8, 16]. One of the common causes of tr ...
Anomalous origin of the radial recurrent artery
... then appears in the cubital fossa, where it ends ...
... then appears in the cubital fossa, where it ends ...
Chapter 7
... • False ribs (vertebrochondral ribs) – Remaining five pairs – Cartilages of the upper three pairs of false ribs join the cartilage of the 7th rib – The last two pairs have no attachment to the sternum, so they are called floating ribs (or vertebral ribs) ...
... • False ribs (vertebrochondral ribs) – Remaining five pairs – Cartilages of the upper three pairs of false ribs join the cartilage of the 7th rib – The last two pairs have no attachment to the sternum, so they are called floating ribs (or vertebral ribs) ...
Phylum Platyhelminthes: Flatworms
... level of organization. c) Germ Layers -The embryos of Flatworms have a third layer between the endoderm and the ectoderm. What is this layer called? _____________________________________________ -Which tissues and organs develop from this layer? ______________________________________________________ ...
... level of organization. c) Germ Layers -The embryos of Flatworms have a third layer between the endoderm and the ectoderm. What is this layer called? _____________________________________________ -Which tissues and organs develop from this layer? ______________________________________________________ ...
Anatomy – Exam 2 (Part 2)
... Describe the position and gross anatomical structure of the seminal vesicles Discuss the route of a sperm cell during emission and ejaculation Describe the anatomy of the posterior wall of the prostatic urethra Define the lobes of the prostate and understand how enlargement effects urine flo ...
... Describe the position and gross anatomical structure of the seminal vesicles Discuss the route of a sperm cell during emission and ejaculation Describe the anatomy of the posterior wall of the prostatic urethra Define the lobes of the prostate and understand how enlargement effects urine flo ...
Anatomy – Exam 2 (Part 2)
... Describe the position and gross anatomical structure of the seminal vesicles Discuss the route of a sperm cell during emission and ejaculation Describe the anatomy of the posterior wall of the prostatic urethra Define the lobes of the prostate and understand how enlargement effects urine flo ...
... Describe the position and gross anatomical structure of the seminal vesicles Discuss the route of a sperm cell during emission and ejaculation Describe the anatomy of the posterior wall of the prostatic urethra Define the lobes of the prostate and understand how enlargement effects urine flo ...
Applied anatomy of the thorax and abdomen
... Except for the first and second ribs, all ribs have a groove for the intercostal nerve and blood vessels at their lower margin, which is at the outer aspect confined by a sharp bony edge. All ribs are different from each other in size, width and curvature. The first rib is the shortest. Its anterome ...
... Except for the first and second ribs, all ribs have a groove for the intercostal nerve and blood vessels at their lower margin, which is at the outer aspect confined by a sharp bony edge. All ribs are different from each other in size, width and curvature. The first rib is the shortest. Its anterome ...
17 Loukas.p65
... anterior belly of the digastric muscle [1, 4, 6, 11, 15, 20, 21, 24]. Norton [11], in 2000, reported a case of bilateral occurrence of accessory digastric muscles, which inserted upon the midline raphe, decussated, and continued to rejoin the contralateral anterior bellies of the digastric muscles b ...
... anterior belly of the digastric muscle [1, 4, 6, 11, 15, 20, 21, 24]. Norton [11], in 2000, reported a case of bilateral occurrence of accessory digastric muscles, which inserted upon the midline raphe, decussated, and continued to rejoin the contralateral anterior bellies of the digastric muscles b ...
Section 28–1 Introduction to the Arthropods
... 1. What is the basic body plan of all arthropods? Arthropods have a segmented body, a tough exoskeleton, and jointed appendages. ...
... 1. What is the basic body plan of all arthropods? Arthropods have a segmented body, a tough exoskeleton, and jointed appendages. ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.